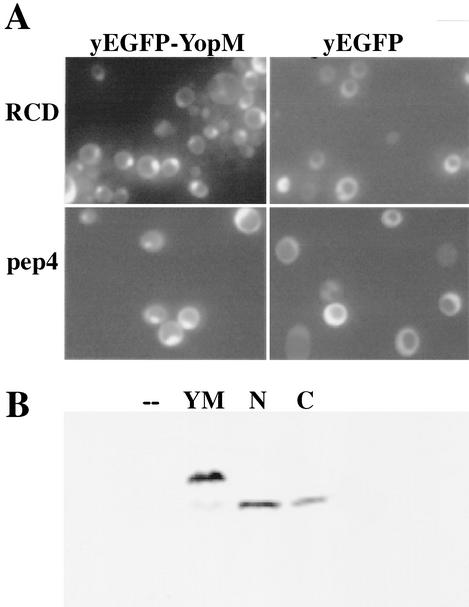
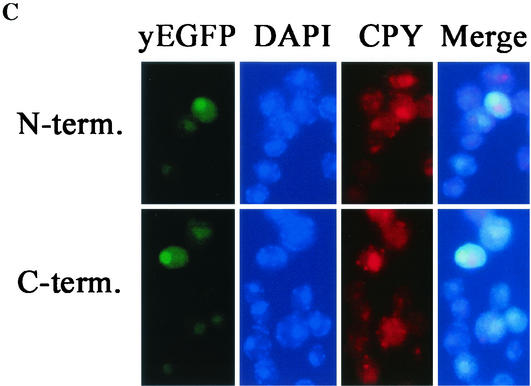
FIG. 6.
Both halves of YopM localize to the nucleus in yeast. (A) A control test showing the localization of yEGFP-YopM and yEGFP alone compared for S. cerevisiae RDC224 (wild type) (top) and the protease-deficient S. cerevisiae y604pep4 (bottom). (B) Immunoblot analysis of proteins extracted from S. cerevisiae y604pep4 after induction by galactose. Lanes: —, vector control expressing only yEGFP; YM, yEGFP-YopM; N, N-terminal half of YopM fused to yEGFP (yEGFP-YopM ΔLRR8-end); C, C-terminal half of YopM fused to yEGFP (yEGFP-YopM Δaa19-LRR7). The blots were probed with a rabbit polyclonal antibody against YopM; hence, yEGFP alone and background yeast proteins are not visualized. (C) The distribution was determined for fluorescence from yEGFP-YopM ΔLRR8-end (the N-terminal half of YopM) and yEGFP-YopM Δaa19-LRR7 (the C-terminal half of YopM) in S. cerevisiae y604pep4. From left to right, yEGFP indicates fluorescence from yEGFP-YopM proteins, DAPI indicates fluorescence from nuclei (DNA) stained with DAPI, CPY indicates fluorescence from CPY in the vacuole, and Merge indicates overlay of the green, blue, and red channels. In the Merge panel, note that the green fluorescence of yEGFP now appears turquoise due to overlap with blue DAPI fluorescence in the nucleus and that there is no overlap of yEGFP-YopM-related fluorescence with the red CPY fluorescence in the vacuole.