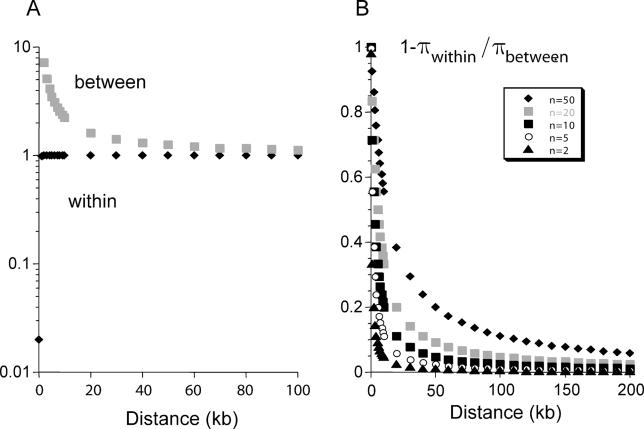
Figure 1. Sequence Diversity Expected at Neutral Sites at Different Distances from a Site under Balancing Selection.
The figure shows the dependence of diversity at neutral sites in a gene on the number of different alleles maintained (n values) and the distance from the selected sites. A recombination rate of 1 cM/Mb is assumed, which is appropriate for humans, but much lower than the estimated rate for A. thaliana or maize. The example calculated is based on equations in the Appendix of [12], which are appropriate for selection at loci, such as MHC, where homozygous genotypes can be formed (e.g., a system with heterozygous advantage in which homozygotes are viable); note, however, that heterozygous advantage is unlikely to maintain very large allele numbers [35,82]. In the example shown, the turnover rate of alleles at the selected locus (or site) is assumed to be 10−7.
(A) Shows predicted nucleotide diversity (π) between and within haplotypes of allelic classes (defined as having different alleles at the selected site or sites) for the case when 50 different alleles are maintained.
(B) Shows the proportion of the overall diversity that is between allelic classes (analogous to FST in a subdivided population), showing differentiation between the haplotypes across several kb when there are many alleles, even when recombination occurs.