Abstract
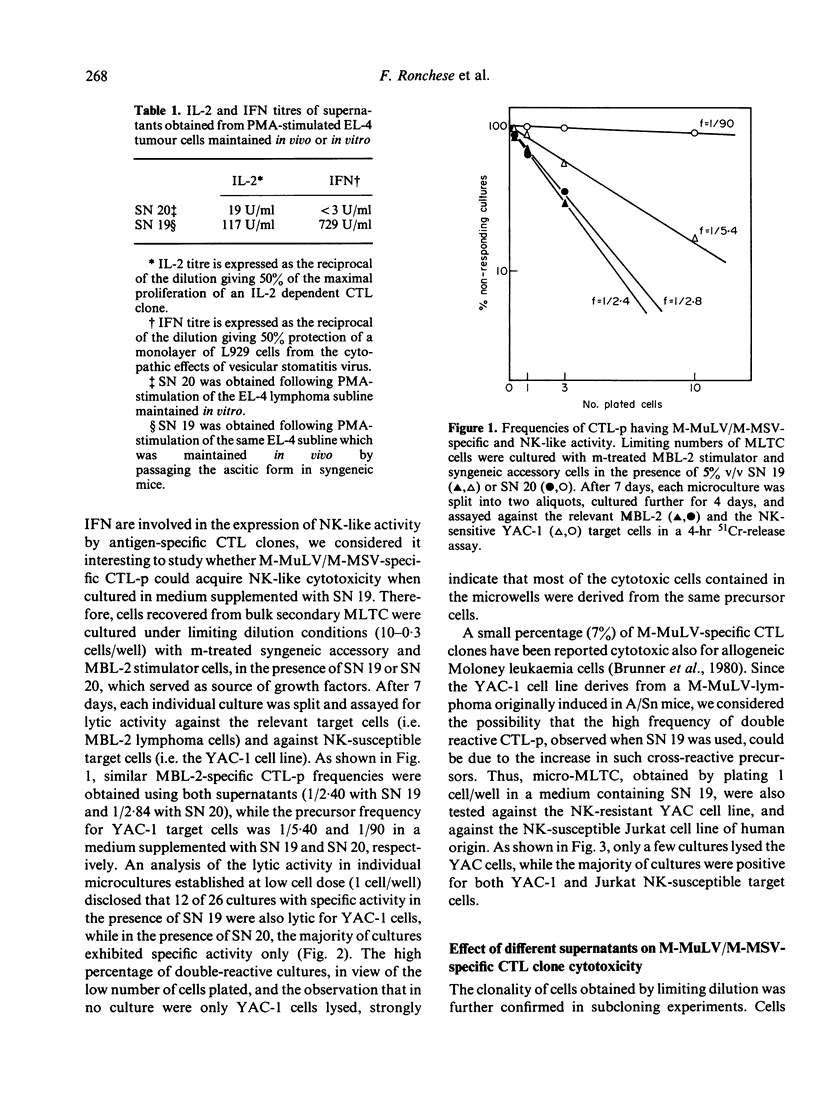
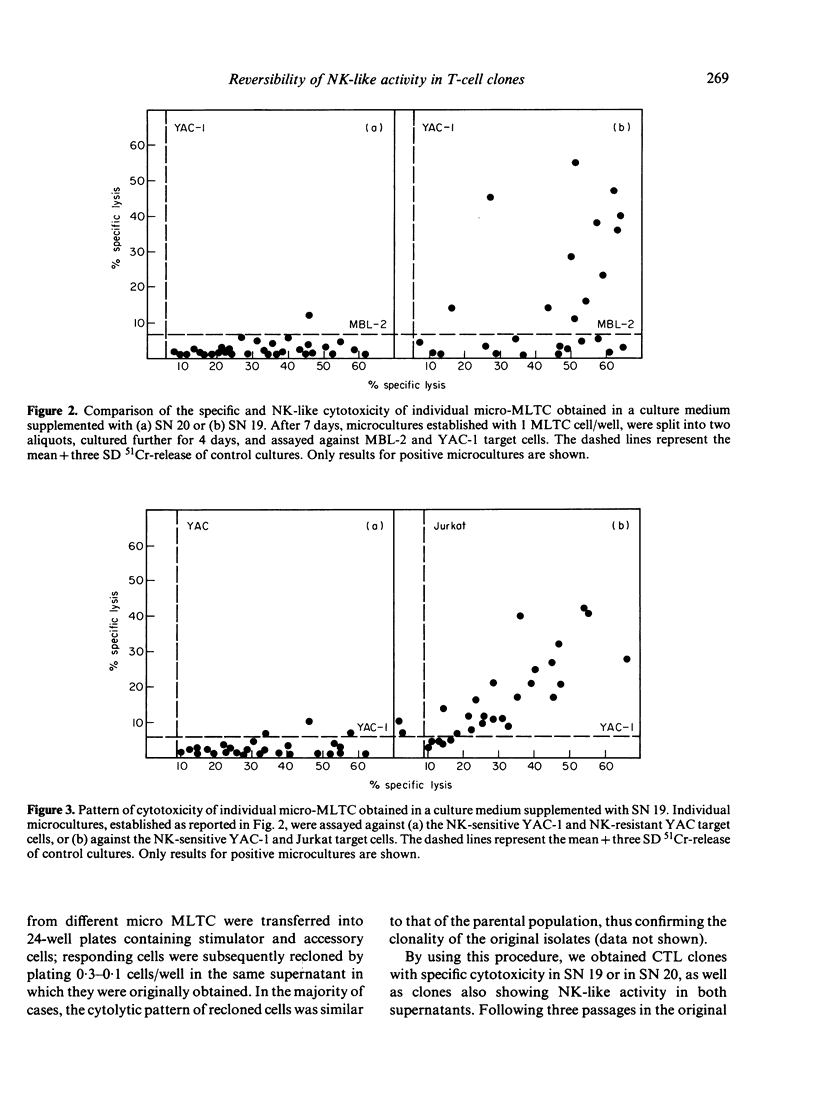
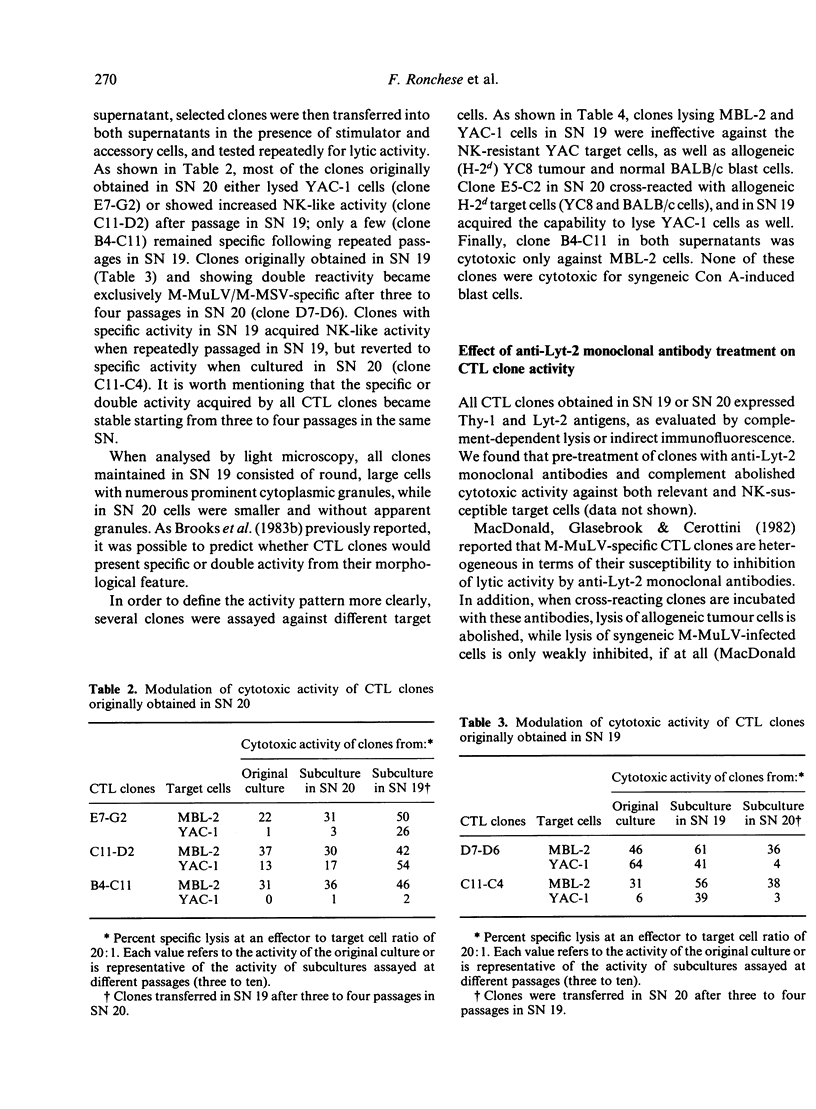
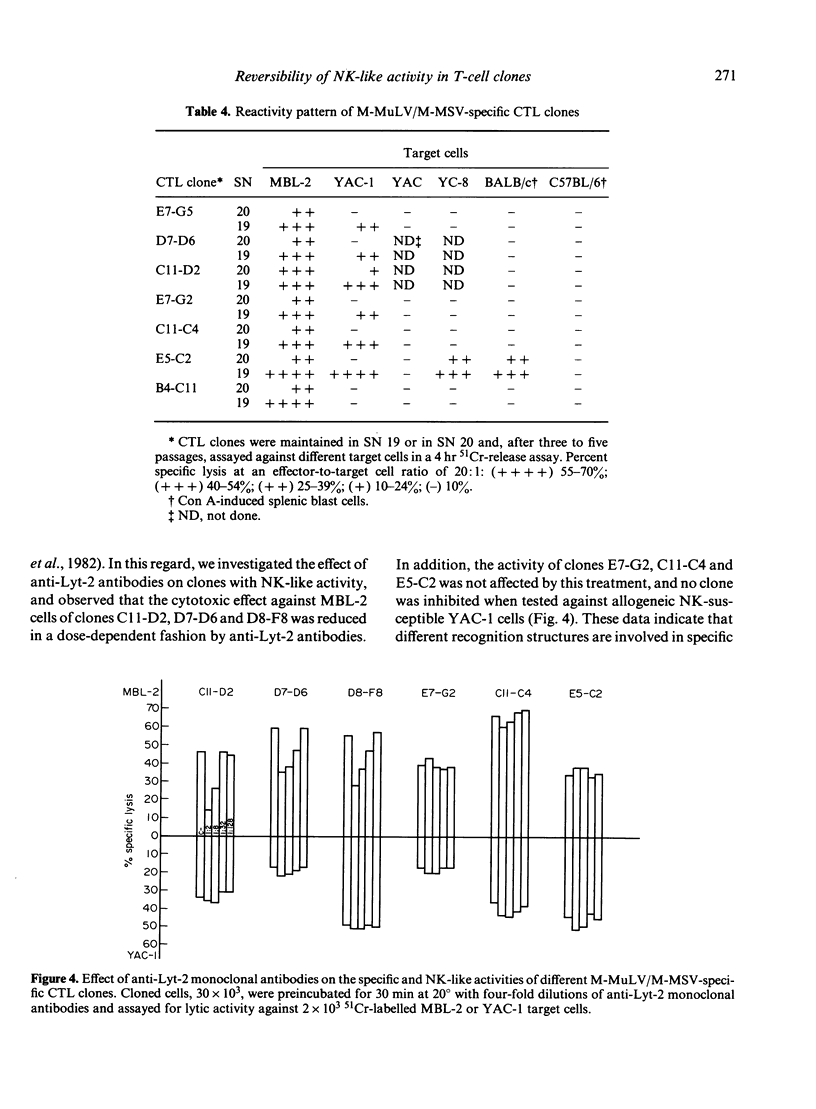
A limiting dilution microculture system, supplemented with a source of interleukin-2 (IL-2), was employed to evaluate the frequency of Moloney-murine leukaemia/sarcoma virus (M-MuLV/M-MSV)-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte precursors (CTL-p) which also exhibited NK-like activity. Spleen cells, obtained from M-MuLV/M-MSV regressor mice, were restimulated in bulk secondary mixed leucocyte-tumour cell cultures (MLTC), and subsequently plated in a culture medium supplemented with two different supernatants (SN) produced following PMA-stimulation of the same EL-4 thymoma cell line. SN 20, obtained from the cell line maintained in vitro, contained IL-2 and only negligible amounts (less than 3 U/ml) of interferon (IFN), while SN 19, obtained after passage of the ascitic form of EL-4 thymoma in syngeneic mice, contained both IL-2 and IFN in high titres. The frequency of CTL-p specific for MBL-2 lymphoma cells was high and comparable in cultures supplemented with both SN (1/2 X 84 cells and 1/2 X 40 cells, respectively), while the frequency of CTL-p directed against NK-susceptible YAC-1 target cells was low in SN 20 (1/90 cells) and high in SN 19 (1/5 X 40 cells). An analysis of individual microcultures established at low cell dose (1 cell/well) indicated that specific and NK-like activity could be ascribed to the same precursor cells. Furthermore, using different long-term CTL clones, we observed that, after passage in SN 20, double-reactive clones gradually lose the capacity to lyse NK-susceptible targets, while most of MBL-2 specific clones acquired NK-like activity following a few passages in SN 19. Therefore, the induction of NK-like activity is reversible and may be modulated by soluble factors present in supernatant in which CTL clones are maintained. Double-reactive clones were unable to lyse NK-resistant allogeneic tumour cells or normal syngeneic blast cells. A few clones cross-reacting with H-2d alloantigens also exhibited NK-like activity when maintained in SN 19. The different pattern of CTL clone activity was associated with a morphological change in the clones themselves: the acquisition of double activity was accompanied by an increase in cell size and the appearance of numerous cytoplasmic granules. All CTL clones were phenotypically Thy-1+ and Lyt-2+ on indirect immunofluorescence and complement-dependent cytotoxicity investigation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acha-Orbea H., Groscurth P., Lang R., Stitz L., Hengartner H. Characterization of cloned cytotoxic lymphocytes with NK-like activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2952–2959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Gillis S., Smith K. A. Monoclonal cytolytic T-cell lines. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):273–278. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Fenner M., Frei D., Wigzell H. Two independent receptors allow selective target lysis by T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1252–1260. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Burton R. C., Pollack S. B., Henney C. S. The presence of NK alloantigens on cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1391–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G. Reversible induction of natural killer cell activity in cloned murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):155–158. doi: 10.1038/305155a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Urdal D. L., Henney C. S. Lymphokine-driven "differentiation" of cytotoxic T-cell clones into cells with NK-like specificity: correlations with display of membrane macromolecules. Immunol Rev. 1983;72:43–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., MacDonald H. R., Cerottini J. C. Antigenic specificity of the cytolytic T lymphocyte (CTL) response to murine sarcoma virus-induced tumors. II. Analysis of the clonal progeny of CTL precursors stimulated in vitro with syngeneic tumor cells. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1627–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collavo D., Ronchese F., Zanovello P., Biasi G., Chieco-Bianchi L. T cell tolerance in moloney-murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV) carrier mice: low cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursor frequency and absence of suppressor T cells in carrier mice with Moloney-murine sarcoma (M-MSV)-induced tumors. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):774–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collavo D., Ronchese F., Zanovello P., Cerundolo V., Biasi G. Reduction in precursors of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and of cells with natural killer-like activity in spleens of cyclophosphamide-treated mice. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1984;6(5):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(84)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engers H. D., Collavo D., North M., von Boehmer H., Haas W., Hengartner H., Nabholz M. Characterization of cloned murine cytolytic T cell lines. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1481–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Fuller-Farrar J., Simon P. L., Hilfiker M. L., Stadler B. M., Farrar W. L. Thymoma production of T cell growth factor (Interleukin 2). J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2555–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi C. E., Zicca A., Cadoni A., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Moretta L. Ultrastructural characteristics of human T cell clones with various cytolytic activities. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):670–677. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Botet M., Moretta A., Moretta L. Natural killer-like cytotoxicity of human T-cell clones against various target cells. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jan;17(1):95–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Glasebrook A. L., Cerottini J. C. Clonal heterogeneity in the functional requirement for Lyt-2/3 molecules on cytolytic T lymphocytes: analysis by antibody blocking and selective trypsinization. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1711–1722. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Moretta L., Cerottini J. C., Mingari M. C. Direct demonstration of the clonogenic potential of every human peripheral blood T cell. Clonal analysis of HLA-DR expression and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):743–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Bucalo L. R., Allard J., Wigzell H., Cantor H. Multiple activities of a cloned cell line mediating natural killer cell function. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1582–1591. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olabuenaga S. E., Brooks C. G., Gillis S., Henney C. S. Interleukin 2 is not sufficient for the continuous growth of cloned NK-like cytotoxic cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2386–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelec G., Hadam M., Müller C., Wernet P. Cloned human T-cell lines with allospecific or natural killer-like cytotoxicity. Immunol Lett. 1982 May;4(5):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(82)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Dobos C. B. Characterization of a "heteroclitic" cytotoxic lymphocyte clone: heterogeneity of receptors or signals? J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):538–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Talal N., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Ledbetter J. A. Surface antigens on mouse natural killer cells: use of monoclonal antibodies to inhibit or to enrich cytotoxic activity. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):982–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K., Wilson A., Scollay R., Chen W. F. Development of large granular lymphocytes with anomalous, nonspecific cytotoxicity in clones derived from Ly-2+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C., MacDonald H. R., Cerottini J. C. Limiting dilution analysis of alloantigen-reactive T lymphocytes. II. Effect of cortisone and cyclophosphamide on cytolytic T lymphocyte precursor frequencies in the thymus. Thymus. 1979 Sep;1(1-2):119–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Yu M. Activation of nonspecific killer cells by interleukin 2-containing supernatants. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1827–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


