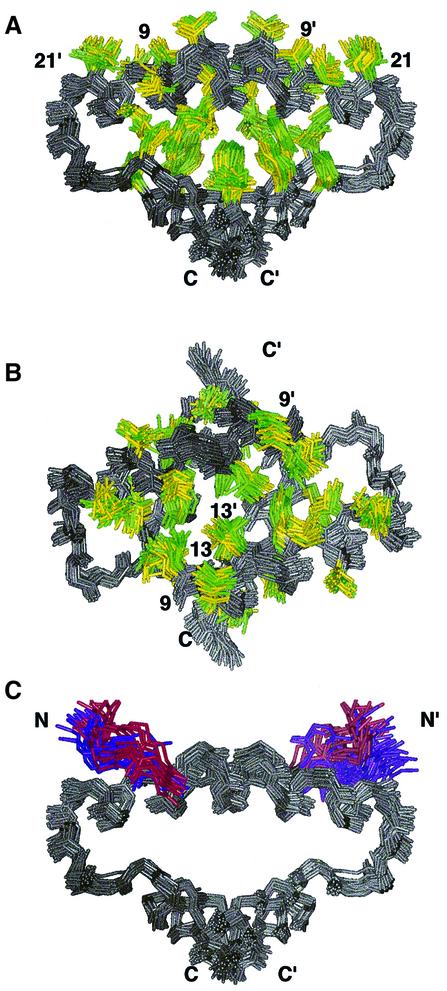
Fig. 2. Representation of the hydrophobic core of RIIα(1–44) in both the free and AKAP-bound structures. The anchoring peptides have been removed for clarity and the first eight or four residues of RIIα are removed. Superposition of the 17, 13 and 10 lowest energy structures of free, Ht31(493–515)- and AKAP79(392–413)-bound RIIα(1–44), respectively. In all views, RIIα(1–44) is colored gray. Hydrophobic residues in free RIIα(1–44) are colored yellow and in both AKAP complexes are colored green. (A) This view emphasizes both the organization of the hydrophobic core and the hydrophobic groove of RIIα(1–44). (B) This view highlights the AKAP binding surface and is a 90° rotation of the view presented in (A). (C) This view is identical to (A) although the backbone atoms of residues 5–8 and 5′–8′ are indicated in either purple or red for the complex or apo-form of RIIα(1–44), respectively. Additionally, the side chain of Ile5 is also depicted and colored.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.