Abstract
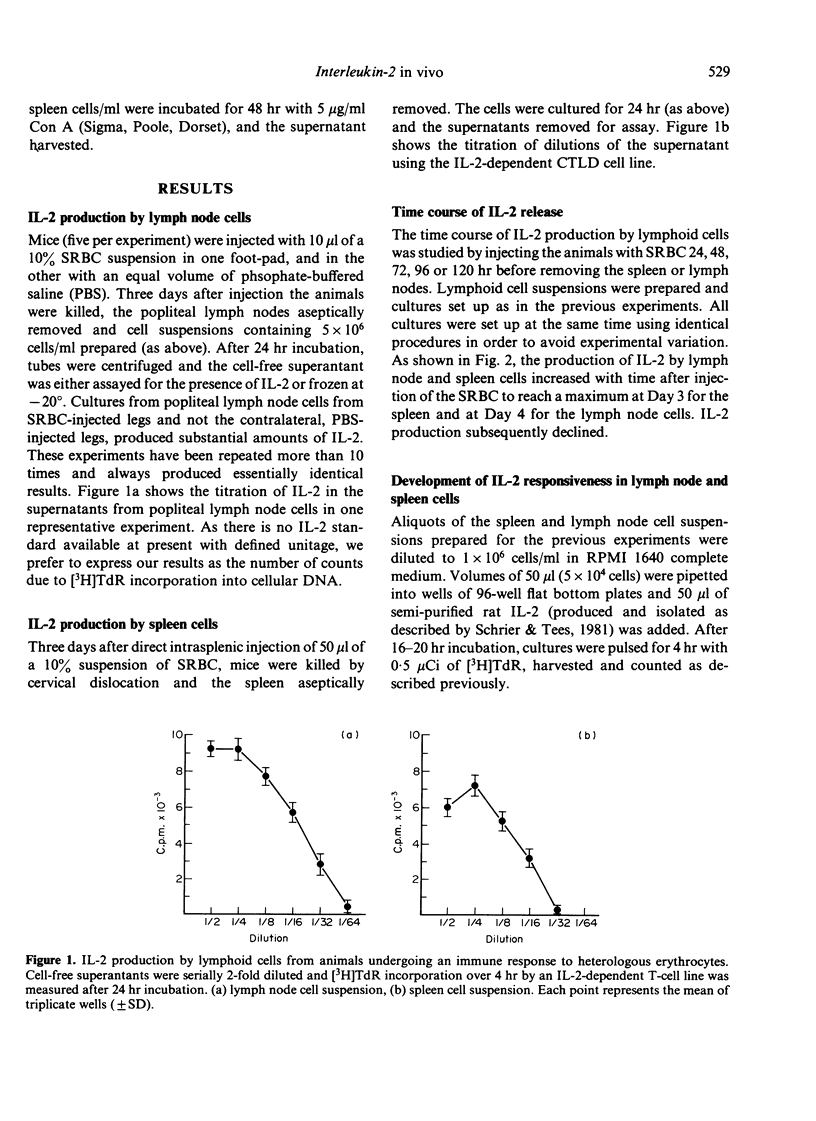
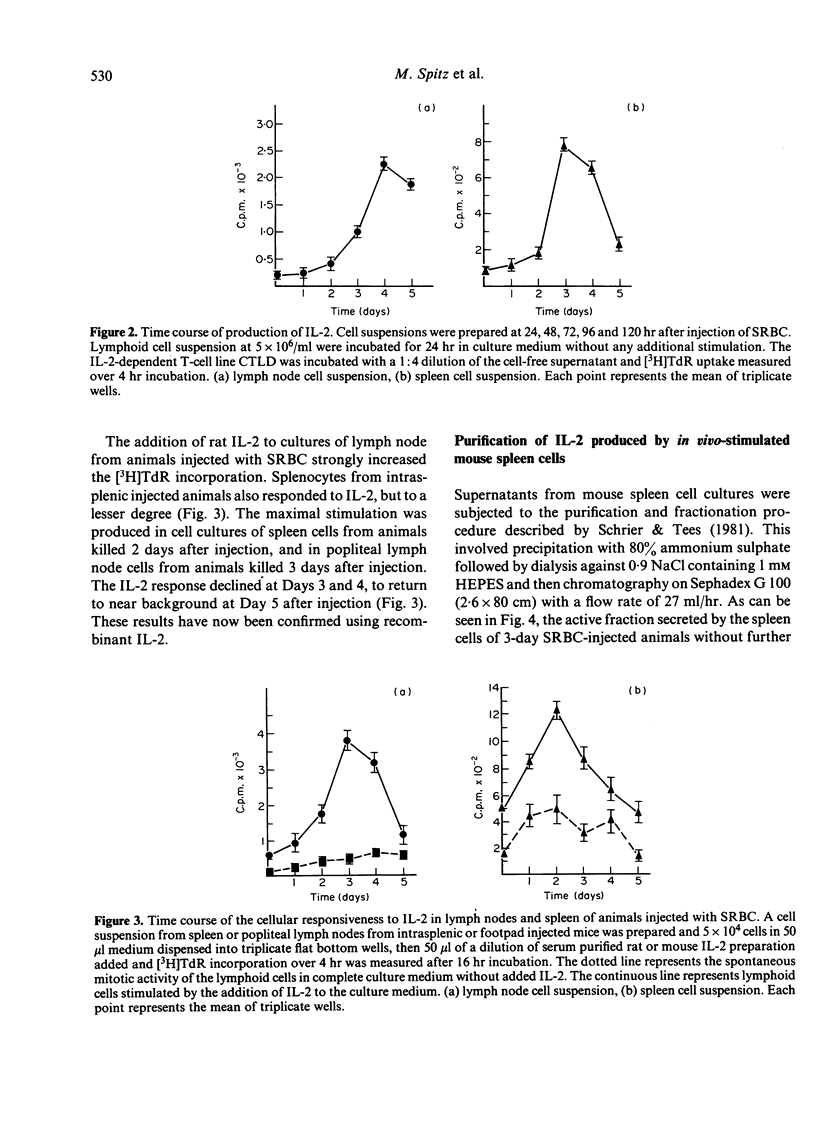
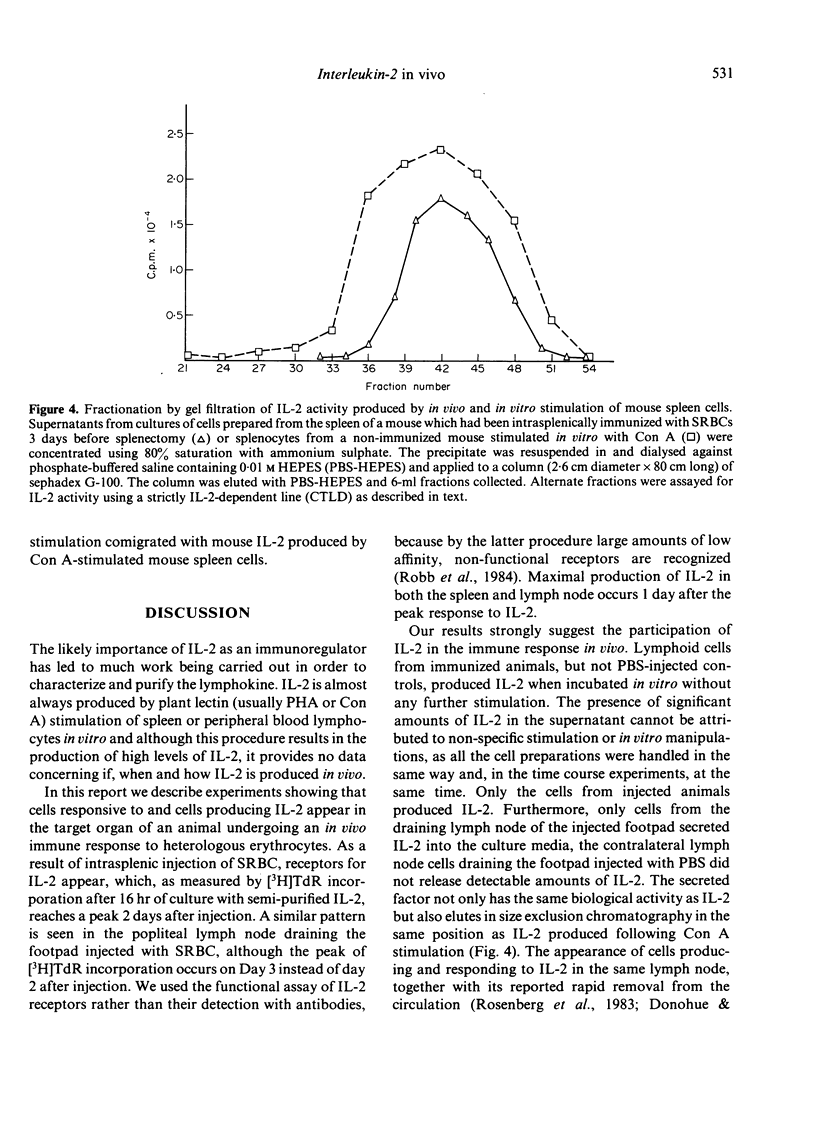
In this report, we describe experiments which demonstrate that antigenic stimulation in vivo causes the appearance of cells in both spleen and lymph node which secrete interleukin-2 (IL-2). Cells also appear in these organs which proliferate in response to IL-2. For these experiments, sheep red cells (SRBC) were injected into the spleens or footpads of mice, and cell suspensions from spleens or popliteal lymph nodes prepared at various times after antigenic stimulation. These cells were assayed for their ability to respond to IL-2, and their cell culture supernatants for secreted IL-2. The proliferative response to IL-2 steadily increased following SRBC injection to reach a peak at Day 2 for spleen cells and at Day 3 for lymph node cells. Maximal production of IL-2 was displaced from the maximal response to the lymphokine by peaking one day later for both organs. Our results strongly implicate the participation of IL-2 in the in vivo immune response and suggest the existence of in vivo regulatory mechanisms, which can control the time of IL-2 production and also the appearance of cells with receptors for IL-2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheever M. A., Greenberg P. D., Fefer A., Gillis S. Augmentation of the anti-tumor therapeutic efficacy of long-term cultured T lymphocytes by in vivo administration of purified interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):968–980. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue J. H., Rosenberg S. A. The fate of interleukin-2 after in vivo administration. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2203–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Simon P. L., Koopman W. J., Fuller-Bonar J. Biochemical relationship of thymocyte mitogenic factor and factors enhancing humoral and cell-mediated immune responses. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1353–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg M., Ivars F., Coutinho A., Larsson E. L. Regulation of T cell growth factor production: arrest of TCGF production after 18 hours in normal lectin-stimulated mouse spleen cell cultures. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattler B. G., Jr, Rocklin R. E., Ward P. A., Rickles F. R. Functional features of lymphocytes recovered from a human renal allograft. Cell Immunol. 1973 Nov;9(2):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefeneider S. H., Conlon P. J., Henney C. S., Gillis S. In vivo interleukin 2 administration augments the generation of alloreactive cytolytic T lymphocytes and resident natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Farrar J. J., Oppenheim J. J., Fuller-Bonar J., Dougherty S. Association of a low molecular weight helper factor(s) with thymocyte proliferative activity. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Medawar P., Hunt R., Palmer L., Doré C. A diet enriched in vitamin A acetate or in vivo administration of interleukin-2 can counteract a tolerogenic stimulus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Feb 22;220(1221):439–445. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato N., Reid L., Bloom B. R. On the heterogeneity of murine natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):750–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., MacDermott R. P., Chess L., Schlossman S. F., David J. R. Studies on mediator production by highly purified human T and B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1303–1316. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitz M., Spitz L., Thorpe R., Eugui E. Intrasplenic primary immunization for the production of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1984 May 11;70(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Heeg K., Röllinghoff M., Pfizenmaier K. T-cell-derived helper factor allows in vivo induction of cytotoxic T cells in nu/nu mice. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):278–278. doi: 10.1038/284278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M. T-T-cell interactions during the vitro cytotoxic allograft responses. I. Soluble products from activated Lyl+ T cells trigger autonomously antigen-primed Ly23+ T cells to cell proliferation and cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1523–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Aarden L. A., Shaw J., Paetkau V. Molecular and quantitative analysis of helper T cell-replacing factors on the induction of antigen-sensitive B and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1633–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


