FIGURE 6.
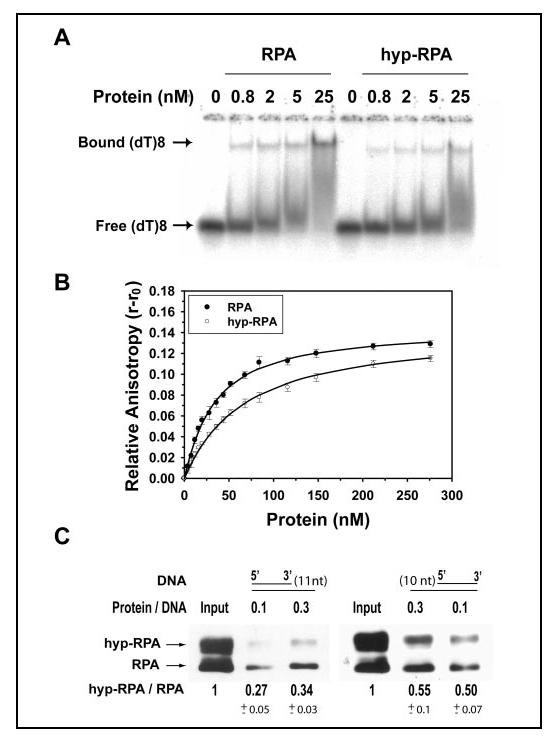
Binding of RPA and hyp-RPA to oligo(dT)8 and partial DNA duplexes. A, RPA was incubated with 1 nM (dT)8 at different molar ratios at 25 °C for 15 min in 20 μl of the binding buffer. The binding products were analyzed on a 4% native polyacrylamide gel. The positions of bound (dT)8 and free (dT)8 are indicated. B, 10 nM (dT)8 with a fluorescein labeled at 5' end was titrated with RPA or hyp-RPA. The anisotropy was measured at 520 nm with excitation at 492 nm. The binding isotherms were best fitted to obtain the equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd,obs). C, binding of RPA and hyp-RPA to partial DNA duplexes containing 5'-protruding 11 nucleotides (DNA-11, left) or 3'-protruding 10 nucleotides (DNA-10, right). DNA-11 and DNA-10 were constructed by annealing a biotinylated 55-mer with its complementary 44- and 45-mer, respectively. The biotinylated partial DNA duplex was incubated with a mixture of RPA and hyp-RPA. The protein bound to DNA was pulled down with streptavidin beads and detected by immunoblotting using an antibody against RPA32. The ratio of hyp-RPA to RPA in each binding was quantified.
