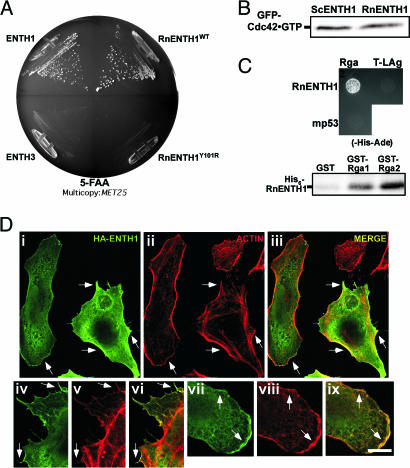
Fig. 6.
Epsin ENTH domain essential patch in higher eukaryotes. (A) Rat ENTH1 domain complements ΔΔ. ΔΔ with MET25 promoter plasmids encoding yeast ENTH1 and ENTH3 or RnENTH1WT and RnENTH1Y101R were grown on 5-FAA plates as in Fig. 1A. (B) RnENTH1 sustains normal levels of activated Cdc42. ΔΔ cells expressing RnENTH1 or yeast ENTH1 and GFP-Cdc42; levels of GFP-Cdc42·GTP were determined as in Fig. 4D. (C) RnENTH1 interacts with the Cdc42 GAPs. Binding of RnENTH1 domain to Cdc42 GAPs was assayed by two-hybrid (Upper) and by in vitro pull down (Lower) as in Fig. 3 A and B. (D) Yeast ENTH1 and ENTH2 domains localize to lamellipodia and filopodia in HeLa cells. HeLa cells transiently transfected with yeast hemagglutinin (HA)-ENTH1 (i–ix) were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with mouse anti-HA antibody, Alexa 448-conjugated secondary antibody, and rhodamine-phalloidin. Representative cells showing ENTH domain localization (i, iv, and vii), actin structures (ii, v, and viii), and merge (iii, vi, and ix) are shown. (Scale bars, 10 μm.)