Abstract
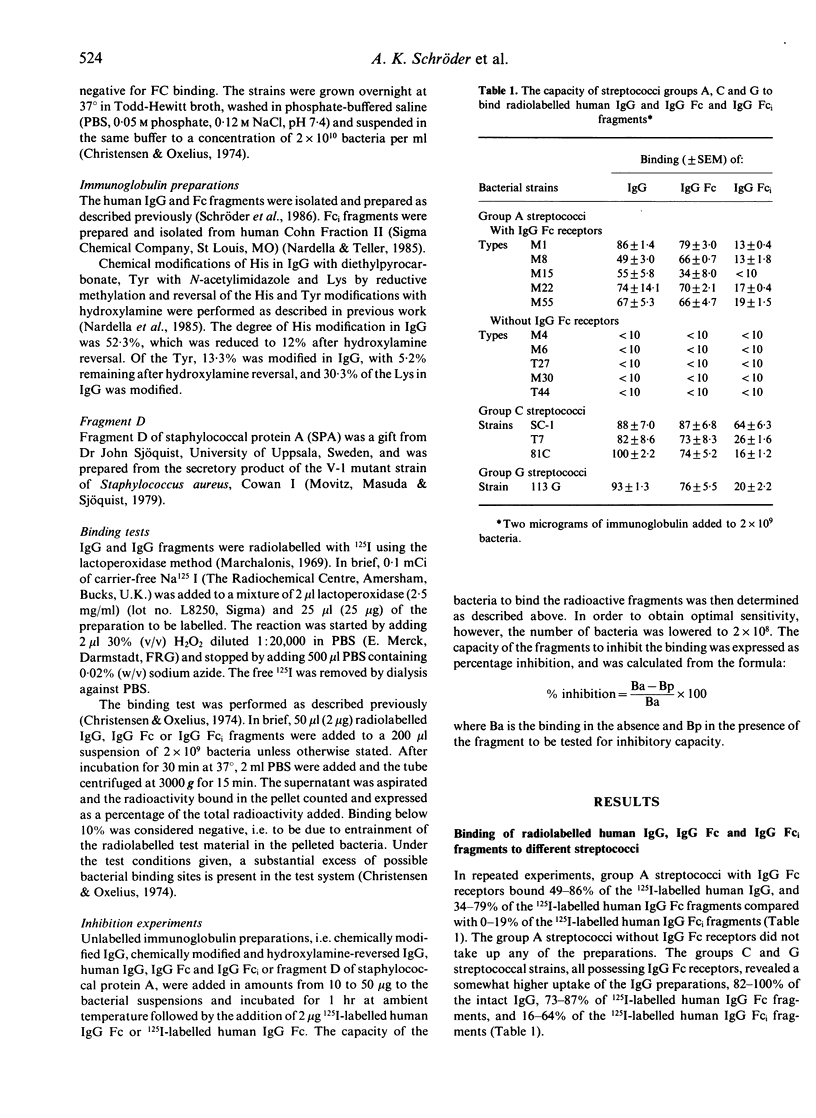
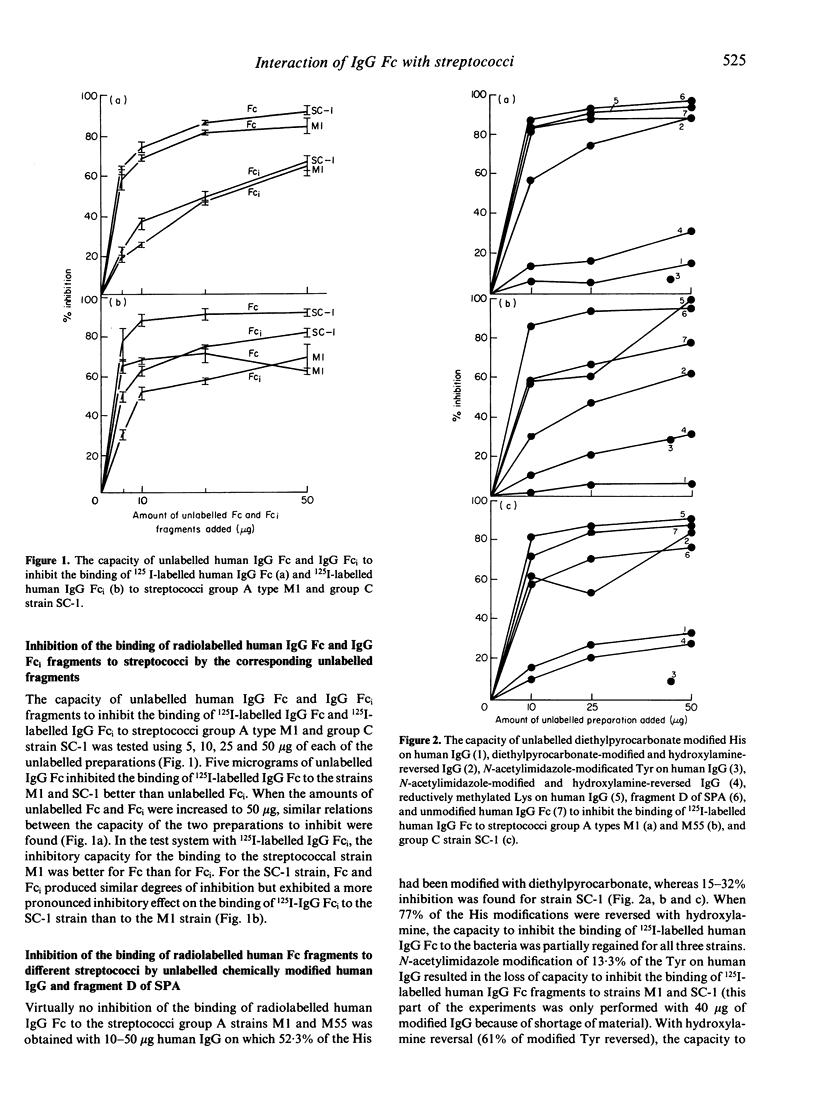
The interaction between living groups A, C and G streptococci and IgG Fc was studied using human IgG, IgG Fc and IgG Fc-intermediate (Fci) fragments, chemically modified human IgG and fragment D of staphylococcal protein A (SPA). Diethylpyrocarbonate modification of His or N-acetylimidazole modification of Tyr of human IgG resulted in the loss of its capacity to inhibit the binding of radiolabelled human IgG Fc to the group A streptococci types M1 and M55, and to the group C strain SC-1, indicating that the amino acids His and Tyr are involved in the binding. Lys seems not to participate in the binding of IgG to these bacteria, however, since reductive methylation of Lys did not reduce its inhibitory capacity. Fragment D of SPA also inhibited the binding of radiolabelled human IgG Fc to strains M1, M55 and SC-1. We have previously shown that these bacteria do not bind to IgG fragments consisting of only the C gamma 2 or C gamma 3 domains. On the basis of these results, and the known relative positions in space of the His and Tyr residues on IgG Fc, it is speculated whether streptococci with IgG Fc receptors, like SPA and rheumatoid factors, interact with IgG in the interface between the C gamma 2 and C gamma 3 domains and involve His 435 and one or more of Tyr 436, His 433 and His 310. The similarities in binding sites on IgG for RFs and these bacterial Fc binding proteins suggest structural similarities between them that may be relevant to the production of rheumatoid factors in rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton D. R., Boyd J., Brampton A. D., Easterbrook-Smith S. B., Emanuel E. J., Novotny J., Rademacher T. W., van Schravendijk M. R., Sternberg M. J., Dwek R. A. The Clq receptor site on immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):338–344. doi: 10.1038/288338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Oxelius V. A. Quantitation of the uptake of human IgG by some streptococci groups A, B, C, and G. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of a human Fc fragment and its complex with fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus at 2.9- and 2.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2361–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson P. J., Schröder A. K., Nardella F. A., Mannik M., Christensen P. Interaction between herpes simplex type 1-induced Fc receptor and human and rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) domains. Immunology. 1986 Jun;58(2):251–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Ito S., Miyazaki T., Ohta T. Structural studies of a human gamma 3 myeloma protein (Jir) bearing the allotypic marker Gm(st). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1865–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S. Rheumatoid factors are anti-idiotypic antibodies against virus-induced anti-Fc receptor antibodies. A hypothesis for the induction of some rheumatoid factors. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Nov;24(5):485–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movitz J., Masuda S., Sjöquist J. Physico- and immunochemical properties of staphylococcal protein A extracellularly produced by a set of mutants from Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(2):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb00441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardella F. A., Schröder A. K., Svensson M. L., Sjöquist J., Barber C., Christensen P. T15 group A streptococcal Fc receptor binds to the same location on IgG as staphylococcal protein A and IgG rheumatoid factors. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):922–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardella F. A., Teller D. C., Barber C. V., Mannik M. IgG rheumatoid factors and staphylococcal protein A bind to a common molecular site on IgG. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardella F. A., Teller D. C. Fc intermediate (Fci), a papain-generated fragment of human IgG, intermediate in charge, molecular weight and cleavage between the Fc and Fc' fragments of IgG. Mol Immunol. 1985 Jun;22(6):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardella F. A., Teller D. C., Mannik M. Studies on the antigenic determinants in the self-association of IgG rheumatoid factor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):112–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nik Jaafar M. I., Lowe J. A., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. Immunogenic and antigenic epitopes of immunoglobulins--VII. The topographical distribution of Fc gamma epitopes and the relationship of an iso-allotypic specificity to the presence of histidine 435. Mol Immunol. 1984 Feb;21(2):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Shigeta S. Appearance of immunoglobulin G Fc receptor in cultured human cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.770-774.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Hansen H. F., Björck L. Extraction and characterization of IgG Fc receptors from group C and group G streptococci. Mol Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder A. K., Nardella F. A., Mannik M., Svensson M. L., Christensen P. Interaction between streptococcal IgG Fc receptors and human and rabbit IgG domains. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):305–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torpier G., Capron A., Ouaissi M. A. Receptor for IgG(Fc) and human beta2-microglobulin on S. mansoni schistosomula. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):447–449. doi: 10.1038/278447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS J. F. ADSORPTION OF SENSITIZED SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES TO HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1364–1365. doi: 10.1038/2021364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Costa J., Hamilton V., Klein G., Rabson A. S. Changes in the expression of Fc receptor produced by induction of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoma cell lines. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


