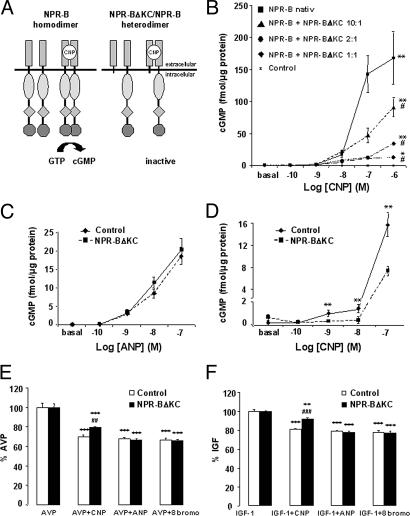
Fig. 1.
NPR-BΔKC acts as NPR-B-specific dominant-negative mutant in vitro. (A) Principle of NPR-B activation and inhibition. (Left) Native receptor. (Right) Dominant-negative mutant. (B) CNP-dependent cGMP response in COS cells cotransfected with NPR-B and various amounts of NPR-BΔKC. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01 vs. control by ANOVA; #, P < 0.05 vs. NPR-B native by ANOVA (n = 6 per group). (C and D) Measurement of cGMP response to ANP (C) or CNP (D) of H9c2 cells. ∗∗, P < 0.01 vs. control (n = 6 per group). (E and F) l-(4,5-3H)leucine incorporation of NPR-BΔKC-transfected H9c2 cells and controls after stimulation with AVP (E) or IGF-1 (F) and treatment with ANP, CNP, or 8-Bromo-cGMP. ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001 vs. single treatment with hypertrophic stimulus; ##, P < 0.01 vs. control AVP plus CNP; ###, P < 0.001 vs. control IGF-1 plus CNP (n = 6 per group).