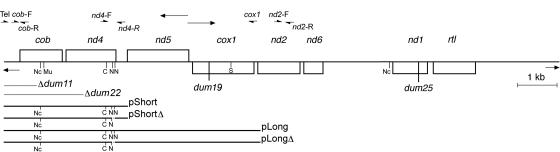
Fig. 1.
Partial physical map of the 15.8-kb mitochondrial genome of C. reinhardtii. The rectangles represent protein-coding genes: cob, gene encoding apocytochrome b of complex III; nd1, 2, 4, 5, and 6, genes encoding the corresponding subunits of complex I; cox1, gene encoding the subunit 1 of complex IV, rtl: reverse transcriptase-like protein. The inverted telomeric ends are represented by short arrows, the bidirectional origin of transcription between nd5 and cox1 by longer arrows. Only restriction sites used in this work are presented: Nc, NcoI; C, ClaI; N, NdeI; S, SstI. Mu, resistance to myxothiazol. Positions of the dum11 and dum22 deletions and of the dum19 and dum25 point mutations are indicated. Fragments of mitochondrial genome contained in pShort, pShortΔ, pLong, and pLongΔ are shown as well as the primers used for PCR amplifications. Using the GenBank u03843 numbering for the Chlamydomonas mitochondrial DNA, primers positions are Tel, 1–21; cob-F, 431–450; cob-R, 564–545; nd4-F, 2765–2780; nd4-R, 3301–3282; cox1, 6653–6634; nd2-F, 6636–6655; and nd2-R, 7343–7323.