Abstract
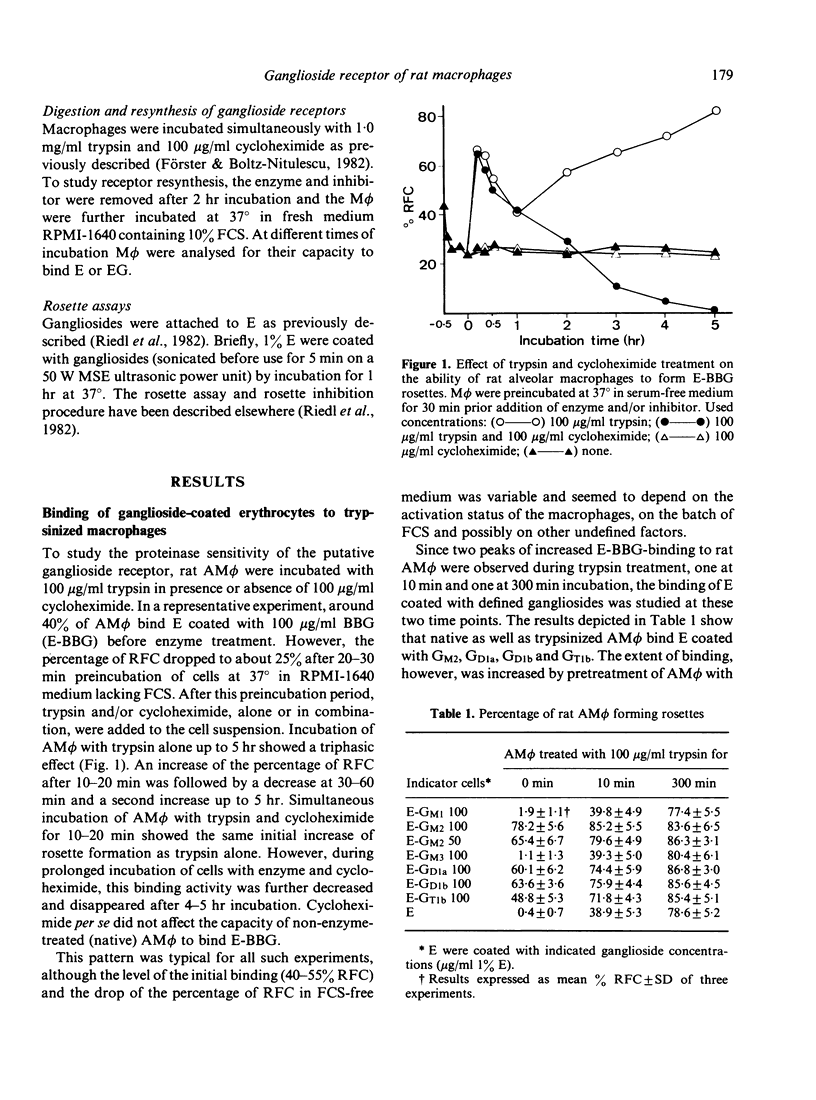
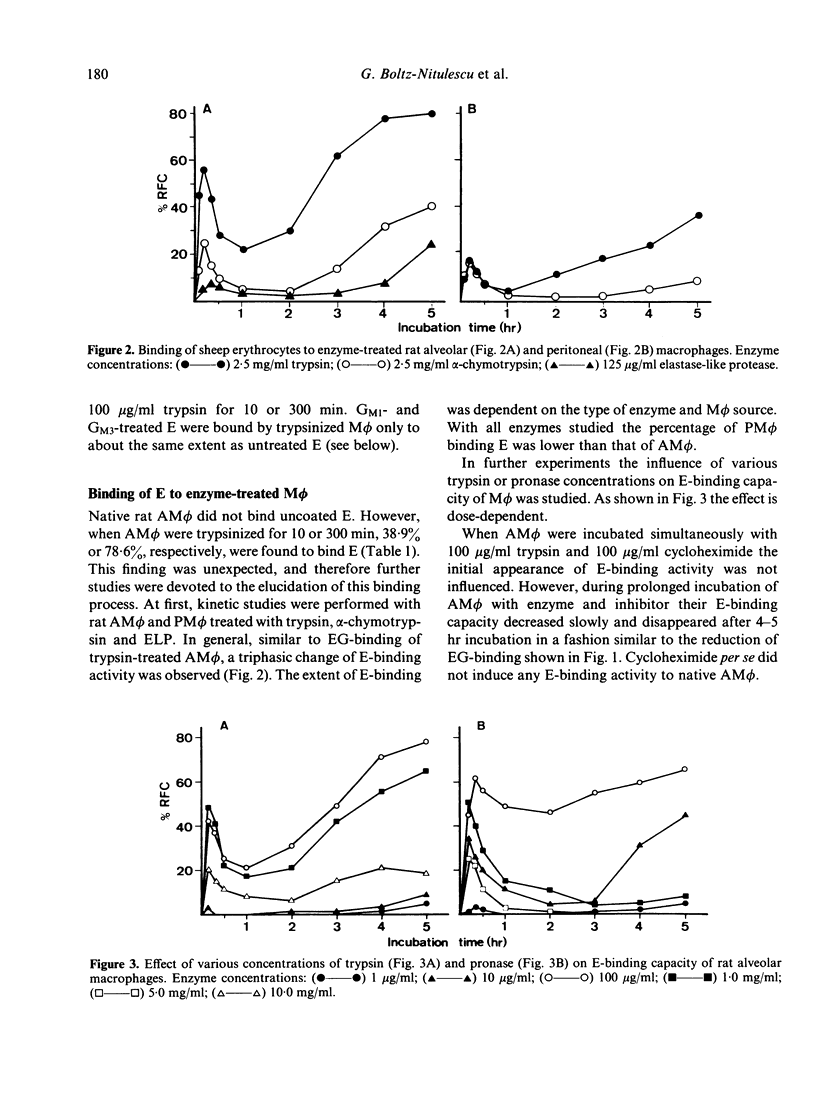
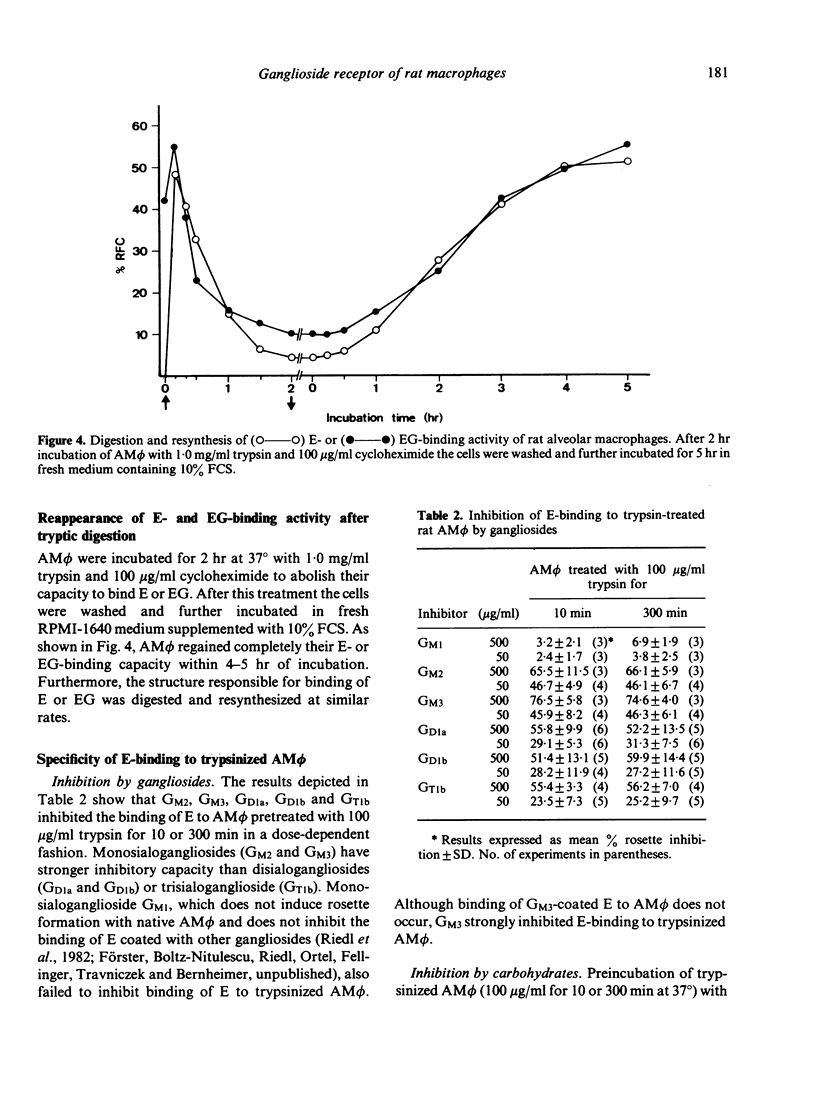
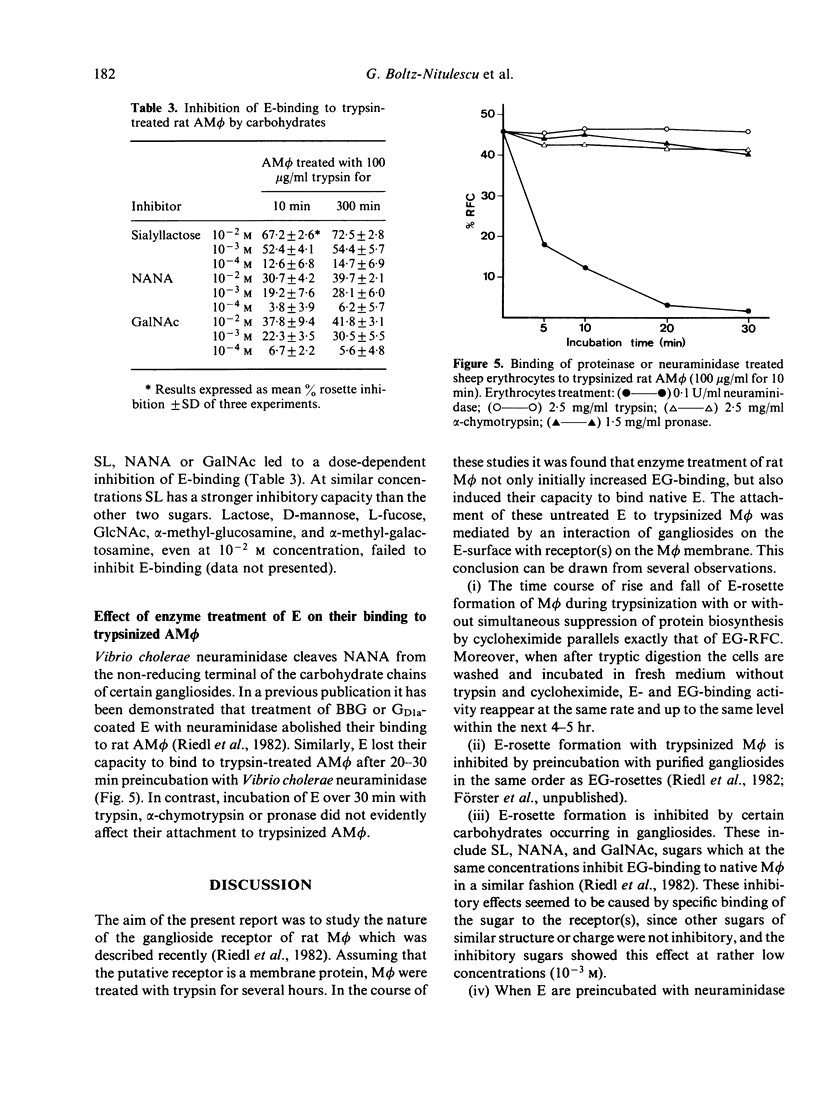
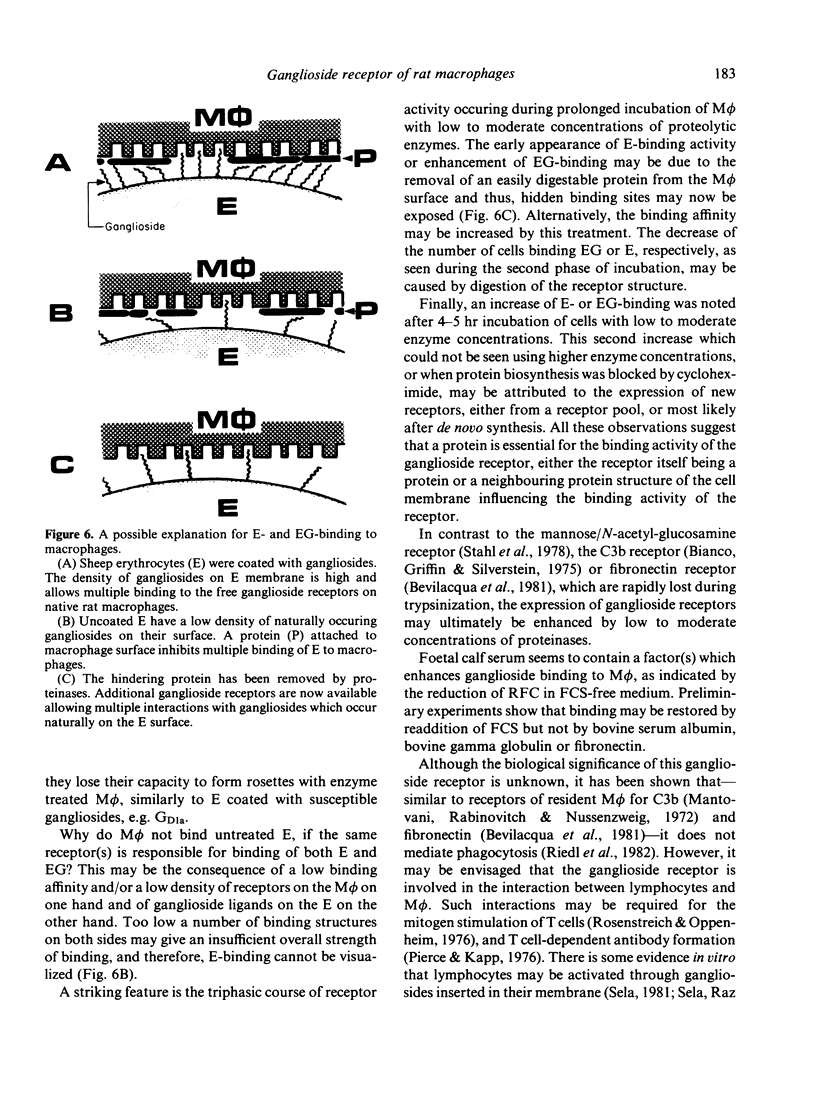
Previous experiments have shown that rat macrophages (M phi) bind specifically sheep erythrocytes (E) coated with various gangliosides (EG). To study the nature of this receptor-like structure, M phi were treated with proteinases, and their capacity to bind EG and/or E was analyzed in a rosette assay. Within 10 min of incubation with appropriate doses of enzymes, a clear enhancement of EG-binding activity was observed. In addition, enzyme-treated M phi bound uncoated E. Inhibition studies with gangliosides and carbohydrates, and enzyme treatment of E showed that this binding is mediated by the same M phi ganglioside receptor. The kinetics of the modulation of binding activity of M phi during trypsin treatment were similar for both E and EG. At optimal enzyme concentration a triphasic effect was noted. Enhancement of EG-binding and appearance of E-binding activity after 10-20 min was followed by a reduction of rosette-forming cells (RFC) with a minimum at about 1 hr and then by an increase of both E-RFC or EG-RFC up to 5 hr. Simultaneous incubation of M phi with trypsin and cycloheximide abrogated the second rise of binding activity and abolished binding on prolonged incubation. When these cells were washed and further incubated in fresh medium, they regained their initial E- and EG-binding capacity after 4-5 hr incubation. Taken together, these results are consistent with the idea that rat M phi bear a ganglioside receptor-like structure which seems to be a membrane protein and which is modulated by enzyme treatment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevilacqua M. P., Amrani D., Mosesson M. W., Bianco C. Receptors for cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin) on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):42–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Studies of the macrophage complement receptor. Alteration of receptor function upon macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1278–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltz-Nitulescu G., Bazin H., Spiegelberg H. L. Specificity of fc receptors for IgG2a, IgG1/IgG2b, and IgE on rat macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):374–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltz-Nitulescu G., Foerster O. Antigenic differences between alveolar and peritoneal macrophages of the rat. Lack of population-specific determinants. Immunology. 1979 Nov;38(3):621–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltz-Nitulescu G., Förster O. Proteinase-induced modulation of the activity of rat macrophages to bind rabbit-IgG-sensitized sheep erythrocytes. Immunobiology. 1982;162(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boltz-Nitulescu G., Spiegelberg H. L. Receptors specific for IgE on rat alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Mar 15;59(1):106–114. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Membrane sialic acid on target particles modulates their phagocytosis by a trypsin-sensitive mechanism on human monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3831–3835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster O., Boltz-Nitulescu G. Digestion and resynthesis of receptors binding IgG-sensitized erythrocytes on rat macrophages. Immunology. 1982 Sep;47(1):107–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H., Friedrich E., Süss R. Lectin mediates homing of sialidase-treated erythrocytes of the liver as revealed by scintigraphy. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Dec;362(12):1609–1614. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.2.1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H., Kolb-Bachofen V. A lectin-like receptor on mammalian macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 29;85(2):678–683. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani B., Rabinovitch M., Nussenzweig V. Phagocytosis of immune complexes by macrophages. Different roles of the macrophage receptor sites for complement (C3) and for immunoglobulin (IgG). J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):780–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogmundsdóttir H. M., Weir D. M. The characteristics of binding of Corynebacterium parvum to glass-adherent mouse peritoneal exudate cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):334–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedl M., Forster O., Rumpold H., Bernheimer H. A ganglioside-dependent cellular binding mechanism in rat macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1205–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela B. A. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous splenocytes incorporated with the tetrasialoganglioside GQ1b. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Apr;11(4):347–349. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela B. A., Raz A., Geiger B. Antibodies to ganglioside GM1 induce mitogenic stimulation and cap formation in rat thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Apr;8(4):268–274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel S., Ravid A., Wilchek M. Involvement of gangliosides in lymphocyte stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5277–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel S., Wilchek M. Membrane sialoglycolipids emerging as possible signal transducers for lymphocyte stimulation. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):572–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P. D., Rodman J. S., Miller M. J., Schlesinger P. H. Evidence for receptor-mediated binding of glycoproteins, glycoconjugates, and lysosomal glycosidases by alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1399–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. A. A macrophage receptor for (mannose/glucosamine)-glycoproteins of potential importance in phagocytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):737–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


