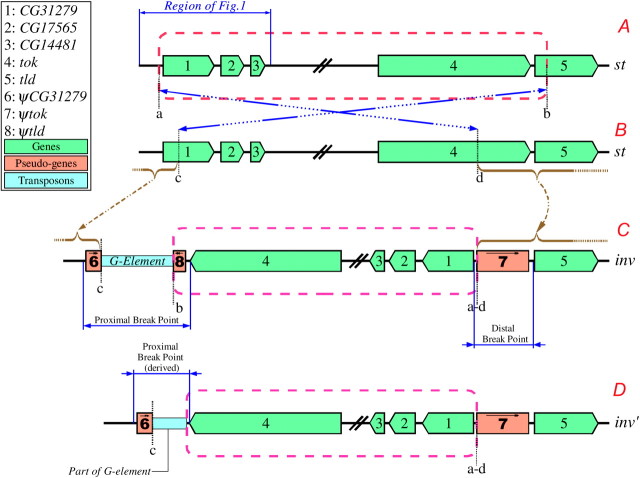
Figure 2.—
Structure of breakpoints for Standard and In(3R)P chromosomes. Both the distal and proximal In(3R)P breakpoints split, and presumably inactivate, known coding genes. Each “split” gene is asymmetrically duplicated at the opposite breakpoint. The boxed text indicates the numbering and color-coding scheme. (A and B) Standard orientation chromosomes showing the inversion breakpoints and putative pattern of the inversion event. (C and D) Inverted chromosomes. The chromosome in D contains a small deletion at the proximal breakpoint and is presumably derived from C. See results and Figure 3 for a detailed description of the breakpoints. This figure is not to scale.