Abstract
The application of monoclonal antibodies to the quantification of blood group antigen sites on erythrocytes was examined. A second antibody technique using labelled anti-mouse IgG could not be used as it was not possible to predict the binding ratio between this and the monoclonal antibody. A series of monoclonal antibodies (R10, R18, BRIC 13, BRIC 14) to the erythrocyte sialoglycoprotein alpha (syn: glycophorin A) showed the number of antigen sites to be from 0.3 X 10(6) to 1.2 X 10(6) per erythrocyte and supported the conclusion that the Wrb antigen is located on this protein. An antibody with a specificity related to the Rh blood group system (R6A) showed 4.6 - 10.4 X 10(4) binding sites to be present on cells of phenotype cCDEe. On cells of phenotype -D- 1.24 X 10(4) binding sites were present but protease treatment increased the number of available sites to 1.3 X 10(5). An antibody to a Kell-related antigen (BRIC 18) recognized 2.5 - 5.9 X 10(3) sites per erythrocyte on cells of phenotype Kk. However, a similar number also appeared to be present on cells of the McLeod and Ko phenotypes although the affinity for the antigen on these cells was very much reduced. The potential of using monoclonal antibodies for this purpose and the value of this in the study of blood group systems has been demonstrated.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advani H., Zamor J., Judd W. J., Johnson C. L., Marsh W. L. Inactivation of Kell blood group antigens by 2-aminoethylisothiouronium bromide. Br J Haematol. 1982 May;51(1):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb07295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstee D. J., Edwards P. A. Monoclonal antibodies to human erythrocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Mar;12(3):228–232. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin H., Monroe M. C., Lachmann P. J. Further studies of the C3g component of the alpha 2D fragment of human C3. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):639–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS R. S., TURNER E., BINGHAM M. STUDIES WITH RADIOIODINATED COLD AGGLUTININS OF TEN PATIENTS. Am J Med. 1965 Mar;38:378–395. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidou J., Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B. Quantitative measurements concerning A and B antigen sites. Vox Sang. 1967 May;12(5):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to the human erythrocyte-membrane glycoproteins glycophorin A and Band 3 [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):334–335. doi: 10.1042/bst0080334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. H., Munro A. C., Williamson A. R., Barrie E. K., Hamilton E. A., Mitchell R. Mouse monoclonal anti-N. I. Production and serological characterization. J Immunogenet. 1982 Oct;9(5):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1982.tb00985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Jokinen M., Andersson L. C. Expression of the major red cell sialoglycoprotein, glycophorin A, in the human leukemic cell line K562. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7442–7448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G. Molecular identification of the human Rho (D) antigen. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 5;140(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80528-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holburn A. M. Quantitative studies with ( 125 I) IgM anti-Le. Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):1019–1026. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
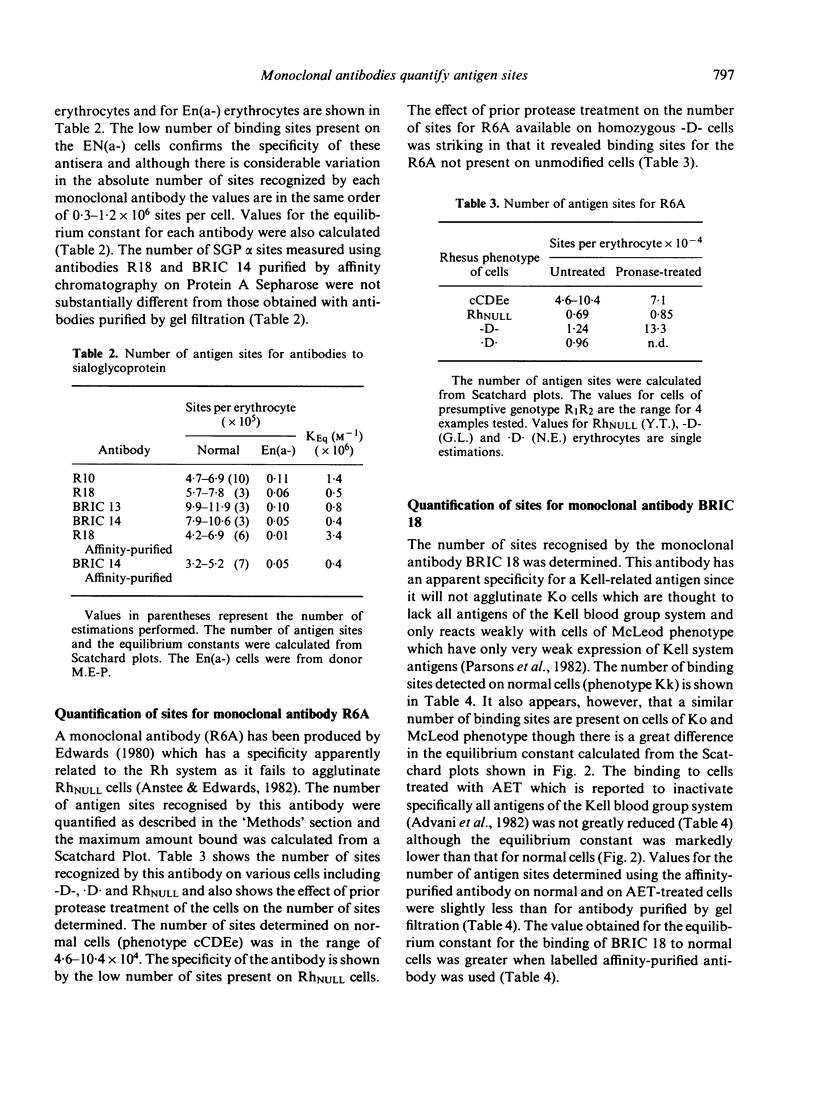
- Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B., Lincoln P. J. Observations of the number of available c,D, and E antigen sites on red cells. Vox Sang. 1971 Sep;21(3):210–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
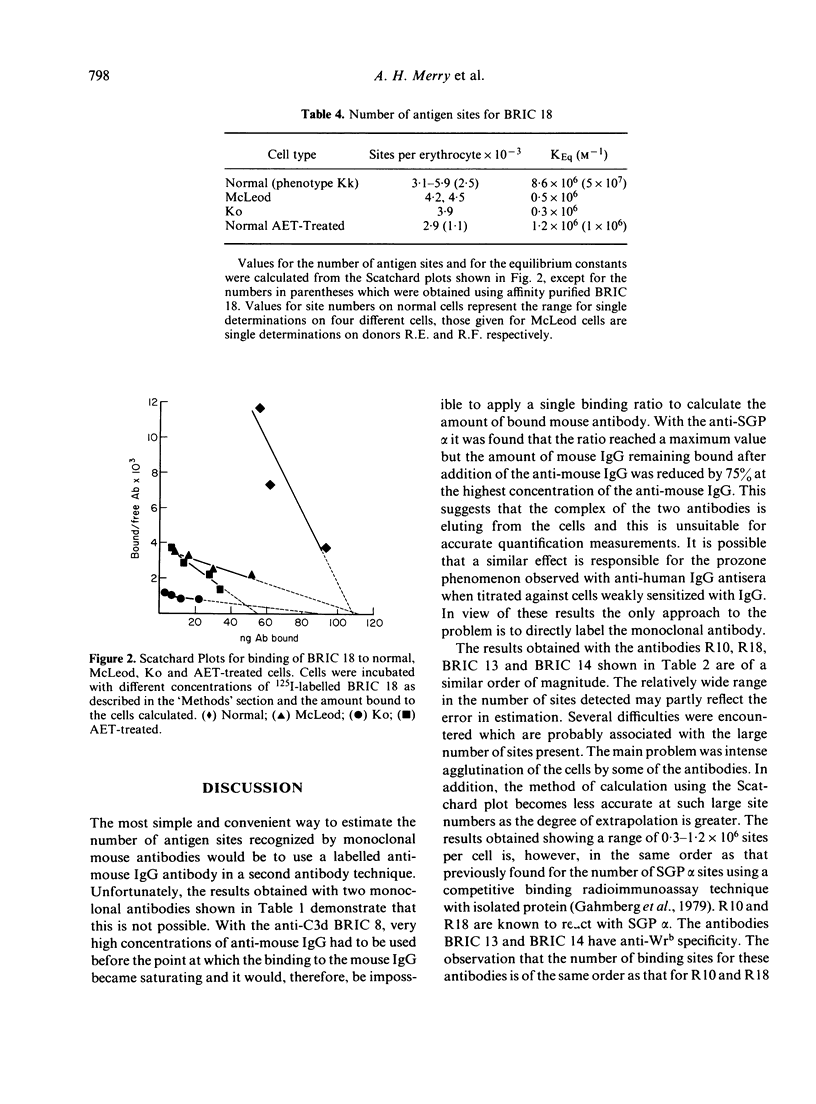
- Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B. The Kell system studied with radioactively-labelled anti-K. Vox Sang. 1971 Aug;21(2):154–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb00572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masouredis S. P., Sudora E., Mahan L., Victoria E. J. Quantitative immunoferritin microscopy of Fya, Fyb, Jka, U, and Dib antigen site numbers on human red cells. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):969–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Woodrow C. F., McClelland D. B. Isolation of membrane components associated with human red cell antigens Rh(D), (c), (E) and Fy. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):529–531. doi: 10.1038/295529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. F., Judson P. A., Anstee D. J. BRIC 18: a monoclonal antibody with a specificity related to the kell blood group system. J Immunogenet. 1982 Dec;9(6):377–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1982.tb00998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M. Sugar composition of oat-coleoptile cell walls. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89(1):144–150. doi: 10.1042/bj0890144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgwell K., Roberts S. J., Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. Absence of two membrane proteins containing extracellular thiol groups in Rhnull human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):267–269. doi: 10.1042/bj2130267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgwell K., Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. The Wrb antigen, a receptor for Plasmodium falciparum malaria, is located on a helical region of the major membrane sialoglycoprotein of human red blood cells. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2090273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov F., Hughes-Jones N. C. Observations on the number of available C antigen sites on red cells. Vox Sang. 1977 Sep;33(3):170–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1977.tb02249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]