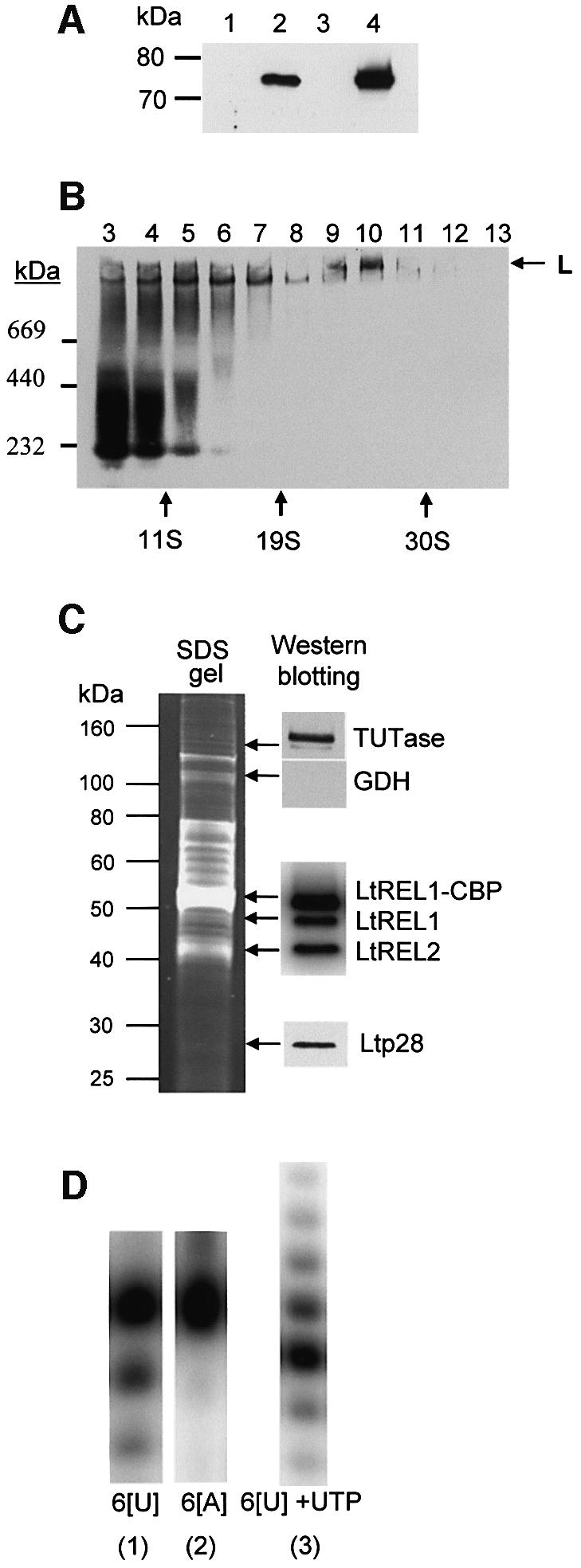
Fig. 4. Expression of LtREL1–TAP fusion protein and affinity isolation of the L-complex. (A) Mitochondrial localization of LtREL1–TAP fusion protein. Total protein (10 µg) from wild-type cells (lane 1), transfected (lane 2) cells, the cytoplasmic fraction of transfected cells (lane 3), and 2 µg of protein from purified mitochondria of transfected cells (lane 4) were analyzed with the PAP reagent for the presence of protein A as a part of the TAP fusion protein. (B) The REL1–TAP fusion protein is incorporated into the L-complex. Mitochondrial S100 extract from transfected cells was fractionated on a 10–30% glycerol gradient in an SW41 rotor for 20 h at 30 000 r.p.m. Each fraction was separated on a 4–12% native gel, and the protein A fusion protein was detected with the PAP reagent. (C) Protein composition of the TAP-purified L-complex. The fraction eluted from the calmodulin column was analyzed for the presence of both LtREL1 and LtREL2 ligases by adenylation, and for TUTase and p28 by western analysis with the respective polyclonal antibodies. (D) Enzymatic activities of the TAP-purified complex. The same fraction as in (C) was analyzed for the presence of 3′–5′ U-specific exonuclease activity by incubating the calmodulin fraction with 5′-labeled synthetic RNA oligonucleotides with six uridine (6[U]) or adenosine (6[A]) residues at the 3′ end. 3′ TUTase activity was detected by including 100 µM UTP. Products were separated on 15% polyacrylamide–urea.
