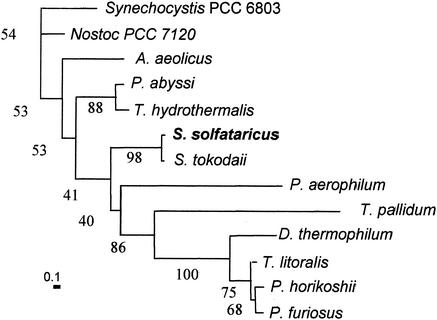
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of α-amylase sequences. A neighbor-joining distance tree is shown, based on comparison of 192 residues. Distances are indicated by the bar in the lower left corner, which represents 10 substitutions per 100 residues. Percent occurrence among 100 trees is given for all nodes. Sequences were as follows: Synechocystis strain PCC 6803 (unknown protein), gi 1001420; Nostoc strain PCC 7120 (hypothetical protein), gi 17228805; Aquifex aeolicus (hypothetical protein), gi 2983309; Pyrococcus abyssi (putative amylopullulanase), gi 14520398; Thermococcus hydrothermalis (type II pullulanase), gi 4731920; S. solfataricus, gi 15898025; S. tokodaii (hypothetical protein), gi 15921357; Pyrobaculum aerophilum (hypothetical protein), gi 18314078; Treponema pallidum (putative α-amylase), gi 3322410; Dictyoglomus thermophilum (1,4-α-d-glucan glucanohydrolase), gi 113763; Thermococcus litoralis (4-α-glucanotransferase), gi 2351202; Pyrococcus horikoshii (putative α-amylase), gi 6647403; and Pyrococcus furiosus (α-amylase), gi 1351936.