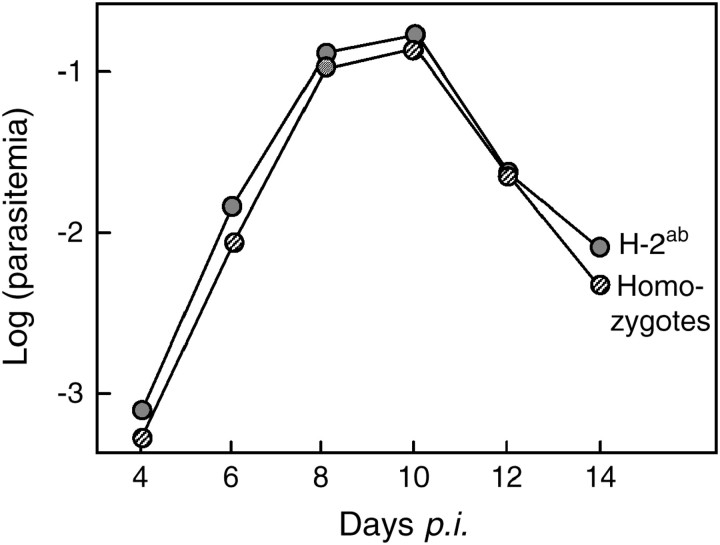
Figure 2.—
The effect of the H-2ab genotype vs. the average effects of the respective homozygote MHC types during infection with P. chabaudi. To test whether the heterozygotes (shaded circles) were as susceptible as the average of the two homozygotes (striped circles), we first equalized the sample size of the homozygous variants before pooling them. We did that by randomly reducing the larger group to the sample size of the smaller group. We then calculated the repeated-measures ANOVAs (fixed factors: heterozygosity, gender, and parasite clone) with the reduced sample size. The average of 10 randomly reduced samples is given. The heterozygosity effect in the repeated-measures ANOVAs (average of 10 runs ± SE) is F1,76 = 6.0 ± 0.62, P = 0.026 ± 0.007. The heterozygosity effect averaged over all days was also significant when tested with the method of linear contrasts on the nonreduced sample size (i.e., using weights of 0.5 for each of the homozygotes and −1 for the heterozygotes and using the between-mouse variance as the residual: t93 = 2.63, P = 0.01).