Figure 4.
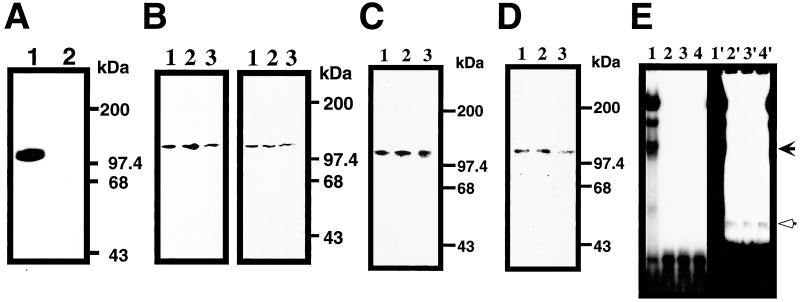
PARP as the cis-element binding protein for Reg gene. (A) Southwesten analysis of RINm5F cell nuclear extract. Nuclear extract from IL-6/dexamethasone (Dx)-treated cells was probed by probe 1 (lane 1) or probe M1 (lane 2). (B) Southwestern and immunoblot analyses of RINm5F cell nuclear extracts. In the left panel, Southwestern blot analysis was performed using probe 1. In the right panel, the blot was then probed by an anti-PARP antibody. Nuclear extracts from untreated, IL-6/dexamethasone (Dx)-, and IL-6/Dx/nicotinamide (NA)-treated cells were applied to lanes 1, 2, and 3, respectively. (C) Effects of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation on the binding ability to the cis-element. Nuclear extracts were separated by SDS/PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane. The membrane was incubated with 1 mM β-NAD+ (lane 1), β-NAD+/1 mM NA (lane 2), and β-NAD+/0.1 mM 3-aminobenzamide (3AB) (lane 3) and probed by 32P-labeled probe 1. (D) Binding of PARP to the cis-element in Southwestern analysis. Purified PARP was subjected to SDS/PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane. The membrane was incubated with 1 mM β-NAD+ (lane 1), β-NAD+/1 mM NA (lane 2), and β-NAD+/0.1 mM 3AB (lane 3) and probed by 32P-labeled probe 1. No binding to PARP was detected using probe M1 (data not shown). (E) Binding of PARP to the cis-element in GMSA. Purified PARP was incubated in the presence of 1 mM β-NAD+ (lane 2), β-NAD+/1 mM NA (lane 3), and β-NAD+/0.1 mM 3AB (lane 4) with 32P-labeled probe 1. Nuclear extract from IL-6/Dx/NA-treated cells was also analyzed as a control (lane 1). Right panel (lanes 1′–4′) represents the long exposure of the left panel (lanes 1–4).