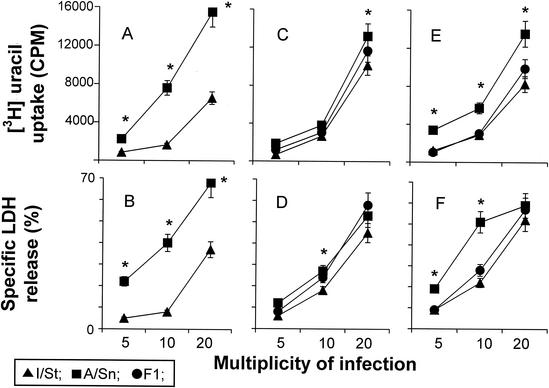
FIG. 8.
Mycobacterial growth in and cytopathic effect on macrophages developed in vitro. Macrophages were developed from progenitors residing in bone marrow (A and B), spleen (C and D), and lungs (E and F) by culturing them for 10 to 14 days in the presence of growth factors as described in Materials and Methods; they were then detached and put into the wells of flat-bottom 96-well plates at 20 × 103/well. The cells were infected with M. tuberculosis at the indicated MOIs, and [3H]uracil uptake (A, C, and E) and LDH release (B, D, and F) in 72-h cultures were measured as described above. The results are shown as means ± SDs for triplicate cultures in one of two similar experiments. In all cases, mycobacteria multiplied more vigorously and killed the host cells more readily in A/Sn than in I/St macrophages. Significant interstrain differences (P < 0.001 to 0.05; Mann-Whitney U test) are marked with asterisks. In all cases, an intermediate type of inheritance by F1 macrophages of the phenotypes under study was observed.