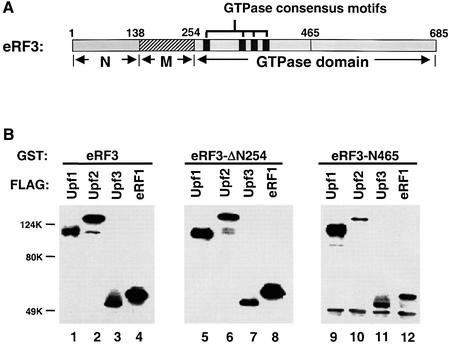
Fig. 6. The Upf proteins and eRF1 interact with the essential GTPase domain of eRF3. (A) Schematic diagram of the domain structure of the yeast release factor eRF3 (Sup35p). (B) GST pull-down experiment. Purified GST–eRF3 (1.0 µg, lanes 1–4), eRF3-N254Δ (1.0 µg, lanes 5–8) or eRF3-N465 (1.0 µg, lanes 9–12) was combined with FLAG-Upf1p (1.0 µg, lanes 1, 5 and 9), -Upf2p (1.0 µg, lanes 2, 6 and 10), -Upf3p (0.5 µg, lanes 3, 7 and 11) or -eRF1 (0.5 µg, lanes 4, 8 and 12). Following incubation and extensive washing, the proteins remaining associated with the beads were resolved on 12% SDS–PAGE and detected by the anti-FLAG antibody.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.