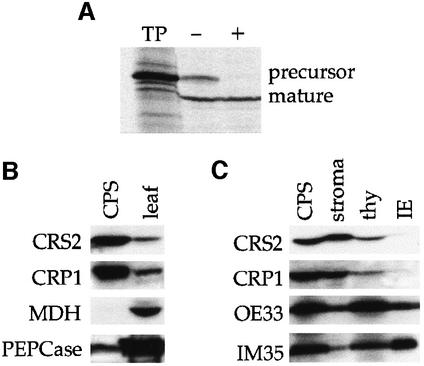
Fig. 3. CRS2 is localized to the chloroplast stroma. (A) Import of the crs2 gene product into isolated pea chloroplasts. Radiolabeled CRS2 was generated by in vitro translation of the full-length crs2 cDNA in the presence of [35S]methionine (TP-translation product). After a 30 min incubation with intact pea chloroplasts, aliquots were further incubated without (–) or with (+) thermolysin to degrade proteins external to the chloroplast. Intact chloroplasts were then repurified and the proteins were fractionated by SDS–PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. (B) CRS2 is enriched in the chloroplast fraction of leaf tissue. Ten micrograms of total leaf protein or 10 µg of protein from purified intact maize chloroplasts (CPS) were fractionated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed on an immunoblot. The blot was sequentially probed with antibodies to CRS2, the chloroplast protein CRP1 (Fisk et al., 1999), the mitochondrial protein malate dehydrogenase (MDH) and the cytosolic protein phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPCase). (C) CRS2 is localized to the chloroplast stroma. Purified chloroplasts from wild-type leaves (CPS) were fractionated into stroma, thylakoid (thy) and inner envelope (IE) fractions. The same proportion of each fraction was separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed on an immunoblot. The blot was probed sequentially with antibodies to CRS2, the stromal protein CRP1 (Fisk et al., 1999), the thylakoid lumen protein OE33 and the inner envelope protein IM35.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.