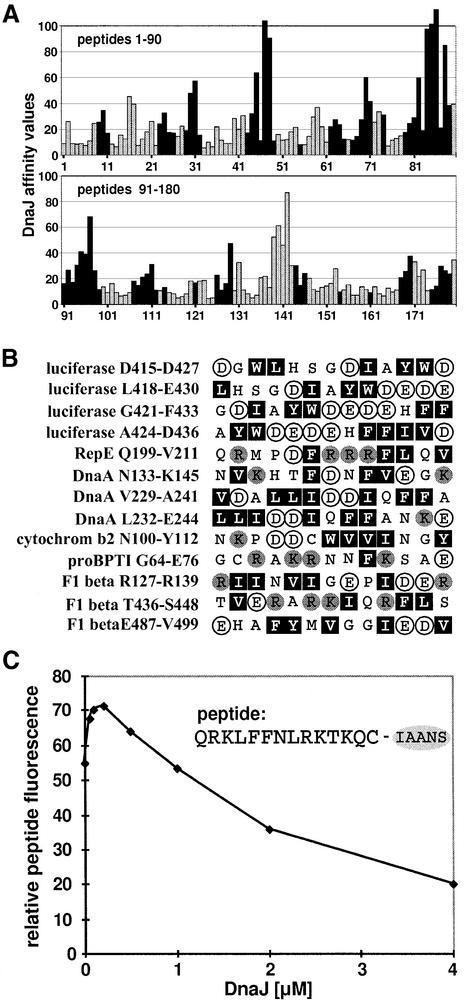
Fig. 3. Comparison of binding of DnaK and DnaJ to peptides. (A) DnaJ- and DnaK-binding peptides in luciferase are in most cases identical. Luciferase-derived peptides that were screened for DnaJ binding (Figure 1) are represented as bars. The length of the bars corresponds to the affinity of the peptide for DnaJ. Black bars represent peptides that were classified as DnaK binders in a previous study (Rüdiger et al., 1997b). (B) Peptides that bind to DnaJ but not to DnaK contain several large hydrophobic and aromatic residues (Leu, Ile, Phe, Trp and Tyr; black boxes) with acidic residues (Glu and Asp; white circles) in between. Basic residues (Arg and Lys) are represented as grey circles. (C) DnaJ can compete with DnaK–peptide binding in solution. A complex of DnaK (0.1 µM) and the peptide σ32-Q132-Q144-C-IAANS (0.5 µM) was titrated with DnaJ (concentration as indicated). The fluorescence of the DnaK–peptide interaction was obtained by subtracting the fluorescence of the DnaJ–peptide interaction in the absence of DnaK from the total signal.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.