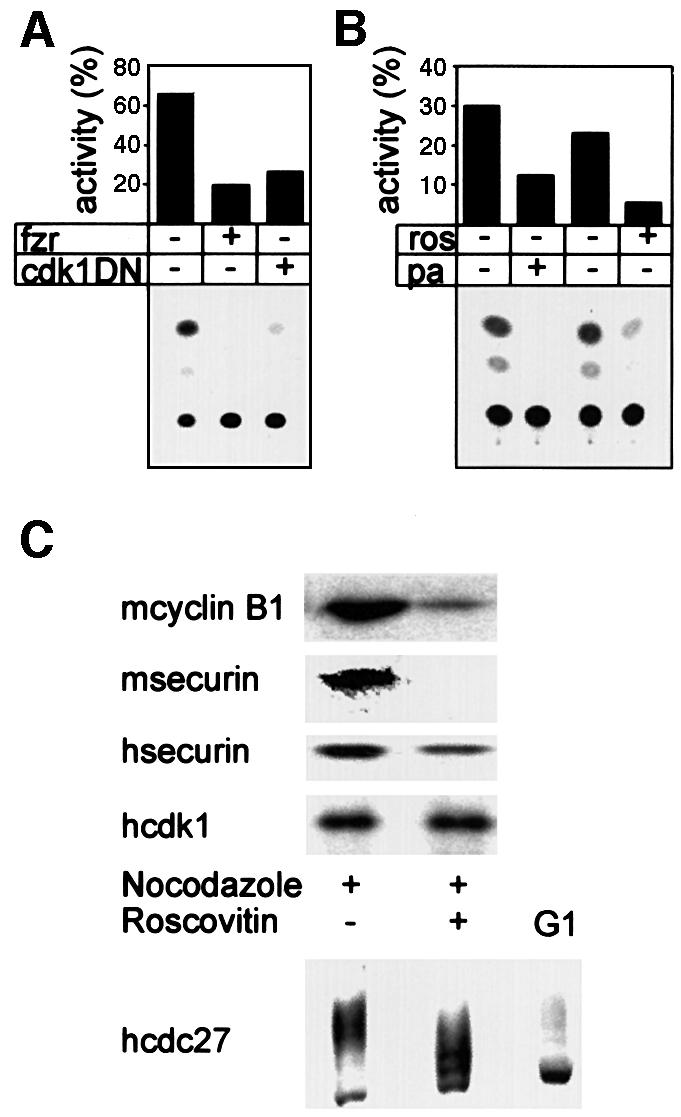
Fig. 4. Fzr overexpression and cdk1 inactivation lead to securin degradation in prometaphase. (A) Cells were co-transfected with securin–CAT with a fzr expression vector, a cdk1DN expression vector or an empty vector. They were arrested with nocodazole, harvested by shake-off and analyzed for CAT activity. Both fzr overexpression and cdk1 inhibition strongly activated the APC/C-specific degradation of securin–CAT in prometaphase. (B) Cells expressing securin–CAT were arrested in prometaphase by nocodazole and subsequently treated for 3 h with the cdk inhibitors roscovitin and purvalanol A, in the presence of nocodazole. They were then assayed for CAT activity. (C) Mouse (m) NIH 3T3 fibroblasts or human (h) HeLa cells were treated as in (B) and immunoblotted with securin, cyclin B1, cdk1 and cdc27 antibodies. The last antibody was used to show that roscovitin indeed leads to cdk1 inhibition in vivo as seen by the decrease in the phosphorylation of cdc27, a known cdk1 phosphorylation substrate.
