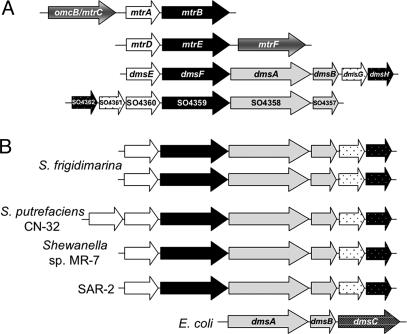
Fig. 1.
Alignments of potential extracellular respiratory gene clusters. Genes are color-coded for putative function in terms of extracellular respiratory modules (white, periplasmic electron carrier; black, outer membrane anchor; gray, extracellular cell-associated terminal reductase). (A) Alignment of gene clusters predicted to encode extracellular respiration pathways in S. oneidensis. (B) Alignment of gene clusters containing homologues of DMSO reductases from sequenced Shewanella sp. and comparison to dmsABC from E. coli. dms G and SO4361 and homologs are predicted to encode TorD-like molybdenum cofactor insertion chaperones, whereas dms H and SO4360 and homologs encode hypothetical proteins. All identified clusters contain genes encoding homologues of MtrA and MtrB. S. frigidimarina, S. putrefaciens, and Shewanella sp. MR-7 sequences were made available through the Integrated Microbial Genomes database at the Joint Genome Institute (http://img.jgi.doe.gov), and sequence for SAR-2 was from by Venter et al. (51).