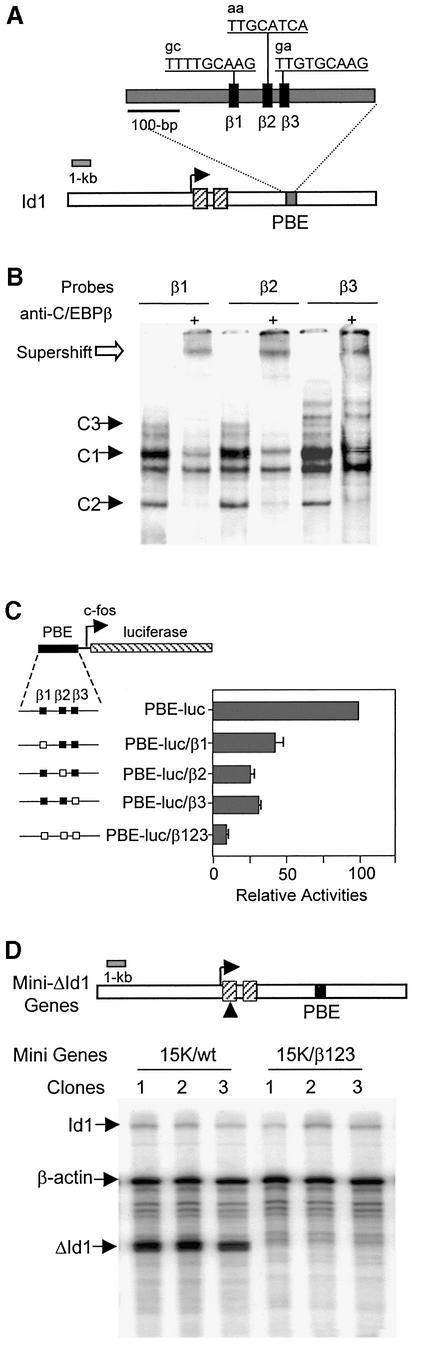
Fig. 1. The C/EBPβ-binding site is required for Id-1 expression. (A) Three C/EBPβ-binding sites are diagrammed as filled boxes, and their sequences shown on top. Mutations are indicated with lower case letters. The position of PBE (gray box) relative to Id-1 exons (hatched boxes) is illustrated. (B) EMSA with each of the three C/EBPβ-binding sites as probes. A 70 bp probe containing the β1, β2 or β3 site was incubated with Ba/F3 nuclear extracts with or without antibodies against C/EBPβ. The binding reactions were analyzed on a 6% poly acrylamide gel in Tris–glycine buffer. C/EBPβ-containing complexes are labeled as C1–C3. Supershifted complexes are marked with an open arrow. Additional bands are non-specific complexes found in all cell types. (C) Mutational analysis in transient transfection assays using Ba/F3 cells. Constructs containing the 460 bp PBE placed upstream of a luciferase reporter gene driven by a c-fos minimal promoter are diagrammed. Filled and open boxes represent wild-type and mutant C/EBPβ sites, respectively. Luciferase activities were normalized against the β-galactosidase activity. The data are presented as activities relative to that of the PBE-luc construct and are averages of at least three independent experiments with standard deviations. (D) Mutational analysis in stable Ba/F3 cell lines. The ΔId-1 gene is diagrammed as in (A). Three independent cell lines stably transfected with the indicated constructs were analyzed using RPAs, and transcripts were detected with the probes as labeled.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.