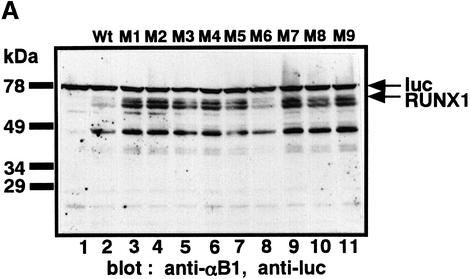
Fig. 4. Stabilization of RUNX1 by substitution of Lys by Arg. (A) P19 cells were transfected with the plasmids expressing wild-type RUNX1 (Wt, lane 2) or mutants with a single amino acid substitution of Lys to Arg (mutants M1–9, lanes 3–11). Whole-cell extracts were analyzed by western blotting using anti-αB1 and anti-luciferase (anti-luc) as an internal control. The positions of RUNX1 and luc are indicated by arrows. (B) Amino acid sequence comparison of the Runt domains of different animal species. Conserved Lys are indicated by bold letter K. The amino acid sequence accession No. of each protein in the Swiss-Prot and DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases is given in parentheses: Runx1 (D13802), residues 50–177; Runx2 (D14636), residues 94–221; RUNX1 (Q01196), residues 50–177; RUNX2 (Q08775), residues 102–219; RUNX3 (Q13761), residues 54–181; xAML1 (O73725), residues 50–177; spRUNT (Q26628), residues 57–184; ceRUNT (O01834), residues 10–137; dLOZENGE (Q24183), residues 278–405; and dRUNT (Q24709), residues 106–233.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.