Abstract
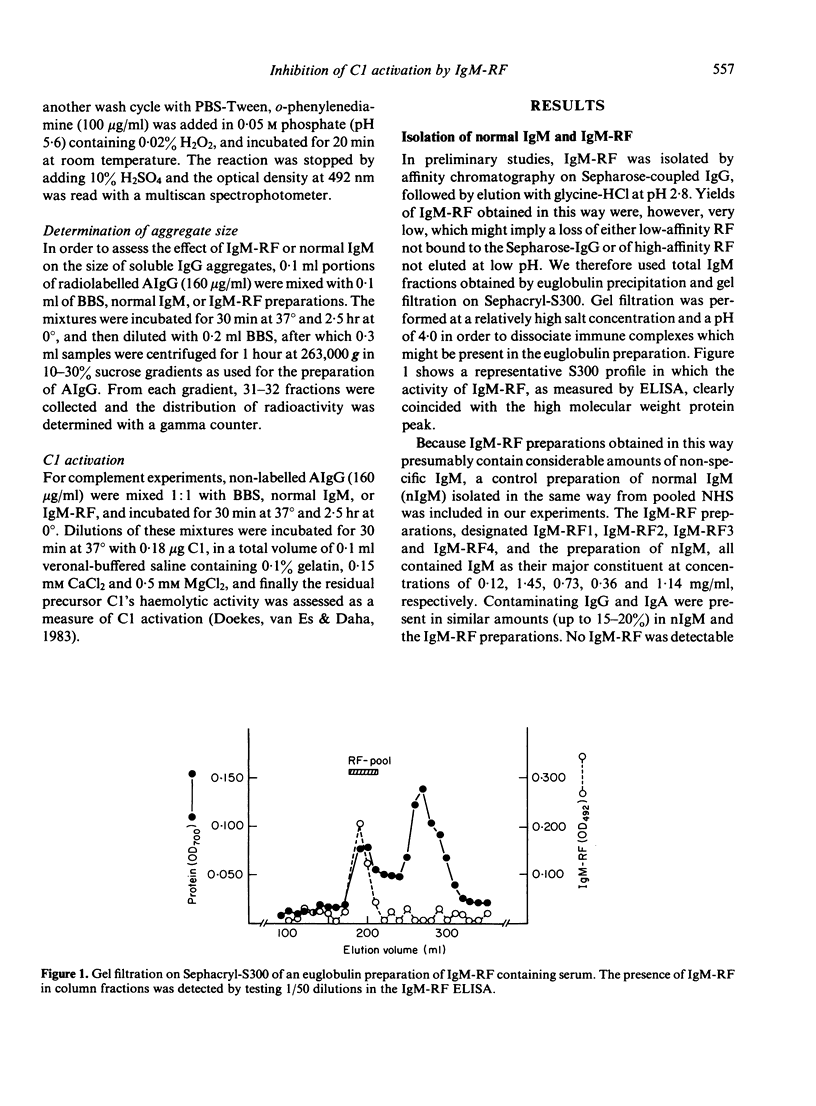
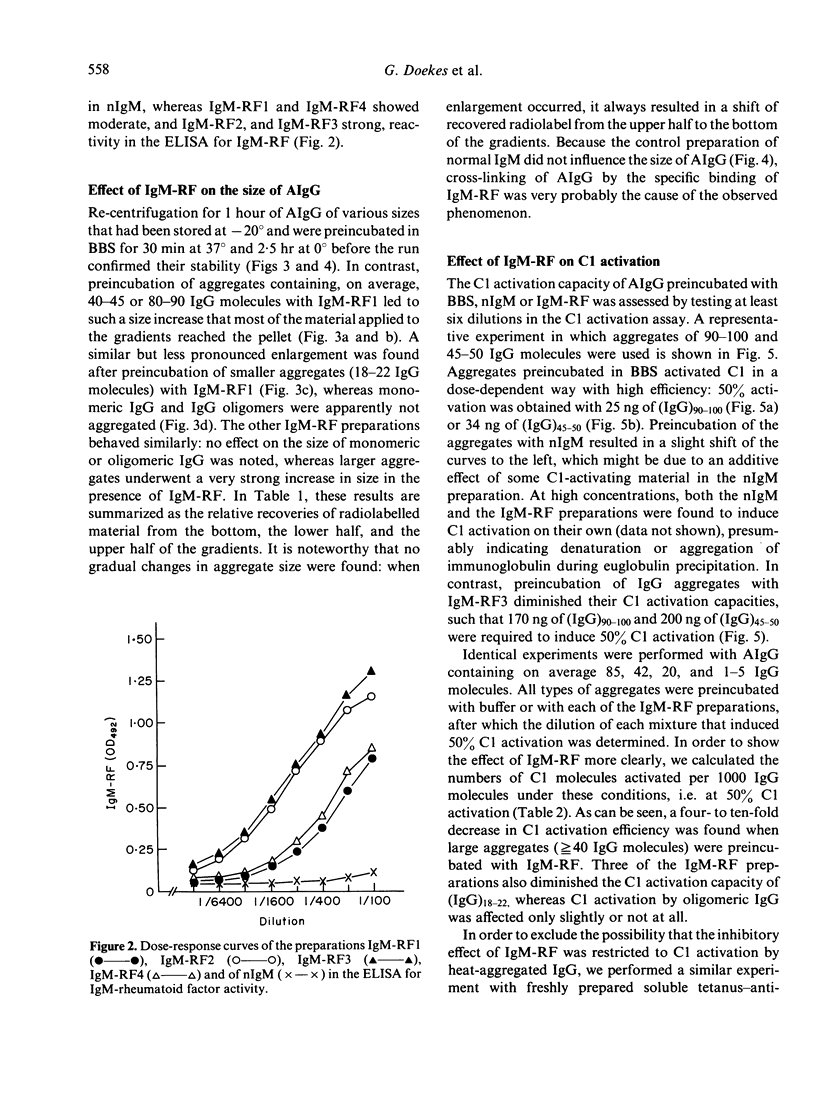
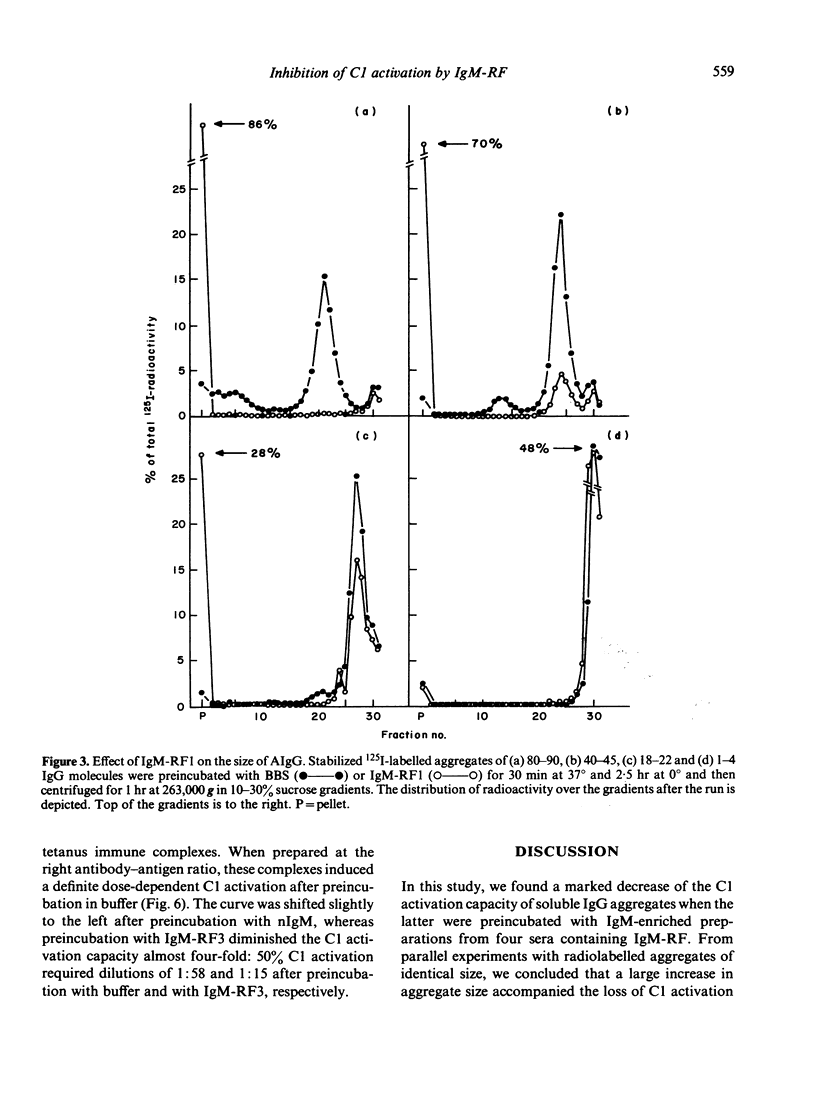
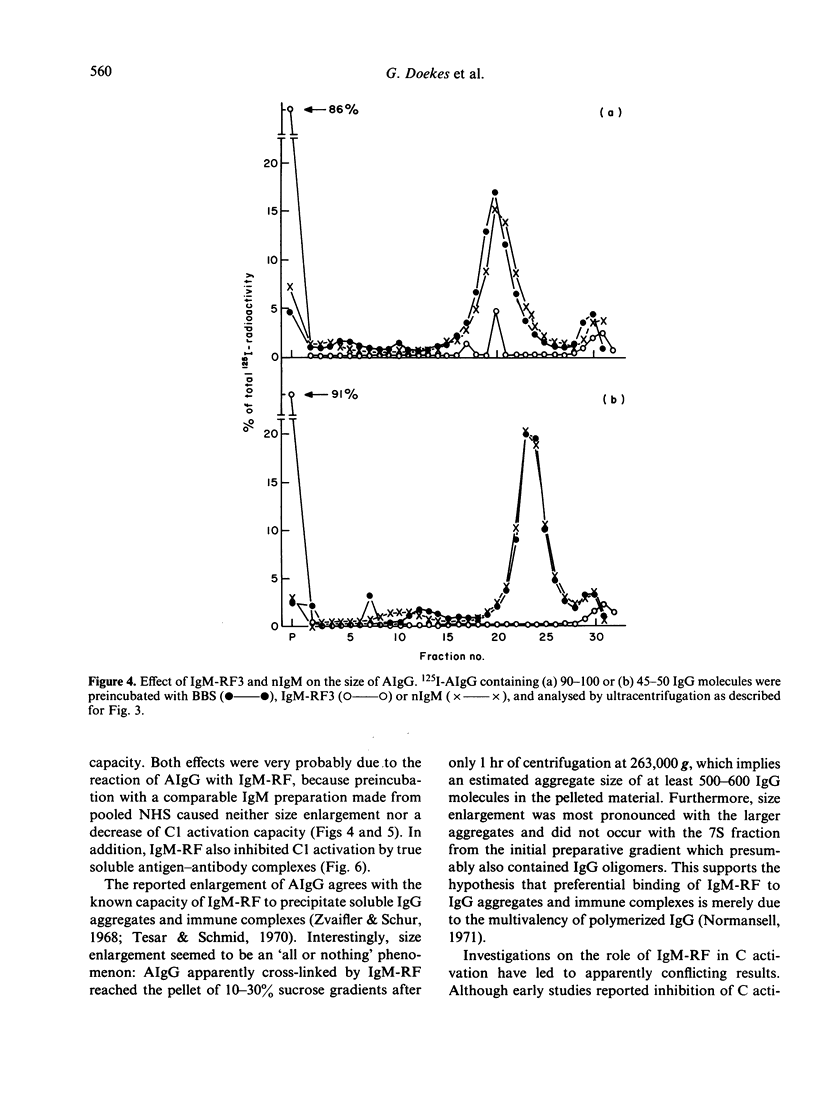
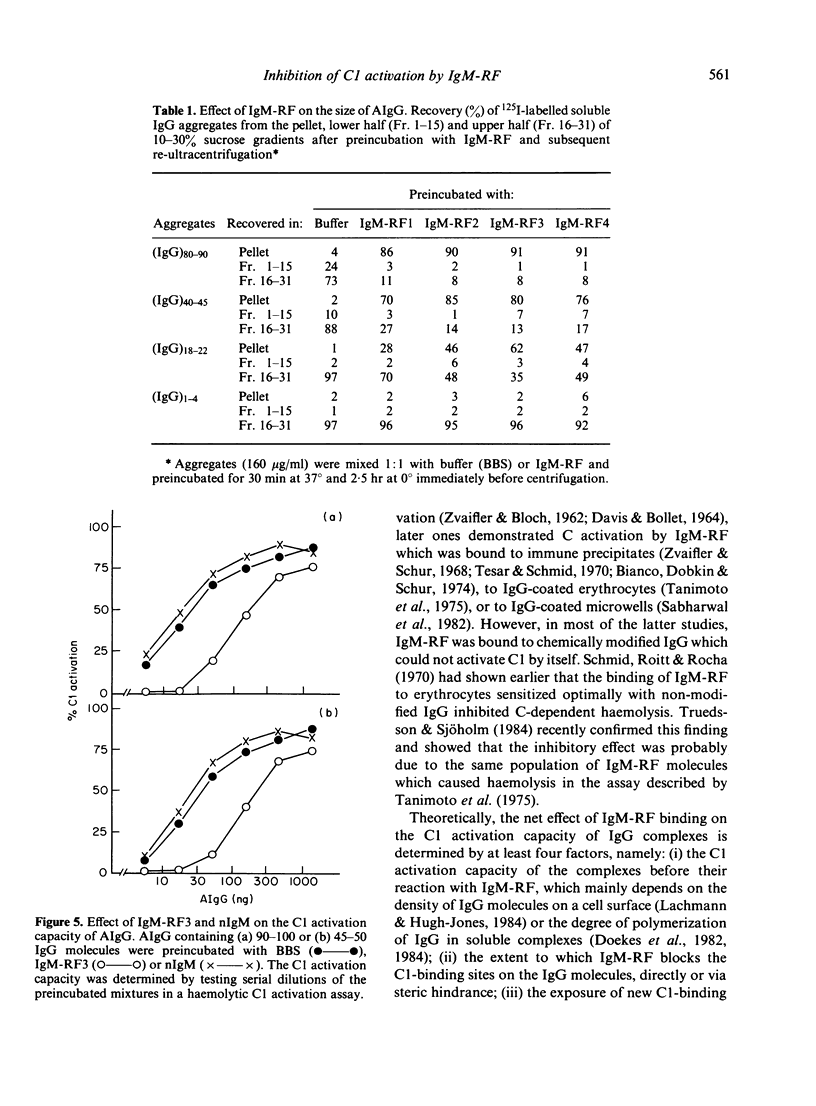
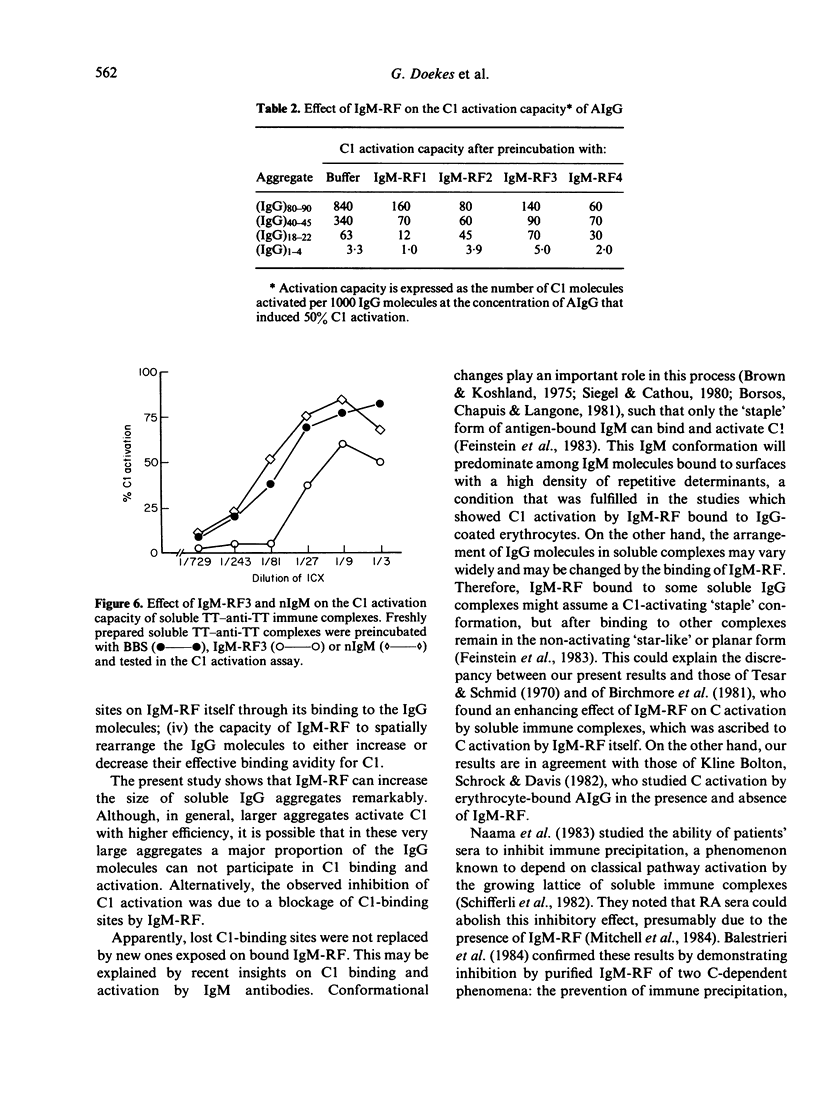
The influence of IgM-rheumatoid factor (IgM-RF) on the activation of isolated C1 by soluble IgG aggregates (AIgG) and immune complexes was studied. IgM preparations obtained from the sera of four patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis markedly reduced the C1 activation capacity of AIgG, especially when large aggregates were tested. The results of parallel experiments with radiolabelled AIgG indicated that this inhibitory effect of IgM-RF was accompanied by a very large increase of the aggregate size. A comparable IgM preparation isolated from pooled normal human serum influenced neither the size nor the C1 activation capacity of AIgG. The inhibitory effect of IgM-RF on C1 activation was also demonstrated for soluble tetanus-anti-tetanus immune complexes. Thus, in spite of the established C activation ability of IgM-RF and the fact that, in general, larger IgG aggregates and immune complexes activate C1 more efficiently, cross-linking and size enlargement of soluble IgG complexes and aggregates by IgM-RF lead to a decrease of the C1 activation capacity. As a consequence, IgM-RF may reduce plasma complement activation by soluble IgG complexes in the circulation of patients with seropositive rheumatic diseases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balestrieri G., Tincani A., Migliorini P., Ferri C., Cattaneo R., Bombardieri S. Inhibitory effect of IgM rheumatoid factor on immune complex solubilization capacity and inhibition of immune precipitation. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Oct;27(10):1130–1136. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco N. E., Dobkin L. W., Schur P. H. Immunological properties of isolated IgG and IgM anti-gamma-globulins (rheumatoid factors). Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):91–101. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmore D. A., Taylor R. P., Waller S. J., Davis J. S., 4th, Morley K. W. Interaction between rheumatoid factor and antibody/DNA complexes: enhancement of complement fixation. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Mar;24(3):527–533. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Schrock J. H., Davis J. S., 4th Rheumatoid factor inhibition of in vitro binding of IgG complexes in the human glomerulus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Mar;25(3):297–303. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Chapuis R. M., Langone J. J. Distinction between fixation of C1 and the activation of complement by natural IgM anti-hapten antibody: effect of cell surface hapten density. Mol Immunol. 1981 Sep;18(9):863–868. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Koshland M. E. Activation of antibody Fc function by antigen-induced conformational changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. S., 4th, BOLLET A. J. PROTECTION OF A COMPLEMENT-SENSITIVE ENZYME SYSTEM BY RHEUMATOID FACTOR. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., Vanes L. A., Daha M. R. Influence of aggregate size on the binding and activation of the first component of human complement by soluble IgG aggregates. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):705–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Activation of C1 by soluble IgG aggregates as detected by a novel one-step hemolytic assay that specifically measures the proenzyme form of C1s. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1924–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Binding and activation of the first complement component by soluble immune complexes: effect of complex size and composition. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Feb;19(2):99–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN W., JOHNSON A., RAGAN C. Observations on a precipitin reaction between serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a preparation (Cohn fraction II) of human gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):235–237. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator-C1s complexes in inflammatory joint disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):521–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Hughes-Jones N. C. Initiation of complement activation. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):143–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01893018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. S., Naama J. K., Veitch J., Whaley K. IgM-RF prevents complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):445–448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naama J. K., Mitchell W. S., Whaley K. Inhibition of complement-mediated solubilization of antigen-antibody complexes by sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):429–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E. Anti- -globulins in rheumatoid arthritis sera. II. The reactivity of anti- -globulin rheumatoid factors with altered G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jul;8(7):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Case D. B., Drayer D. E., Reis S., Lorenzo B. Development of antinuclear antibody in patients treated with high doses of captopril. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 May;27(5):579–581. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabharwal U. K., Vaughan J. H., Fong S., Bennett P. H., Carson D. A., Curd J. G. Activation of the classical pathway of complement by rheumatoid factors. Assessment by radioimmunoassay for C4. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Feb;25(2):161–167. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Woo P., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. I. Role of the classical and alternative pathways. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):555–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. R., Roitt I. M., Rocha M. J. Complement fixation by a two-component antibody system: immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M anti-globulin (rheumatoid factor). Parodoxical effect related to immunoglobulin G concentration. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):673–693. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. C., Cathou R. E. Conformation of Immunoglobulin M. III. Structural requirements of antigen for complement fixation by equine IgM. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):1910–1915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Cooper N. R., Johnson J. S., Vaughan J. H. Complement fixation by rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):437–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI107949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesar J. T., Schmid F. R. Conversion of soluble immune complexes into complement-fixing aggregates by IgM-rheumatoid factor. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1206–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J., Schur P. Reactions of aggregated mercaptoethanol treated gamma globulin with rheumatoid factor--precipitin and complement fixation studies. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Aug;11(4):523–536. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


