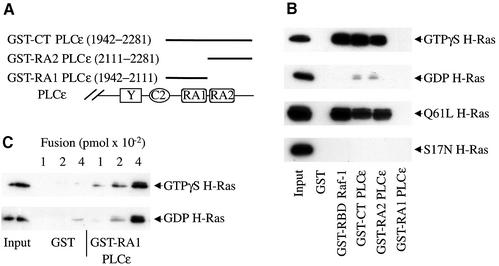
Fig. 3. H-Ras binding to RA domains of PLCε and the Ras-binding domain (RBD) of Raf-1. (A) Schematic diagram of regions of PLCε used in the GST fusion proteins. (B) H-Ras binding to RA domains of PLCε and the RBD of Raf-1. GST pull-down assays were used to determine Ras binding. GST and GST fusion proteins, as indicated, were incubated with GTPγS- or GDP-loaded H-Ras (upper two panels) or lysates from COS-7 cells overexpressing mutant active (Q61L H-Ras) and inactive (S17N H-Ras) H-Ras, all shown with arrows. An image of an autoradiograph of a typical western blot stained with anti-Ras is shown. Input, 1:4-fold dilution, is the amount of Ras added per lane. Approximately 100 pmol of each fusion protein was loaded on each lane. Representative of three similar experiments. (C) GTP-independent binding of Ras to the RA1 domain of PLCε. Binding of GTPγS- and GDP-loaded H-Ras to increasing concentrations of GST or GST–RA1 PLCε fusion protein is shown. The input was diluted 20-fold compared with the input in (B). Representative of two similar experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.