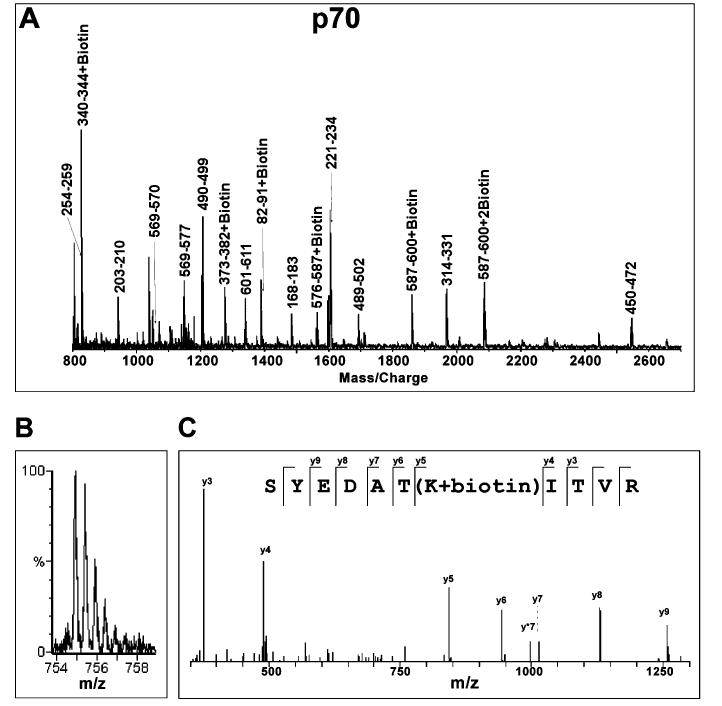
Figure 2:
Mass spectrometric analysis of biotinylation of RPA protein. (A) A typical MALDI-TOF spectrum of tryptic digestion of biotinylated RPA70. Monoisotopic resolution for all of the peptide peaks was obtained, allowing unequivocal assignment of singly charged unmodified and biotinylated peptide fragments. (B) A typical Q-TOF spectrum of the doubly charged biotinylated p70 peptide fragment. The molecular mass of this ion in the form of m/z (mass per charge) corresponds to peptide fragment 325-335 + biotin. (C) MS/MS analysis of the parent ion (m/z) 754.91) shown in (B) confirms that lysine 331 is biotinylated. The y ion series were derived from internal fragmentation of the peptide bonds, providing sequence information read from the C-terminus (left) to the N-terminus (right). The mass increment between y4 and y5 ions corresponds to a biotinylated lysine while the masses of the remaining y ions correspond perfectly to the amino acid sequence of the fragment.