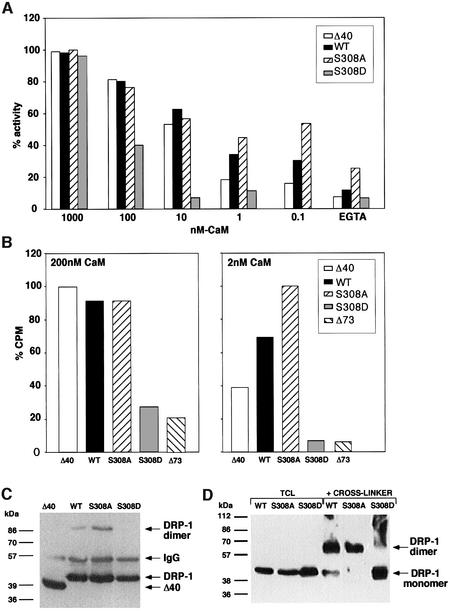
Fig. 7. DRP-1 mutant forms differ in the binding affinity and activation by CaM and in their dimerization status. (A) Differential activation by CaM of DRP-1 mutant forms. Δ40, wild-type, S308A and S308D DRP-1 constructs were transfected into 293 cells, immunoprecipitated and eluted from the beads with an excess of HA peptide. Equal amounts of the various DRP-1 mutants (estimated by western blotting) were then assayed in an in vitro kinase assay towards MLC in the presence of various concentrations of CaM (0–1000 nM). (B) Differential affinity to CaM by DRP-1 mutant forms. Δ40, wild-type, S308A and S308D DRP-1 constructs were transfected into 293 cells and immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies. Equal amounts of the various DRP-1 mutants were then subjected to CaM binding assay with 200 or 2 nM 35S-labelled CaM as described in Materials and methods. For each CaM concentration the highest binding value was set as 100% (25 227 and 1055 c.p.m. for 200 and 2 nM CaM, respectively); the remaining values were calculated accordingly. (C) The immunoprecipitated beads carrying the various DRP-1 mutants were fractionated on gels and reacted with anti-HA antibodies. The position of DRP-1 monomers and dimers as well as of the immunoglobulin heavy chain is indicated by arrows. (D) Samples of clarified cell extracts (20 µg; 2 µg/µl) were subjected to cross-linking with glutardialdehyde as described in Materials and methods, then separated on gels and western blotted. Another sample from each extract (10 µg) was run in parallel without a prior cross-linking (TCL, total cell lysate). The immunoblots were reacted with anti-HA antibodies. The cross-linked dimer runs faster than predicted due to the globular conformation maintained by the cross-linking agent.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.