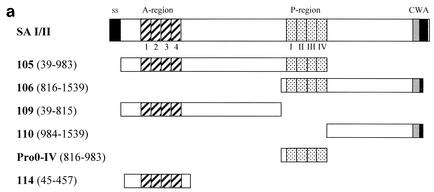
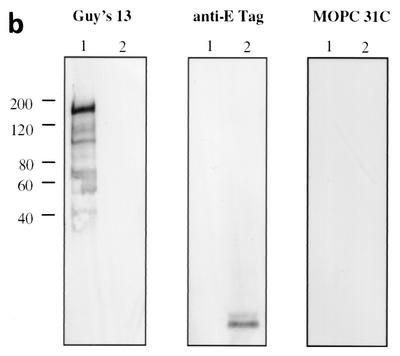
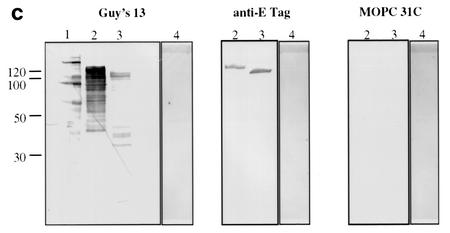
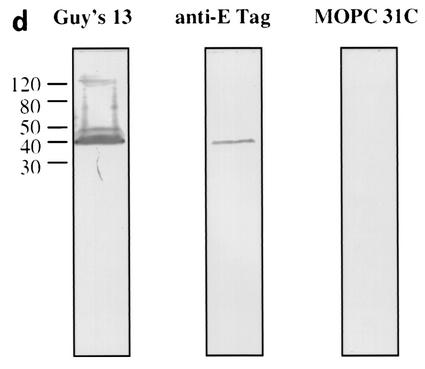
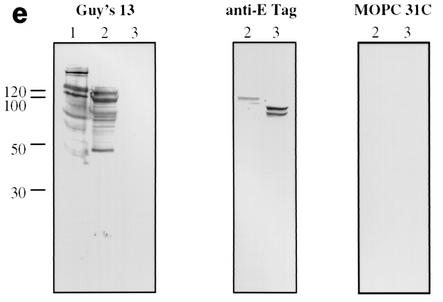
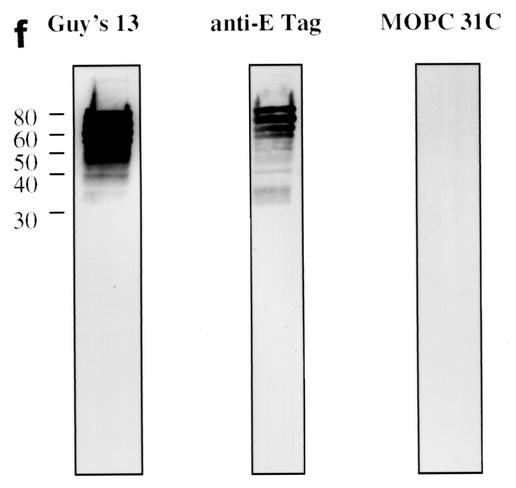
FIG. 1.
Immunoblotting of SA I/II and recombinant SA I/II fragments. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the amino acid residues of SA I/II encoded by the recombinant fragments of SA I/II. The open reading frames expressed by each clone are aligned below the SA I/II sequence. Amino acid residues of SA I/II encoded by each clone are shown in parentheses. The signal sequence (ss) (residues 1 to 38) and sequences associated with anchoring of the protein to the bacterial cell wall CWA (residues 1464 to 1561) as well as the alanine-rich and proline-rich repeat regions (A- and P-regions, respectively) are indicated. The four A-region repeats comprise residues 121 to 201, 202 to 283, 284 to 365, and 366 to 447 of SA I/II, while the four P-region repeats consist of residues 840 to 878, 879 to 917, 918 to 956, and 957 to 983. (b) Immunoblotting of SA I/II (20 ng) (lane 1) and E. coli lysate of Guy's 13-scFv (produced using the pScFvΔ expression system) (lane 2). (c) Immunoblotting of SA I/II (20 ng) (lane 1), E. coli lysates expressing recombinant fragments 105 (lane 2) and 106 (lane 3) cloned in pScFvΔ, or nonrecombinant pScFvΔ (lane 4). (d) Immunoblotting of Pro0-IV cloned in pScFvΔ. (e) Immunoblotting of SA I/II (20 ng) (lane 1) or E. coli lysates expressing fragments 109 (lane 2) and 110 (lane 3) cloned in pScFvΔ. (f) Immunoblotting of 114 cloned inpEXssΔ3. E. coli lysates were electrophoresed on SDS-acrylamide gels, blotted to nitrocellulose, and probed with a 0.5-μg/ml concentration of either Guy's 13 IgG, mouse anti-E tag serum, or MOPC 31C as indicated, followed by detection with AP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The theoretical Mrs of the following recombinant polypeptides are as indicated: 105 (106,600), 106 (83,900), 109 (88,300), 110 (65,500), Pro0-IV (22,600), and 114 (51,100). The positions of molecular mass standards (BRL 10-kDa ladder) are shown.