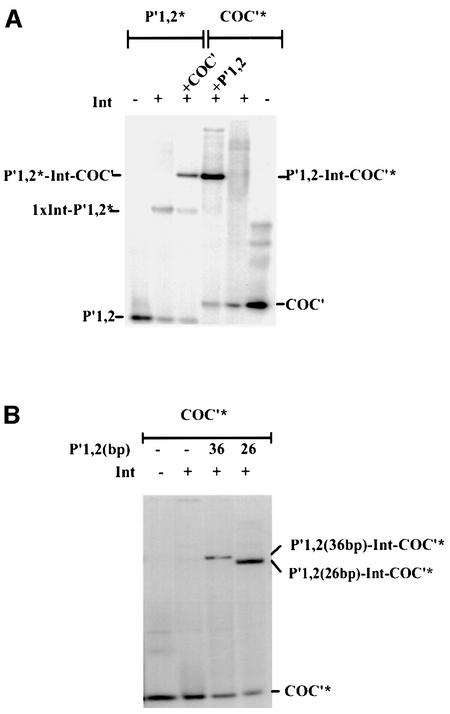
Fig. 5. The effect of arm-type oligonucleotide on Int binding to core-type DNA. (A) Int binding to core-type DNA in the presence and absence of arm-type oligonucleotide. Left panel: 32P-labeled 26 bp arm-type DNA (P′1,2*) at 0.28 µM was incubated in the absence or presence of Int (0.55 µM) and in the absence or presence of 0.1 µM unlabeled core-type DNA (COC′). Right panel: 32P-labeled core-type DNA (COC*) at 0.1 µM was incubated in the absence or presence of Int (0.55 µM) and in the absence or presence of 0.28 µM unlabeled arm-type DNA (P′1,2) for 25 min at room temperature. The reactions were analyzed by electrophoresis on native 7% polyacrylamide gels and visualized by autoradiography (see Materials and methods). One complex dependent on all three components appears to be labeled by either [32P]COC′ or [32P]P′1,2. (B) The mobility of a COC′-labeled ternary complex of Int depends on the size of the P′1,2 oligonucleo tides. Using the same conditions described in (A), Int complexes were formed with 32P-labeled COC′ in the presence of either a 26 or 36 bp P′1,2 oligonucleotide. The reactions were analyzed on a 7% polyacrylamide gel and visualized by autoradiography.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.