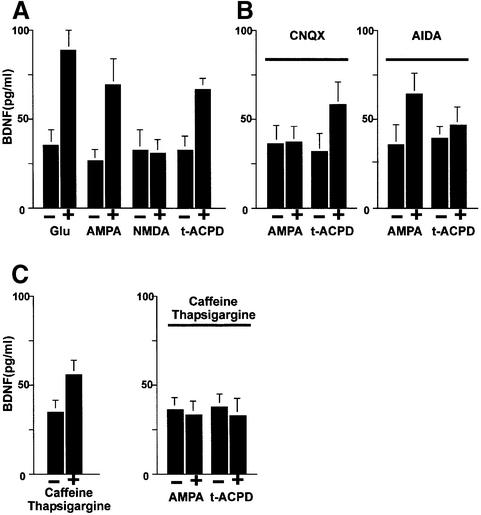
Fig. 9. Analysis of the signal transduction pathway(s) leading to BDNF secretion by glutamate. (A) BDNF secretion initiated by glutamate receptor agonists in cultured hippocampal neurons. Primary cultures of hippocampal neurons were infected with AdCMV-BDNF for 36–48 h. After an equilibration time of 60 min, basal levels of secreted BDNF were determined in the medium collected over a 10 min period under ‘static’ conditions. Stimulation of neurons for 10 min with glutamate (50 µM), AMPA (100 µM) or t-ACPD (100 µM) resulted in increased concentrations of BDNF in the incubation medium. NMDA had no effect. (B) Hippocampal neurons, pre-treated with the specific antagonists of AMPA and mGluRI receptors, CNQX (50 µM) and AIDA (500 µM), respectively, were tested for the effects of AMPA and t-ACPD. (C) Influence of Ca2+ stores on AMPA- and t-ACPD-mediated BDNF secretion. In hippocampal neurons, treatment with thapsigargine (10 µM) and caffeine (3 mM) initiated BDNF secretion but abolished the subsequent secretion of BDNF induced by AMPA and t-ACPD. The values given represent the mean ± SE (n = 6).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.