Abstract
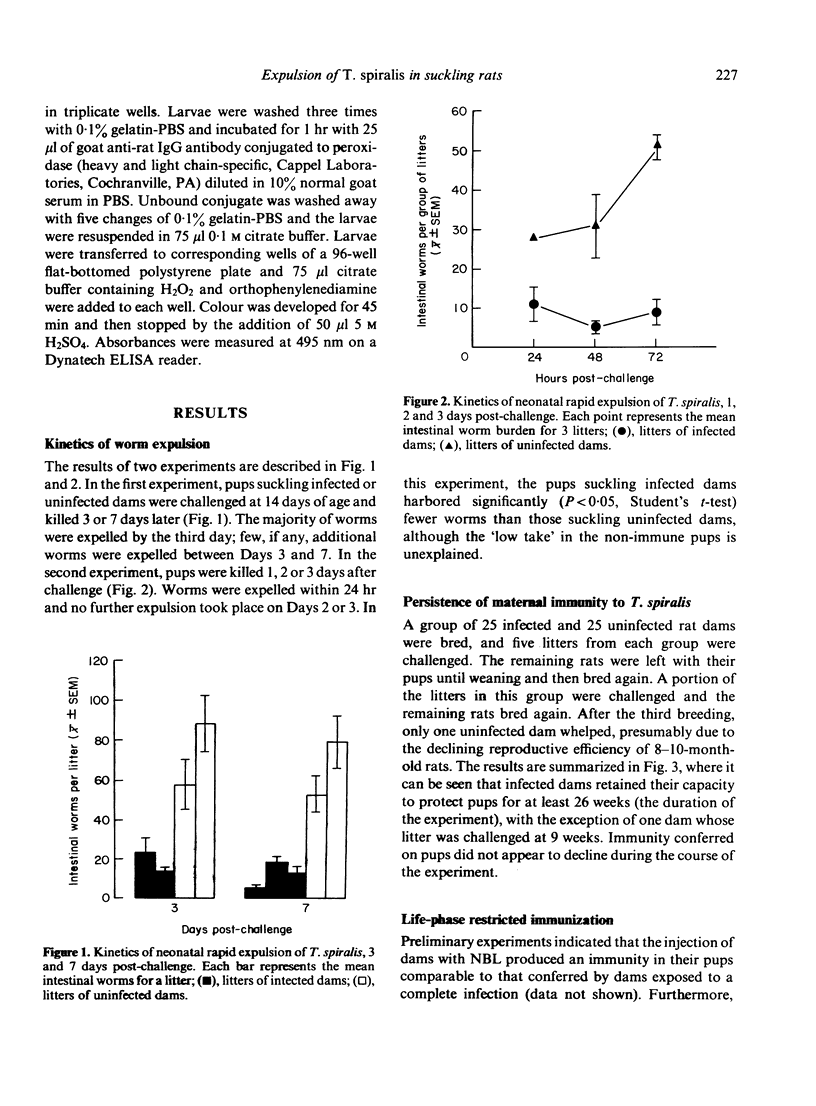
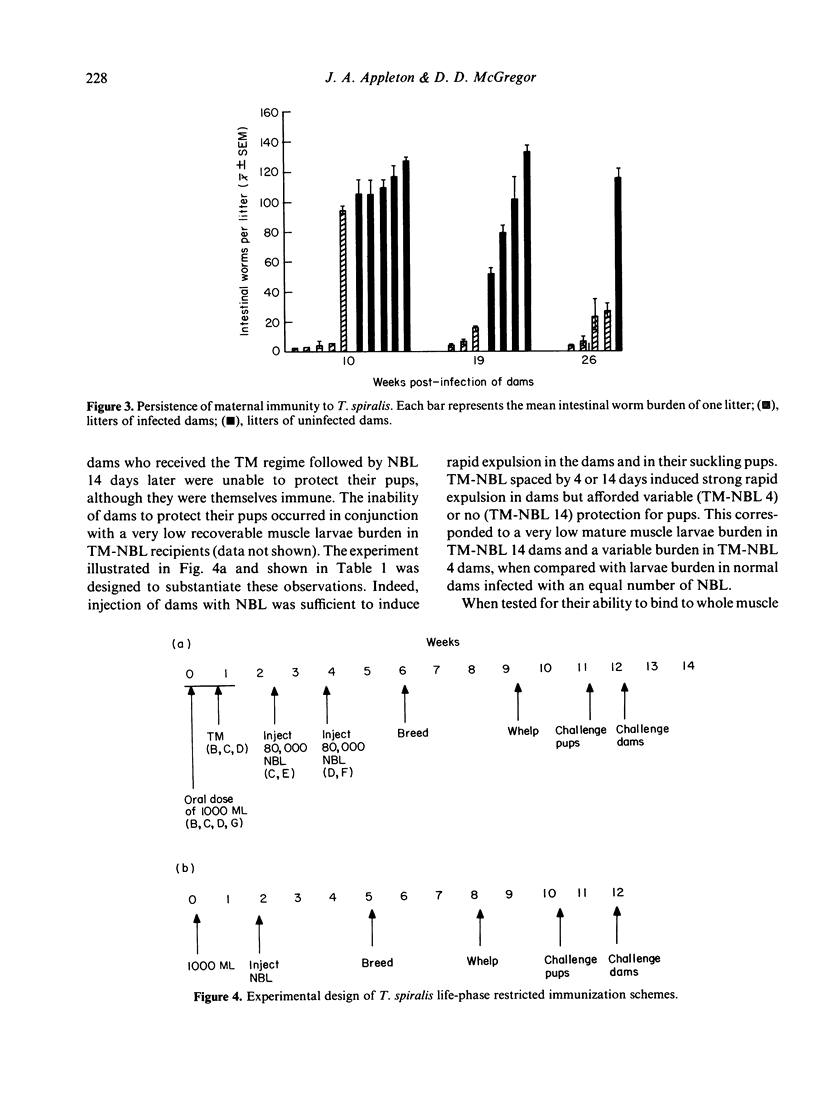
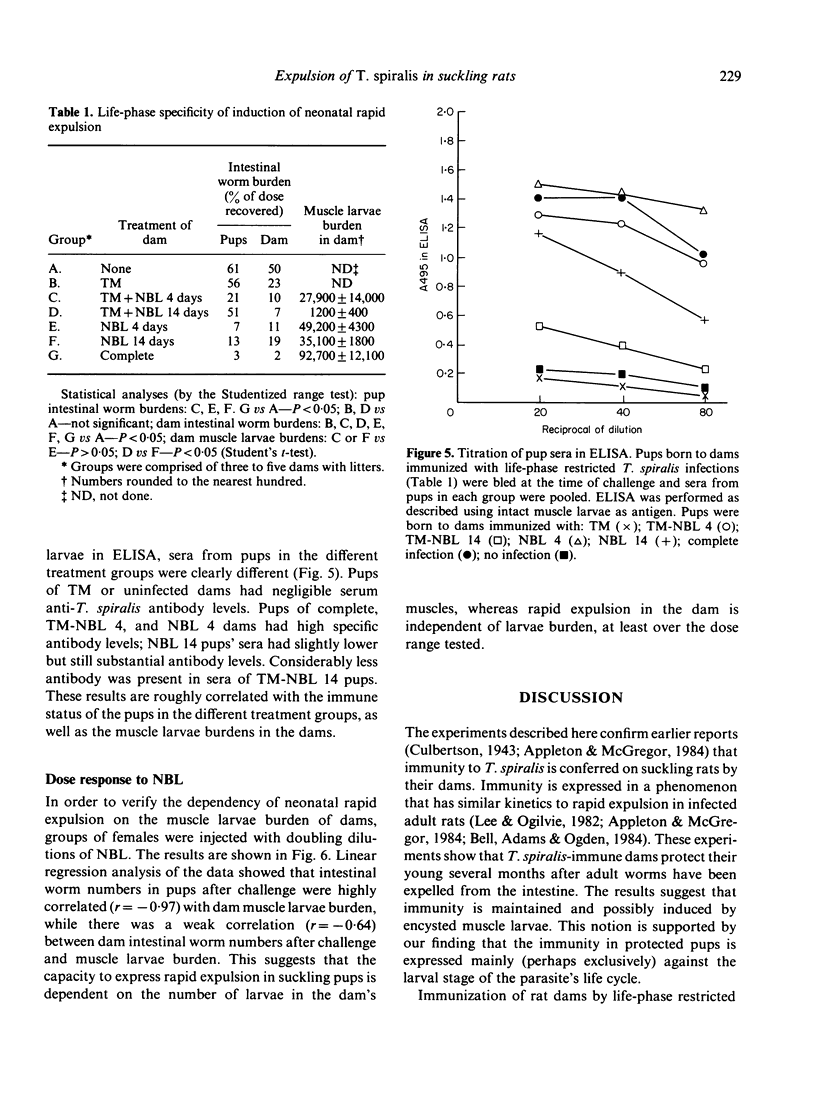
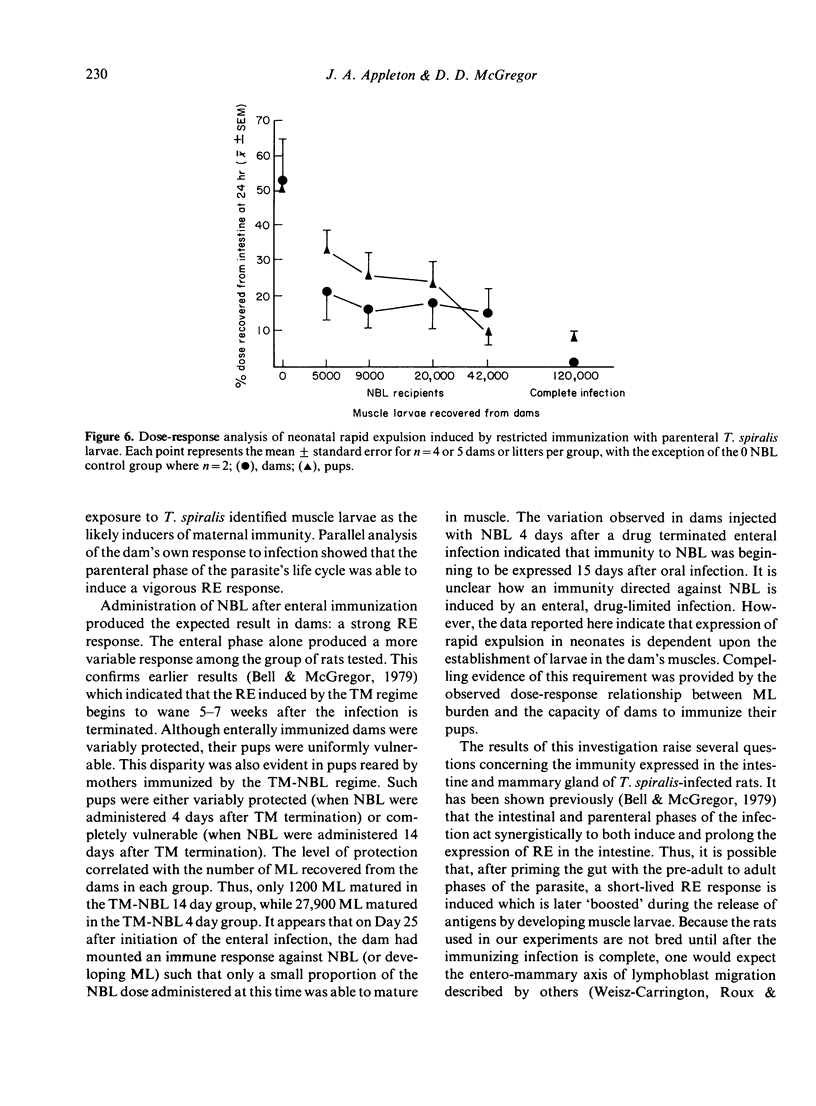
Rat dams infected with 1000 Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae, 4 weeks prior to breeding, provided their suckling offspring with immunity to challenge with 200 muscle larvae at 2 weeks of age. The immunity was expressed in the elimination of 75-99% of the challenge dose within 24 hr. The intestinal worm burden did not decline significantly after the initial expulsion. Infected dams continued to protect their offspring during three breeding cycles, for as long as 26 weeks after infection. Immunity was conferred upon pups by dams that had been selectively immunized with the parenteral phase of the parasite's life cycle. Immunization with a drug-terminated enteral infection was ineffective as was enteral immunization followed by the parenteral phase. Further analysis revealed that rapid expulsion by pups was dependent on the number of mature muscle larvae recovered from dams immunized with NBL. By comparison, the expulsive capacity of the same dams was not improved by increasing the numbers of NBL within the range tested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. G., Adams L. S., Ogden R. W. Intestinal mucus trapping in the rapid expulsion of Trichinella spiralis by rats: induction and expression analyzed by quantitative worm recovery. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.267-272.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. G., McGregor D. D., Adams L. S. Trichinella spiralis: characterization and strain distribution of rapid expulsion in inbred mice. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Jun;53(3):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. G., McGregor D. D. Rapid expulsion of Trichinella spiralis: coinduction by using antigenic extracts of larvae and intestinal stimulation with an unrelated parasite. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):194–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.194-199.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. G., McGregor D. D. Trichinella spiralis: role of different life cycle phases in induction, maintenance, and expression of rapid expulsion in rats. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Aug;48(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro G. A., Badial-Aceves F., Adams P. R., Copeland E. M., Dudrick S. J. Response to immunized, parenterally nourished rats to challenge infection with the nematode, Trichinella spiralis. J Nutr. 1976 Oct;106(10):1484–1491. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.10.1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum E. D., Despommier D. D., McGregor D. D. Immunity to Trichinella spiralis. I. Transfer of resistance by two classes of lymphocytes. Immunology. 1977 Dec;33(6):787–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B., Morris R. The digestion and transmission of labelled immunoglobulin G by enterocytes of the proximal distal regions of the small intestine of young rats. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):427–442. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin D., Lloyd M. Immunity to primary and challenge infections of Trichinella spiralis in mice: a re-examination of conventional parameters. Parasitology. 1976 Apr;72(2):173–182. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000048472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassom D. L., Wakelin D., Brooks B. O., Krco C. J., David C. S. Genetic control of immunity to Trichinella spiralis infections of mice. Hypothesis to explain the role of H-2 genes in primary and challenge infections. Immunology. 1984 Apr;51(4):625–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz-Carrington P., Roux M. E., Lamm M. E. Plasma cells and epithelial immunoglobulins in the mouse mammary gland during pregnancy and lactation. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1306–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


