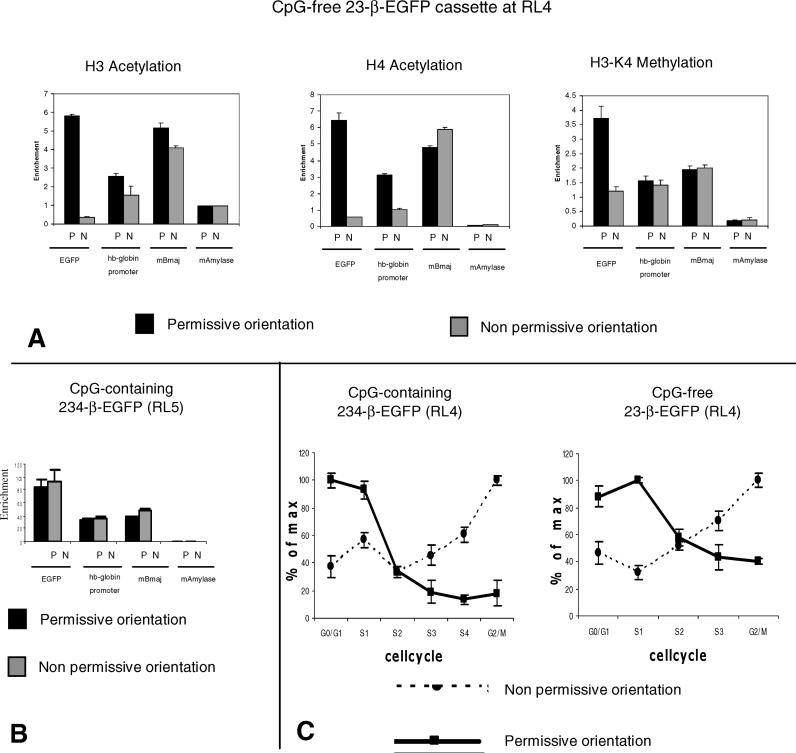
Figure 2. CpG-Free Silencing Is Associated with Lack of Acetylation of H3 and H4, Lack of Methylation of H3-K4, and Replication in Late S Phase.
(A) Histone modification analysis by ChIP assays. The histograms summarize the results of quantitative PCR measurements of abundance of the EGFP coding sequence, the hβ-globin promoter, the mouse β-major promoter region (mBmaj), and a fragment of the mouse amylase coding sequence (mAmylase) in chromatin from cells containing cassette 23-β-EGFP at RL4 precipitated with polyclonal antibodies against acetylated H3-tails (left), acetylated H4-tails (middle), and methylated H3-K4-tails. The enrichment of specific sequences in modified chromatin compared to total chromatin was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Both the EGFP coding sequence and the β-globin promoter of the CpG-free 23-β-EGFP cassette are enriched when acetylated on H3 and H4 and H3-K4 methylation and when they are in the P orientation, but not when they are in the N orientation.
(B) ChIP analysis of the CpG-containing cassette inserted at RL5 in the N or P orientation. The two orientations are similar, and, as at RL4, the enrichment is higher for the EGFP coding sequences than for the promoter.
(C) Timing of replication analysis: The histograms summarize the results of quantitative PCR measurements of the abundance of the CpG-free and CpG-containing EGFP coding sequence in FACS-separated, BrdU-immunoprecipitated newly replicated DNA fragments from cells containing the CpG-containing (left) or the CpG-free (right) LCR-β-EGFP cassettes. Both cassettes replicate early when they are in the P orientation and late when they are in the N orientation. Controls were as in Figure 3.
N, non-permissive orientation; P, permissive orientation.