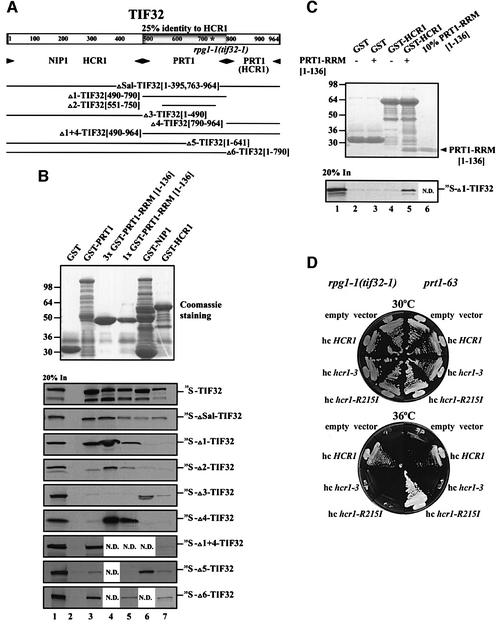
Fig. 4. Physical and functional interactions between homologous domains in TIF32/RPG1 and HCR1 and the PRT1 RRM. (A) Schematic of the TIF32 amino acid sequence, with the domain showing 25% identity to HCR1 (HLD) shaded and the asterisk indicating the single amino acid substitution made by rpg1-1. Arrowheads beneath the schematic delimit boundaries of the minimal segments required for interactions with the indicated proteins, based on the results shown in (B). The lines beneath the arrowheads depict the 35S-labeled segments of TIF32 used for the binding assays shown in (B), designated by clone name and the TIF32 amino acids present (in brackets). (B) Homologous domains in HCR1 and TIF32 bind to the PRT1 RRM in vitro. Binding of different GST fusion proteins (labeled across the top of the upper panel) to the various 35S-labeled segments of TIF32 labeled to the right of the lower panels. Binding experiments were conducted as described in Figure 1C. Lanes 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 show binding to GST alone, GST–PRT1, 3× GST–PRT1 RRM[1–136], 1× GST–PRT1 RRM[1–136], GST–NIP1 and GST–HCR1, respectively. Lane 3 contains three times (3×) the arbitrary amount of GST–PRT1 RRM[1–136] loaded in lane 4 (1×). Lane 1 shows 20% of the input amounts of in vitro translated proteins added to each reaction (20% In). (C) The PRT1 RRM can bridge interaction between HCR1 and TIF32 in vitro. A 10 µg aliquot of GST alone or GST–HCR1 was mixed with 10 µl of [35S]Δ1-TIF32 (lanes 2–4) in the presence (10 µg) (lanes 3 and 5) or absence (lanes 2 and 4) of PRT1 RRM[1–136] at 4°C for 2 h, essentially as described in Figure 1C. The PRT1 RRM[1–136] fragment was cleaved from the GST moiety in GST–PRT1 RRM[1–136] using factor Xa (Pharmacia) as recommended by the vendor. Lane 1 shows 20% of the input amount of in vitro translated [35S]Δ1-TIF32 added to each reaction (20% In). Lane 6 shows 10% (∼1 µg) of the PRT1 RRM[1–136] fragment (indicated by an arrowhead) purified away from the GST moiety and used in this experiment. (D) Allele-specific suppression of the Ts– phenotypes of rpg1-1 and prt1-63 strains by different HCR1 alleles in high copy number. Transformants of rpg1-1(tif32-1) strain YLV314U (left-hand sectors) and prt1-63 strain TC-26-3 (right-hand sectors) containing high-copy-number plasmids (hc) carrying empty vector (YEplac181), HCR1 (YEpLVHCR1), hcr1-R215I (YEpLVhcr1-R215I) or hcr1-3 (YEpLVhcr1-3) were examined for growth at 30°C (upper block) and 36°C (lower block) on YPD medium.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.