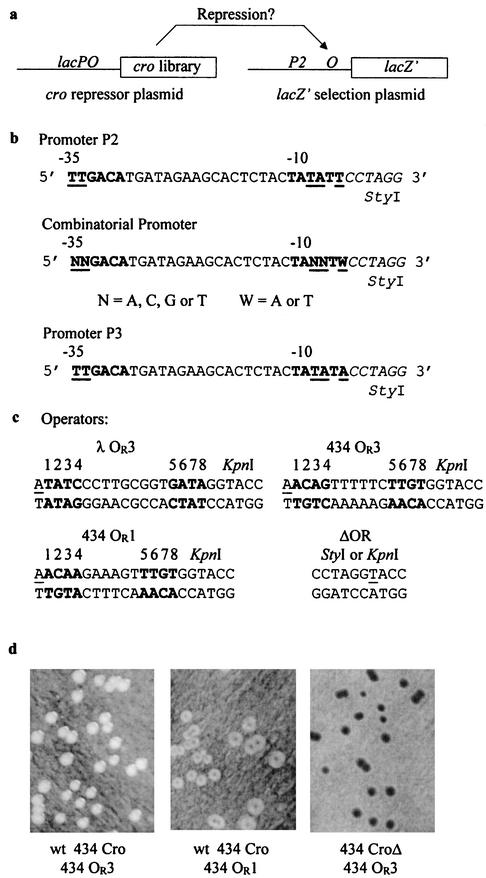
FIG. 1.
Screening for repressor variants. (a) An in vivo combinatorial two-plasmid system for the selection of functional DNA binding variants. The system consists of a repressor plasmid that encodes a variegated cro gene and a compatible reporter plasmid containing a lacZ gene under transcriptional control of a promoter and target operator sequence. LacZ-dependent β-galactosidase activities can be easily visualized on X-Gal-containing medium. (b) Partial sequence of the P2, P3, and combinatorial promoters used. The indicated mutations in the combinatorial promoter were synthesized with the degeneracies at the positions shown. P3 was selected for use with lacZ+ reporters. (c) Target operator sequences of the reporter plasmids used. The operator sequences were cloned between StyI and KpnI sites of the reporter plasmids. The putative +1 position of the promoter is underlined in each of the operators. Pseudopalindromic sequences of the operators are in bold type and are marked with numerals 1 to 8. The construct marked ΔOR shows the fused StyI-KpnI region of pP2ΔOR. (d) Black-and-white photographs of E. coli colonies containing various repressor and reporter plasmid combinations on plates containing X-Gal (and isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside [IPTG] to induce 434 Cro transcription and chromosomal lacZΔ 77 15). Left panel, repressor plasmid p434cro2 (wt 434 Cro) and reporter plasmid pP2434OR3 (P2 434 OR3 operator-lacZ′). Middle panel, repressor plasmid p434cro2 (wt 434 Cro) and reporter plasmid pP2434OR1 (P2 434 OR1 operator-lacZ′). Right panel, repressor plasmid p434croΔ (434 Cro with HTH deletion) and reporter plasmid pP2434OR3 (P2 434 OR3 operator-lacZ′). The repression phenotypes of these colonies were designated +++ (white colonies) (left panel), + (white colonies with a light blue middle) (center panel), and −− (dark blue colonies) (right panel). Intermediate phenotypes, designated ++ and +−, had white colonies with less intense or more intense blue middles relative to the + phenotype (center panel).