Abstract
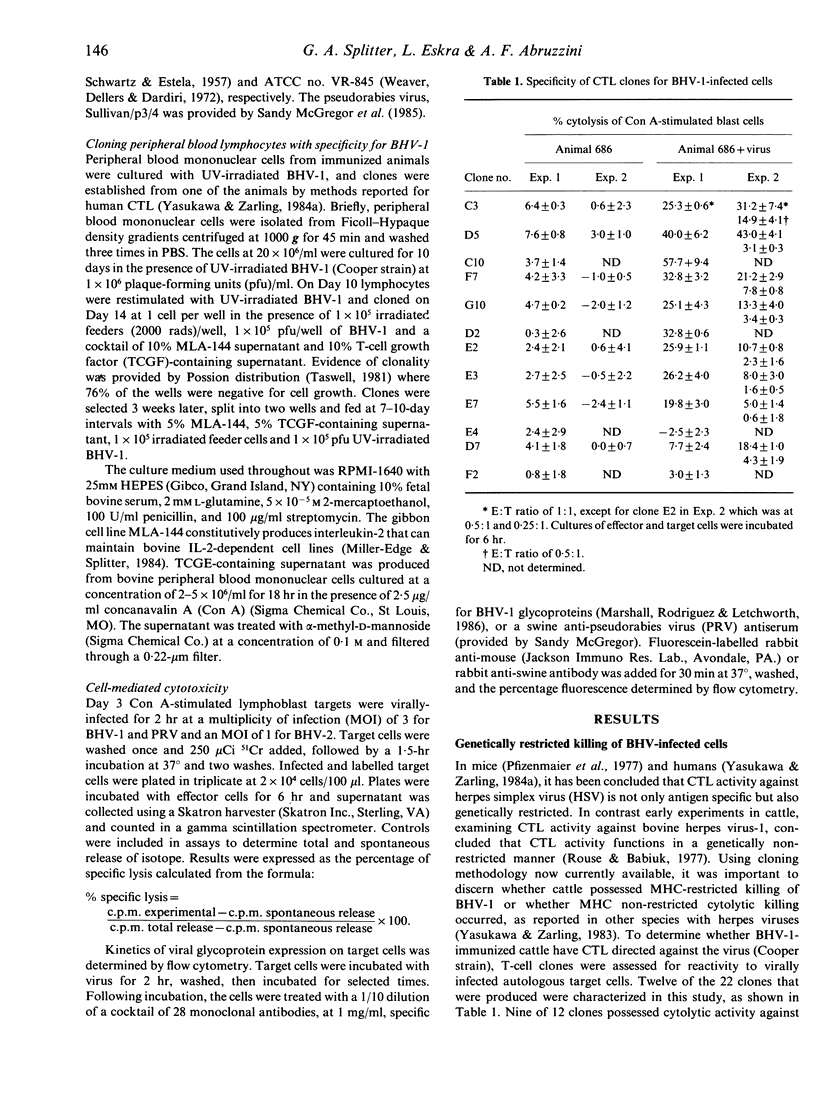
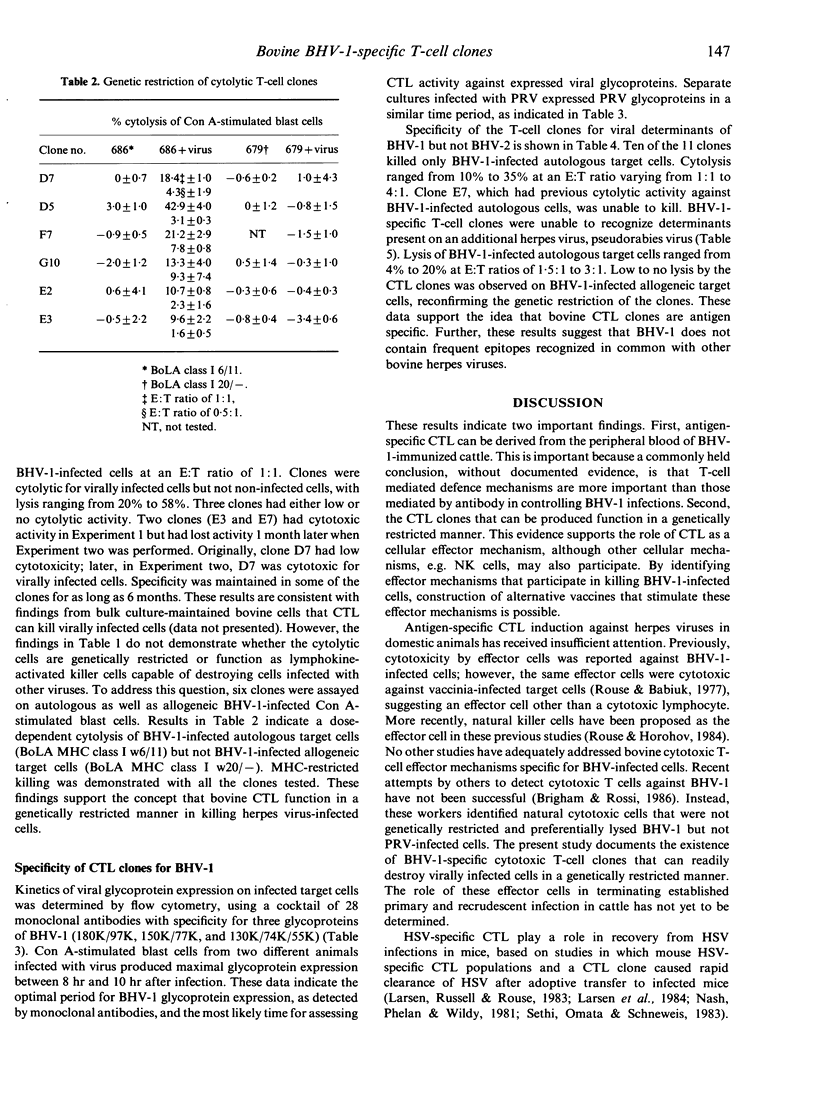
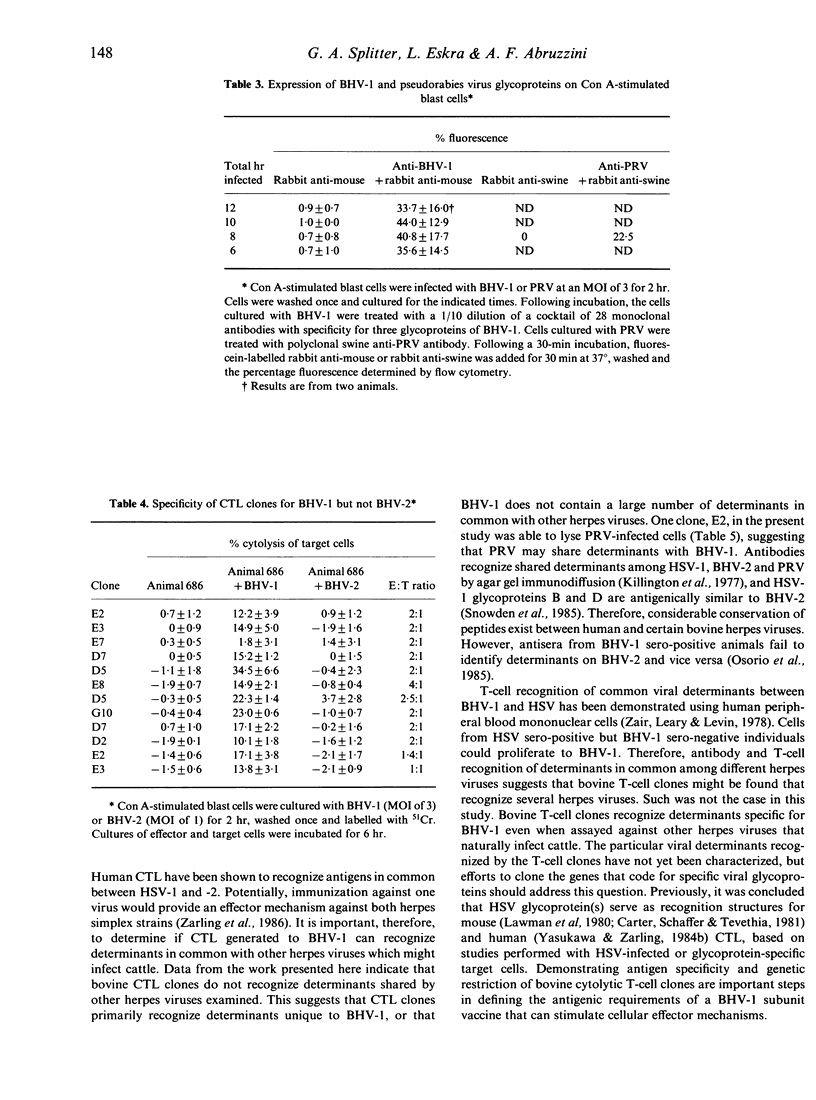
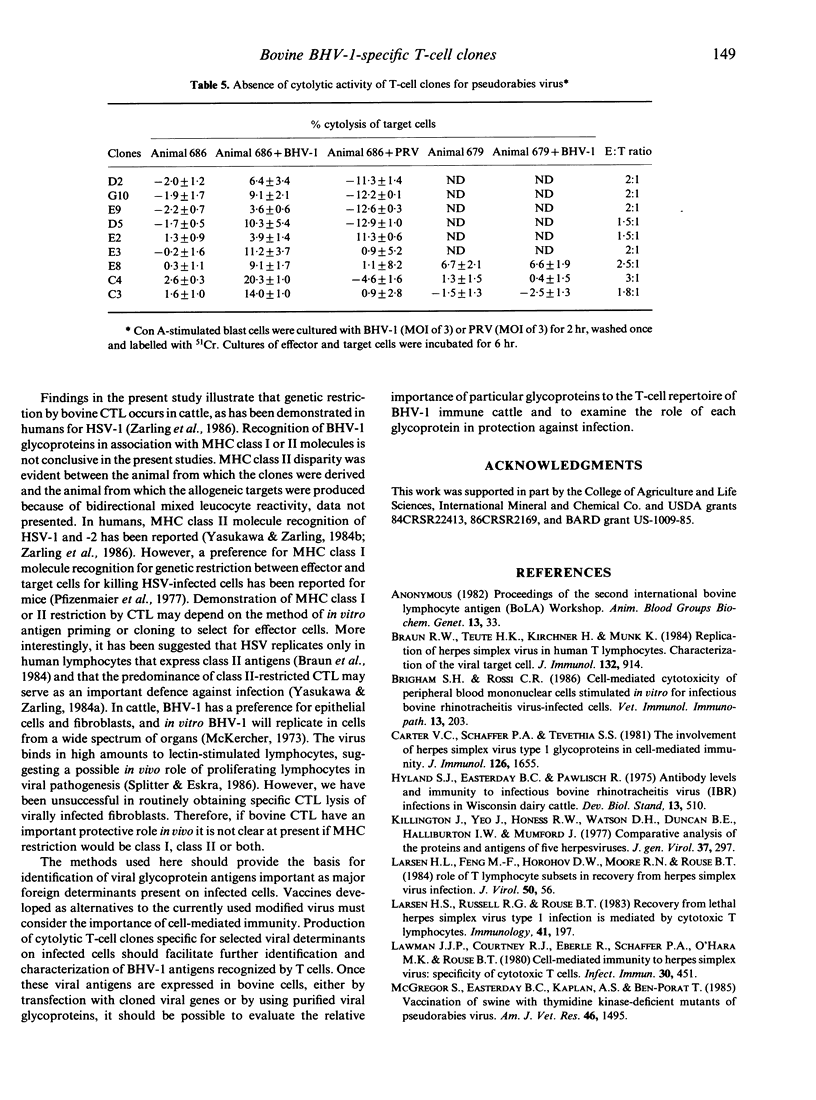
The inability to demonstrate bovine herpes virus-1 (BHV-1)-specific lymphocyte responses from BHV-1-infected cattle has been a major difficulty in confirming the importance of cellular effector mechanisms during BHV-1 infection. We have examined the capacity of bovine cytolytic T-cell clones to lyse BHV-1-infected, concanavalin A-stimulated blast cells. Cytolysis was as high as 58% at an effector to target (E:T) ratio of 1:1. All cytolytic T-cell clones produced were genetically restricted in killing cells of the autologous genotype. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) clones were specific for BHV-1 but not related herpes viruses, i.e. BHV-2 and pseudorabies virus. These results provide evidence that cytolytic T lymphocytes have an antigen-specific role in the immune response of cattle against BHV-1, and that CTL may serve as effector cells in the identification of glycoproteins useful in recombinant vaccine preparation since only determinants of BHV-1 were recognized.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun R. W., Teute H. K., Kirchner H., Munk K. Replication of herpes simplex virus in human T lymphocytes: characterization of the viral target cell. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham S. H., Rossi C. R. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated in vitro for infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus-infected cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Nov;13(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter V. C., Schaffer P. A., Tevethia S. S. The involvement of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins in cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1655–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyland S. J., Easterday B. C., Pawlisch R. Antibody levels and immunity to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus (IBR) infections in Wisconsin dairy cattle. Dev Biol Stand. 1975;28:510–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killington R. A., Yeo J., Honess R., Watson D. H., Duncan B. E., Halliburton I. W., Mumford J. Comparative analyses of the proteins and antigens of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):297–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen H. S., Russell R. G., Rouse B. T. Recovery from lethal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection is mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):197–204. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.197-204.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. L., Rodriguez L. L., Letchworth G. J., 3rd Characterization of envelope proteins of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus (bovine herpesvirus 1) by biochemical and immunological methods. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):745–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.745-753.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Edge M., Splitter G. A. Bovine interleukin 2 (IL-2) production and activity on bovine and murine cell lines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Sep;7(2):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Edge M., Splitter G. Detection of impaired T cell-mediated immune responses to herpesvirus (BHV-1) in cattle. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Sep;13(1-2):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Edge M., Splitter G. Patterns of bovine T cell-mediated immune responses to bovine herpesvirus 1. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Dec;13(4):301–319. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias A. J., Roizman B. Infection with herpes-simplex viruses 1 and 2. 3. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 11;289(15):781–789. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310112891505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A., Phelan J., Wildy P. Cell-mediated immunity in herpes simplex virus-infected mice: H-2 mapping of the delayed-type hypersensitivity response and the antiviral T cell response. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1260–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E. Role for cell-mediated immunity in the resistance of mice to subcutaneous herpes simplex virus infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.166-172.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio F. A., Reed D. E., Van der Maaten M. J., Metz C. A. Comparison of the herpesviruses of cattle by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis and serologic analysis. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Oct;46(10):2104–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Jung H., Starzinski-Powitz A., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. The role of T cells in anti-herpes simplex virus immunity. I. Induction of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. The direct antiviral cytotoxicity by bovine lymphocytes is not restricted by genetic incompatibility of lymphocytes and target cells. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):618–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Horohov D. W. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes in herpesvirus infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;6(1-2):35–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Omata Y., Schneweis K. E. Protection of mice from fatal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by adoptive transfer of cloned virus-specific and H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Stroehmann I., Brandis H. Human T-cell cultures from virus-sensitized donors can mediate virus-specific and HLA-restricted cell lysis. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):718–720. doi: 10.1038/286718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden B. W., Kinchington P. R., Powell K. L., Halliburton I. W. Antigenic and biochemical analysis of gB of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 and of cross-reacting glycoproteins induced by bovine mammillitis virus and equine herpesvirus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):231–247. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splitter G. A., Eskra L. Bovine T lymphocyte response to bovine herpesvirus-1: cell phenotypes, viral recognition and acid-labile interferon production. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Mar;11(3):235–250. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C. Limiting dilution assays for the determination of immunocompetent cell frequencies. I. Data analysis. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1614–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. D., Dellers R. W., Dardiri A. H. Bovine herpes mammillitis in New York. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Jun 15;160(12):1643–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YORK C. J., SCHWARZ A. J., ESTELA L. A. Isolation and identification of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Apr;94(4):740–744. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Autologous herpes simplex virus-infected cells are lysed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2011–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. I. Lysis restricted by HLA class II MB and DR antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. II. Bifunctional clones with cytotoxic and virus-induced proliferative activities exhibit herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 specific or type common reactivities. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2736–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Leary P. L., Levin M. J. Specificity of the blastogenic response of human mononuclear cells to herpesvirus antigens. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):646–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.646-651.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Moran P. A., Burke R. L., Pachl C., Berman P. W., Lasky L. A. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed against herpes simplex virus-infected cells. IV. Recognition and activation by cloned glycoproteins gB and gD. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4669–4673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


