Abstract
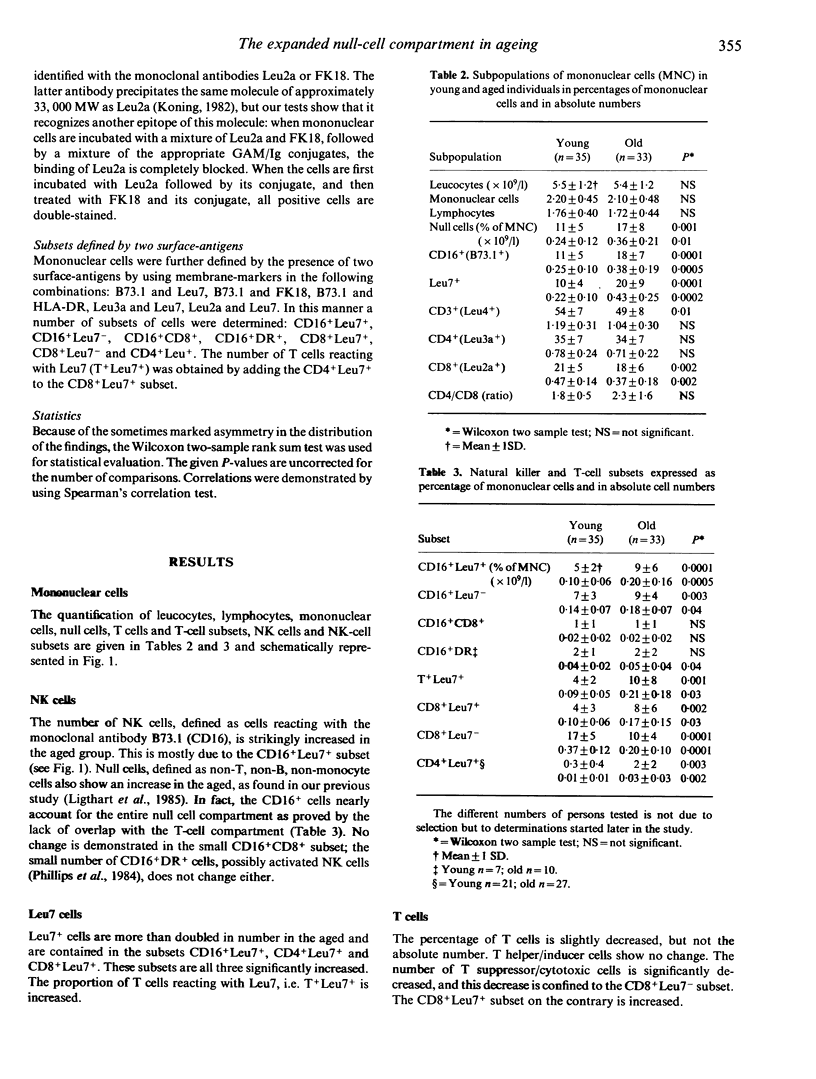
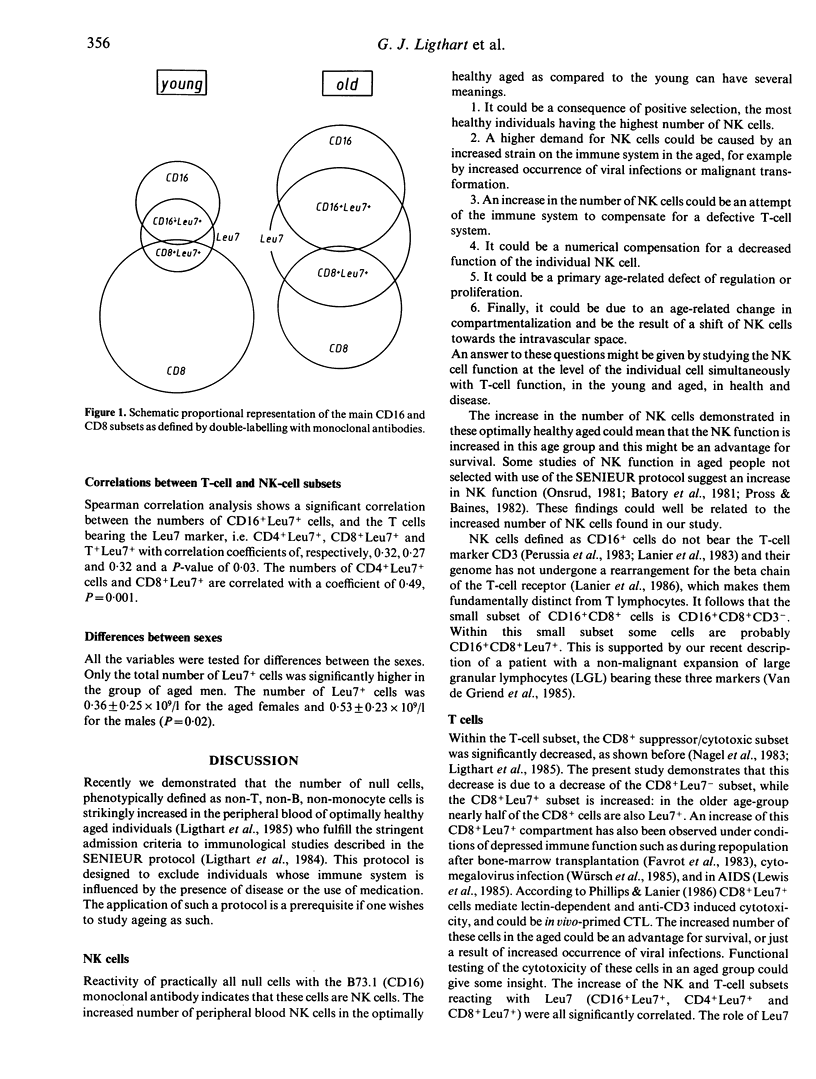
Analysis of the subpopulations of mononuclear cells in human blood in ageing has revealed a striking increase in the number of null cells, defined as non-T, non-B, non-monocyte cells, and a decrease in the number of T and B cells. By using recently developed monoclonal antibodies against natural killer cells in combination with T-cell markers in two-wavelength immunofluorescence, we were able to define 13 subpopulations of mononuclear cells and compare them in two groups of persons, respectively aged 25-34 and 75-84 years, all fulfilling the stringent admission criteria for immunogerontological studies described in the SENIEUR protocol, and thus all to be considered as optimally healthy and immunologically uncompromised. We found that the increased null cell population in the aged is a result of an increase in the numbers of NK cells, mostly the CD16+Leu7+ subset. The number of CD8+ suppressor/cytotoxic cells is decreased. This is due to a decrease of the number of CD8+Leu7- cells. All NK and T-cell subsets bearing the Leu7 antigen, namely CD16+ Leu7+, CD4+Leu7+ and CD8+Leu7+, are increased. These changes can be due to defects of the ageing immune system, but they can also represent the optimal state of the immune system in the healthy aged and may be linked to survival. These values can be used as reference values for the 75-84 years age group and serve to monitor attempts to reconstitute the immune defects in ageing.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. II. Distinguishing phenotypic and functional properties of natural killer cells from activated NK-like cells. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1758–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Postnatal expansion of the natural killer and keller cell population in humans identified by the monoclonal HNK-1 antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bátory G., Benczur M., Varga M., Garam T., Onody C., Petrányi G. G. Increased killer cell activity in aged humans. Immunobiology. 1981 Jun;158(5):393–402. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(81)80010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favrot M., Janossy G., Tidman N., Blacklock H., Lopez E., Bofill M., Lampert I., Morgenstein G., Powles R., Prentice H. G. T cell regeneration after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):59–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B. Identification of three different human lymphocyte populations by surface markers. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:114–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Lobo P. I. Characterizaiton of two populations of human lymphocytes bearing easily detectable surface immunoglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1464–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI108227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Pross H. Surface markers on human b and t lymphocytes. VI. Cytotoxicity against cell lines as a functional marker for lymphocyte subpopulations. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):596–605. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Makinodan T. Relationship between aging and immune system. Prog Allergy. 1981;29:134–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Cwirla S., Federspiel N., Phillips J. H. Human natural killer cells isolated from peripheral blood do not rearrange T cell antigen receptor beta chain genes. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):209–214. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. E., Puck J. M., Babcock G. F., Rich R. R. Disproportionate expansion of a minor T cell subset in patients with lymphadenopathy syndrome and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):555–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligthart G. J., Corberand J. X., Fournier C., Galanaud P., Hijmans W., Kennes B., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Steinmann G. G. Admission criteria for immunogerontological studies in man: the SENIEUR protocol. Mech Ageing Dev. 1984 Nov;28(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(84)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel J. E., Chrest F. J., Pyle R. S., Adler W. H. Monoclonal antibody analysis of T-lymphocyte subsets in young and aged adults. Immunol Commun. 1983;12(2):223–237. doi: 10.3109/08820138309066871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Lectin-dependent and anti-CD3 induced cytotoxicity are preferentially mediated by peripheral blood cytotoxic T lymphocytes expressing Leu-7 antigen. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1579–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G. Studies of human natural killer cells. I. In vivo parameters affecting normal cytotoxic function. Int J Cancer. 1982 Apr 15;29(4):383–390. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit H. R., Hijmans W., Asma G. E. Identification of mononuclear cells in human blood. I. Qualitative and quantitative data on surface markers after formaldehyde fixation of the cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. Identification of mononuclear cells in human blood. II. Evaluation of morphological and immunological aspects of native and formaldehyde-fixed cell populations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):567–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Human natural killer cells: biologic and pathologic aspects. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):489–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Würsch A. M., Gratama J. W., Middeldorp J. M., Nissen C., Gratwohl A., Speck B., Jansen J., D'Amaro J., The T. H., De Gast G. C. The effect of cytomegalovirus infection on T lymphocytes after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Nov;62(2):278–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


