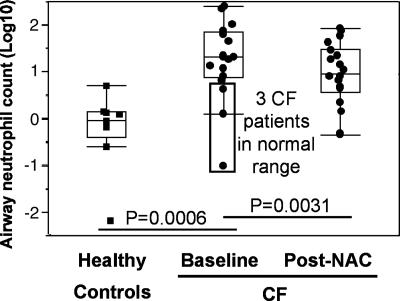
Fig. 2.
Short-term high-dose oral NAC decreases neutrophil count in CF airways. Airway neutrophil count (expressed in absolute count) follows a logarithmic distribution in CF patients, reflecting the self-amplifying characteristic of CF airway inflammation. Upon NAC treatment, airway neutrophil count was markedly reduced in patients, even more so when the three patients with baseline airway neutrophil count in the normal range were excluded from the analysis (Table 1). Identical results were obtained when neutrophil count was expressed in relative numbers per unit of sputum volume or weight. Data are shown as box plots (see Materials and Methods).