Abstract
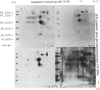
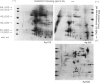
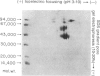
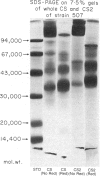
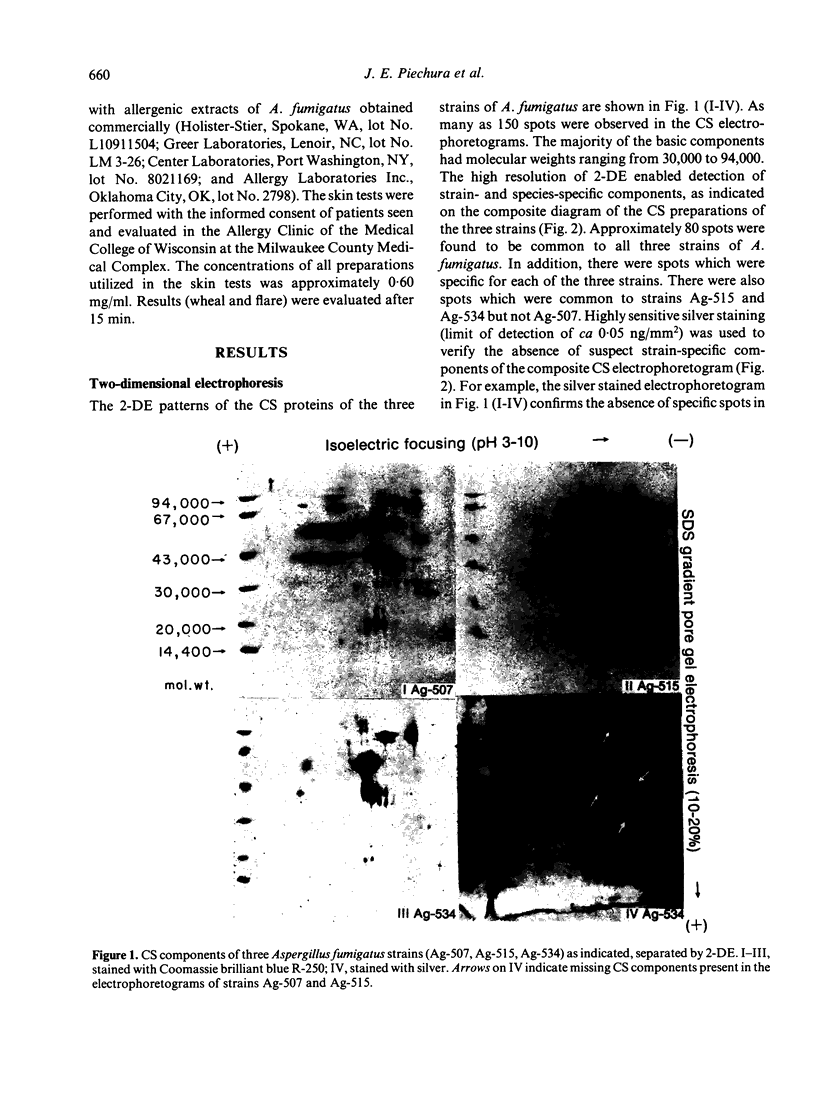
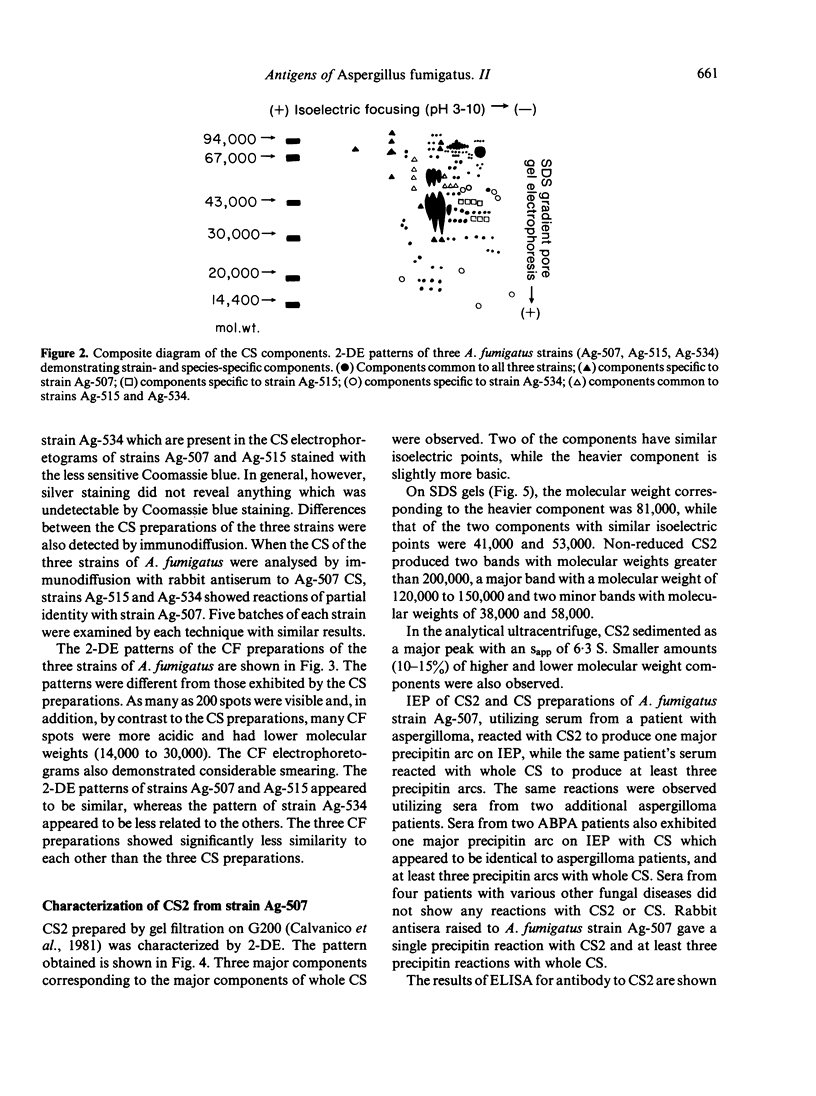
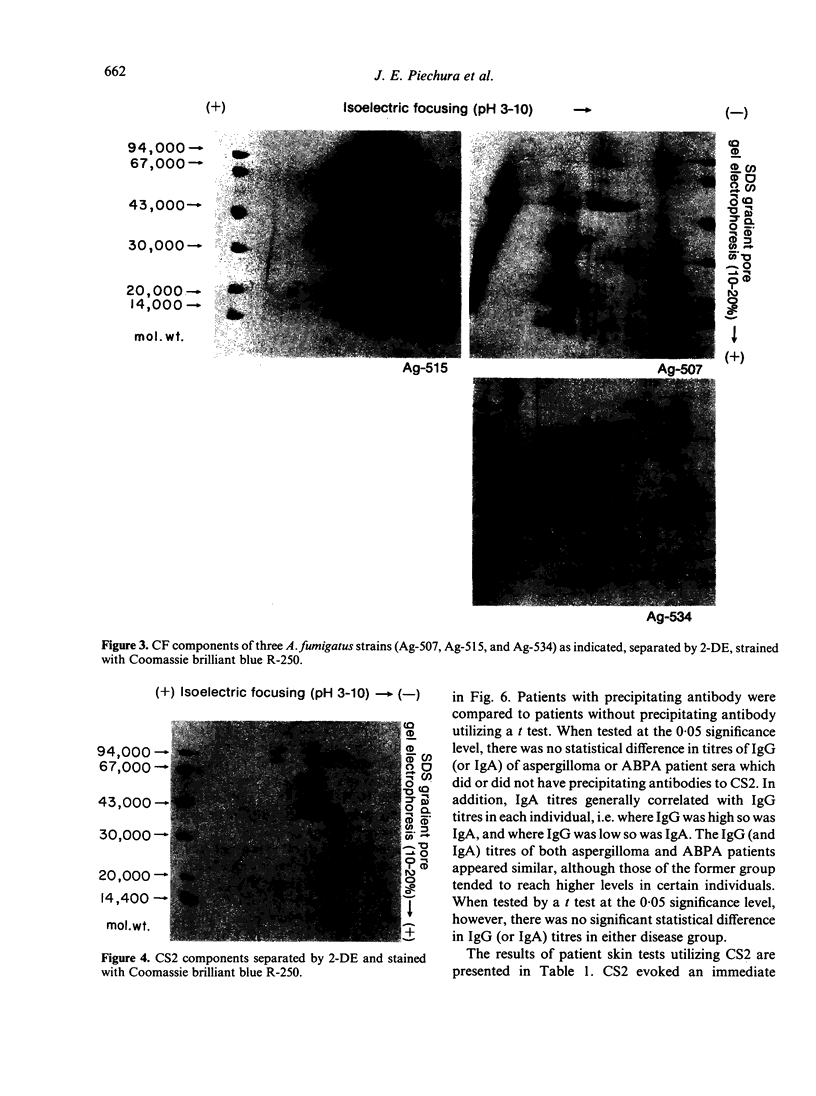
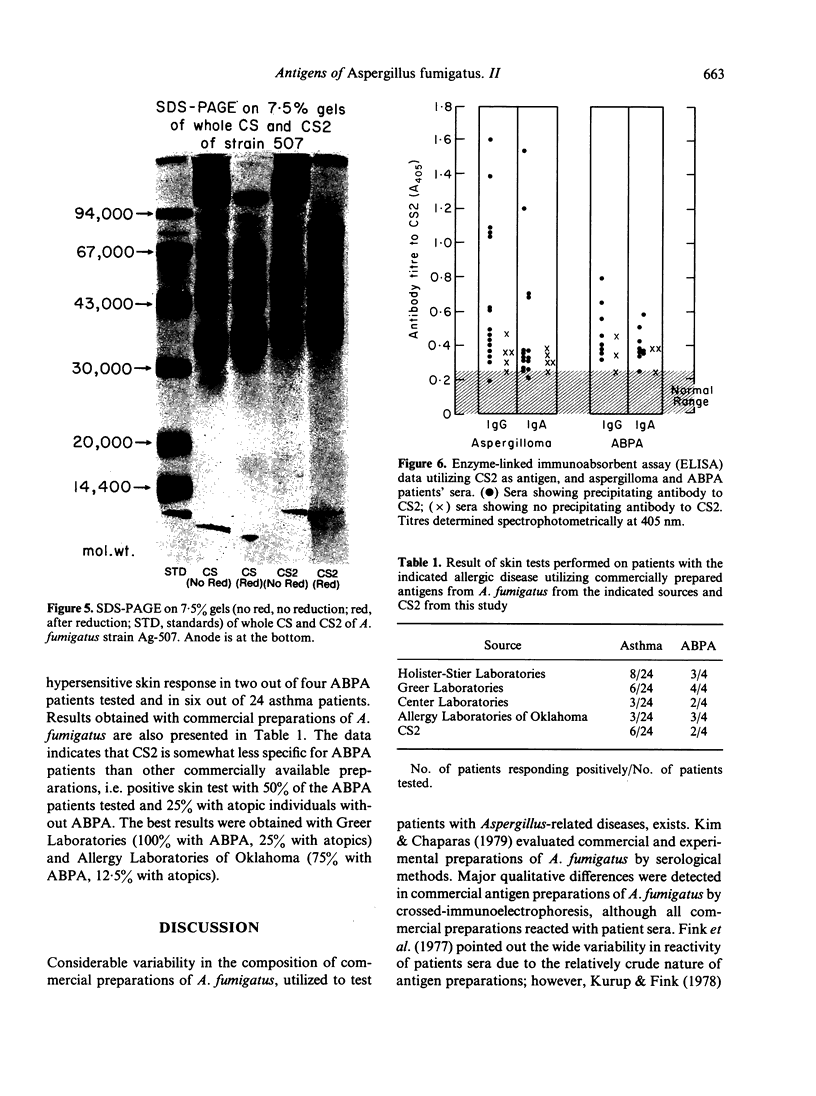
Cell sap (CS) and culture filtrate (CF) preparations of Aspergillus fumigatus strains Ag-507, Ag-515, and Ag-534 were analysed by two dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE; i.e., first dimension isoelectric focusing, second dimension sodium dodecyl sulphate gradient pore gel), which enabled detection of strain- and species-specific components. In CS preparations it was shown that CS2, a fraction isolated from strain Ag-507 by gel filtration, consists of the major protein components in the CS of the three A. fumigatus strains tested. Culture filtrate preparations of the three A. fumigatus strains analysed by 2-DE exhibited patterns dissimilar to the CS patterns, as well as to each other, presumably due to proteolysis. Culture filtrate preparations are therefore a less reliable source of standardized antigens than CS preparations. CS2 has a major component with a mol. wt. of approximately 150,000 and an sapp of 6.3 S. CS2 reacts on immunoelectrophoresis, producing one major precipitin arc with aspergilloma or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) patient sera. Antibody titres of the IgG and IgA classes to CS2, as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), were demonstrated to be similar in aspergilloma and ABPA patients; IgG titres were higher than IgA. Similar titres were also obtained utilizing sera of patients that did or did not exhibit precipitating antibodies to CS2. In the diagnosis of ABPA, skin tests with CS2 were comparable in specificity to currently available commercial preparations. Importantly, CS2 is a standardized major antigenic preparation of the CS of three A. fumigatus strains which has been shown to be diagnostically useful.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L., Anderson N. G. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of human plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5421–5425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvanico N. J., Du Pont B. L., Huang C. J., Patterson R., Fink J. N., Kurup V. P. Antigens of aspergillus fumigatus. 1. Purification of a cytoplasmic antigen reactive with sera of patients with aspergillus-related disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Sep;45(3):662–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structure and history of an ancient protein. Sci Am. 1972 Apr;226(4):58–passim. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0472-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. N., Barboriak J. J., Kurup V. P., Scribner G. H. Variability of extracts used in immunoprecipitin tests. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Oct;60(4):238–241. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber J. D., Jones R. D. Immunologic significance of aspergillin antigens of six species of Aspergillus in the serodiagnosis of aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Nov;108(5):1124–1129. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.5.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Chaparas S. D. Characterization of antigens from Aspergillus fumigatus. III. Comparison of antigenic relationships of clinically important aspergilli. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1297–1303. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N., Barboriak J. J., Scribner G. The detection of circulating antibodies against antigens from three strains of Aspergillus fumigatus. Mykosen. 1980 Jul;23(7):368–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1980.tb02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N. Evaluation of methods to detect antibodies against Aspergillus fumigatus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Apr;69(4):414–417. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.4.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N., Scribner G. H., Falk M. J. Antigenic variability of Aspergillus fumigatus strains. Microbios. 1977;19(77-78):191–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda R., Longbottom J. L., Pepys J. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for IgG and IgE antibodies to protein and polysaccharide antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus. Clin Allergy. 1979 Jul;9(4):359–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1979.tb02494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]