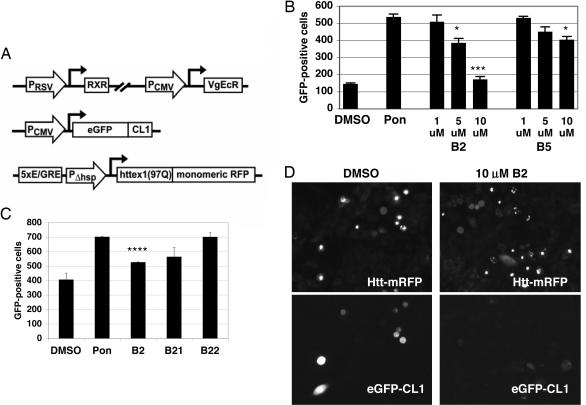
Fig. 2.
B2 treatment prevents Htt-induced proteasome dysfunction. (A) Schematic representation of constructs stably transfected into CHO-K1 cells. CHO-K1 cells contained a heterodimeric ecdysone receptor, a CMV promoter-driven proteasome reporter (EGFP fused to the degradation peptide CL1), and an ecdysone-inducible fusion protein of the first exon of Htt (with 97Q) and mRFP. (B) Treatment of proteasome reporter cells with compounds. Ponasterone (pon) induction of mutant Htt leads to a build-up of proteasome reporter (EGFP–CL1). B2 treatment rescues the accumulation of proteasome substrate, in a dose-dependent fashion. B5 exhibits a similar, but weaker, effect. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗∗, P < 0.005. (C) Treatment of proteasome reporter lines with B2 vs. analogs of B2. As in the polyQ–EGFP reporter assay shown in Fig. 1C, modifications to B2 led to a decrease in activity in B21 and an elimination of activity in B22. ∗∗∗∗, P < 0.0005. (D) Fluorescence microscopy of cells from proteasome reporter line. Fewer cells exhibit build-up of EGFP–CL1 proteasome reporter when treated with B2. (Magnification: ×20.)