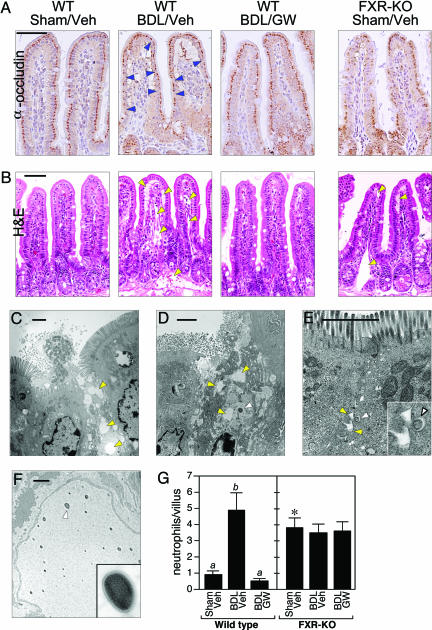
Fig. 4.
FXR activation blocks mucosal injury. (A and B) Transverse sections of terminal ileum are shown for WT mice subjected to sham operation and vehicle treatment (WT/Sham/Veh), BDL and vehicle treatment (WT/BDL/Veh), or BDL and GW4064 treatment (WT/BDL/GW) and FXR-KO mice subject to sham operation and vehicle treatment (FXR-KO/Sham/Veh). The sections were immunostained with anti-occludin antisera (A) or stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (B). Occludin immunostaining (dark brown) is detected in the enterocytes of the villus epithelium. Notable examples of diminished occludin immunostaining are indicated by blue arrowheads in the WT/BDL/Veh section. Occludin immunostaining is drastically reduced in ileum from the FXR-KO/Sham/Veh mice. Edema and dilated lymphatic vessels are indicated by yellow arrowheads in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections. (Scale bars: 50 μm.) (C–F) Electron microscopy performed with sections of terminal ileum prepared from BDL WT mice (C and D) and sham-operated FXR-KO mice (E and F). C–E are oriented with the epithelial brush border at the top. Edema is indicated in C–E by yellow arrowheads. Bacteria in the mucosa are indicated in D and E by white arrowheads. (E Inset) A higher magnification of the bacterium and the surrounding edema. (F) Bacteria in the lymphatic vessels of a sham-operated FXR-KO mouse. (Inset) A higher magnification view of the bacterium indicated by the white arrowhead. (Scale bars: 2 μm.) (G) Neutrophils were quantified in transverse sections of terminal ileum prepared from WT and FXR-KO mice subjected to sham operation and vehicle treatment (Veh), BDL and vehicle treatment, or BDL and GW4064 (GW) treatment. Neutrophils were counted in 10 randomly chosen villi from four mice in each treatment group. The presence of different lowercase letters indicates statistical significance (P < 0.05) within each strain. The asterisk indicates statistical significance (P < 0.01) between sham-operated, vehicle-treated FXR-KO mice and sham-operated, vehicle-treated WT mice.