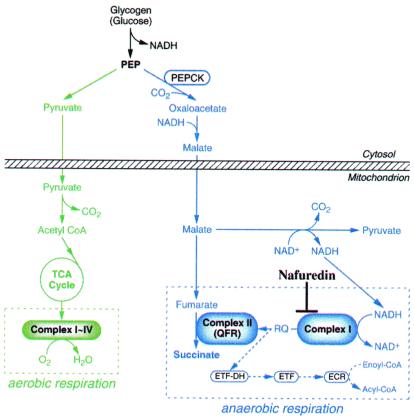
Figure 1.
NADH-fumarate reductase system in A. suum adult
mitochondria and inhibition site of nafuredin. In the
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)-succinate
pathway, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) produced by a
glycolytic process is carboxylated to form oxaloacetate and is then
reduced to malate. The cytosolic malate is transported into the
mitochondria, where it is first reduced to fumarate, and finally to
succinate by the rhodoquinol-fumarate reductase activity of complex II.
The terminal step is catalyzed by the NADH-fumarate reductase system
comprising complex I, rhodoquinone (RQ), and complex II, as described
in the text. Aerobic and anaerobic respiratory chains are boxed in
broken lines. Electron-transfer flavoprotein (ETF)
dehydrogenase:rhodoquinone branch
( ) is also included. ETF-DH,
ETF-dehydrogenase; ECR, enoyl-CoA reductase.
) is also included. ETF-DH,
ETF-dehydrogenase; ECR, enoyl-CoA reductase.