Figure 1.—
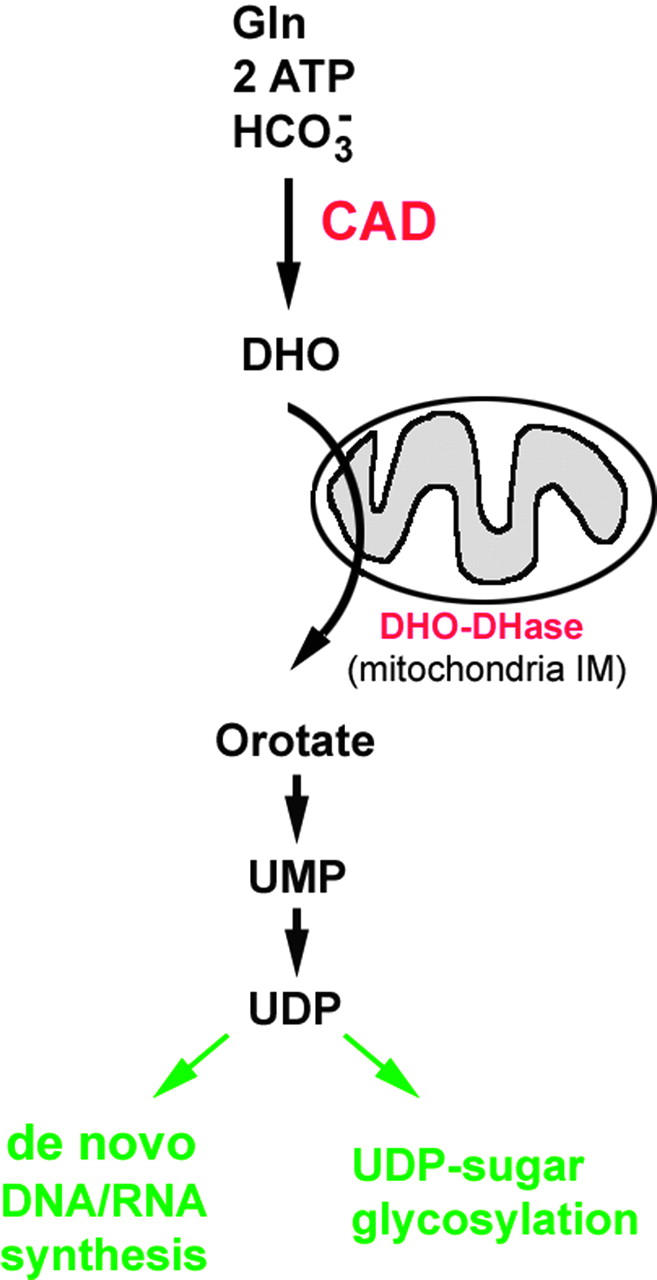
Illustration of the role of the carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase2-aspartate transcarbamylase-dihydroorotase enzyme (CAD) in de novo biosynthesis of dihydroorotate (DHO) and its rapid conversion to uridine diphosphate (UDP). CAD utilizes glutamine (Gln), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and bicarbonate HCO−3 to synthesize DHO. All reactions take place in the cell cytoplasm except for that of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHO-DHase), which occurs at the mitochondria inner membrane (IM). Loss of CAD activity can affect DNA/RNA nucleotide biosynthesis as well as UDP-dependent protein glycosylation events.
