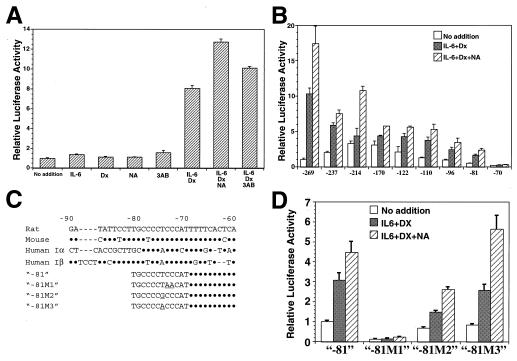
Figure 2.
IL-6/dexamethasone/PARP inhibitor-sensitive cis-element of Reg promoter. Luciferase activities were expressed relative to the level of luciferase activity in untreated control cells (no addition), which was assigned a value of 1.0. Values represent mean ± SEM of three to eight independent transfection experiments. Statistical analyses were performed using Student's t test. (A) Induction of Reg/luciferase hybrid gene expression by IL-6, dexamethasone (Dx), and PARP inhibitors. Luciferase activities were significantly increased by the addition of IL-6/Dx, IL-6/Dx/NA, and IL-6/Dx/3AB (P < 0.001). (B) Localization of IL-6/Dx/nicotinamide (NA)-responsive region in the Reg promoter. In all of the constructs except for −70, luciferase activities were significantly increased by the addition of IL-6/Dx and IL-6/Dx/NA (P < 0.05). (C) Alignment of Reg gene promoter regions. Rat (18), mouse (52), and human (16, 31) Reg I gene promoter regions were aligned. Nucleotide substitutions in the cis-element are indicated by underlines. Dots indicate residues that are identical to the rat promoter, and sequence gaps resulting from optimization of alignment are indicated by dashes. (D) Site-directed mutagenesis of the cis-element within the Reg promoter. In all of the mutants except for −81 M1, significant increases in luciferase activities by the stimulation of IL-6/Dx and IL-6/Dx/NA were retained (P < 0.01).