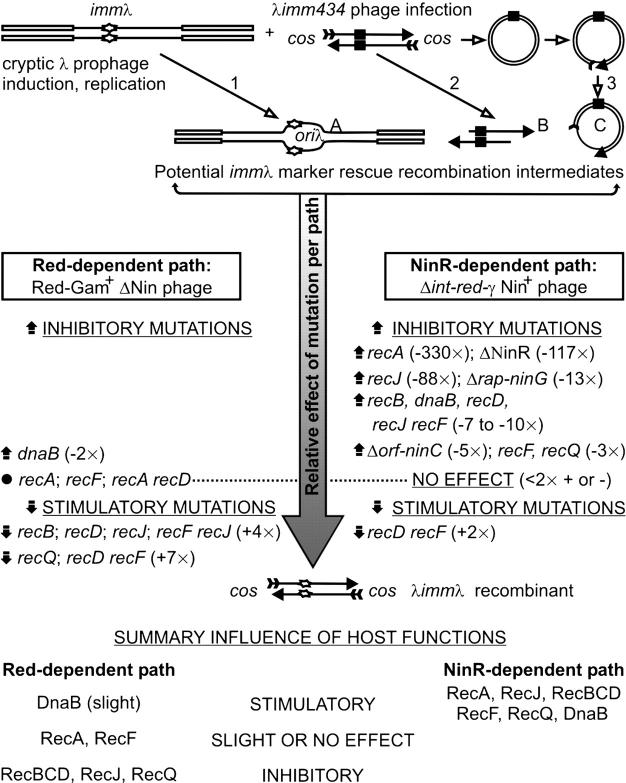
Figure 3.—
Summary of recombination factors influencing NinR-dependent and Red-dependent phage-prophage marker rescue. The open rectangles are DNA strands of circular E. coli chromosome; thin lines are λDNA, as infecting phage or as cryptic prophage within the E. coli chromosome; the solid rectangle is imm434; the stretched diamond is immλ; the feathered tails of arrows and the solid arrowheads respectively represent the 5′- and 3′-ends of phage DNA strands. The potential immλ recombination intermediates include: 1, replication D-loop formed within cryptic prophage after replication initiation from oriλ when the cells are placed at or above 39°, generating intermediate A; 2, exonucleolytic activity at 5′-ends of linear infecting λimm434 phage, resulting in 3′-single-stranded DNA overhangs generating intermediate B; 3, a nick is introduced into the circularized monomeric phage genome [or cos end(s) remains unligated], which is converted to a gap by the joint action of a DNA helicase and a single-stranded 5′–3′ exonuclease producing intermediate C.