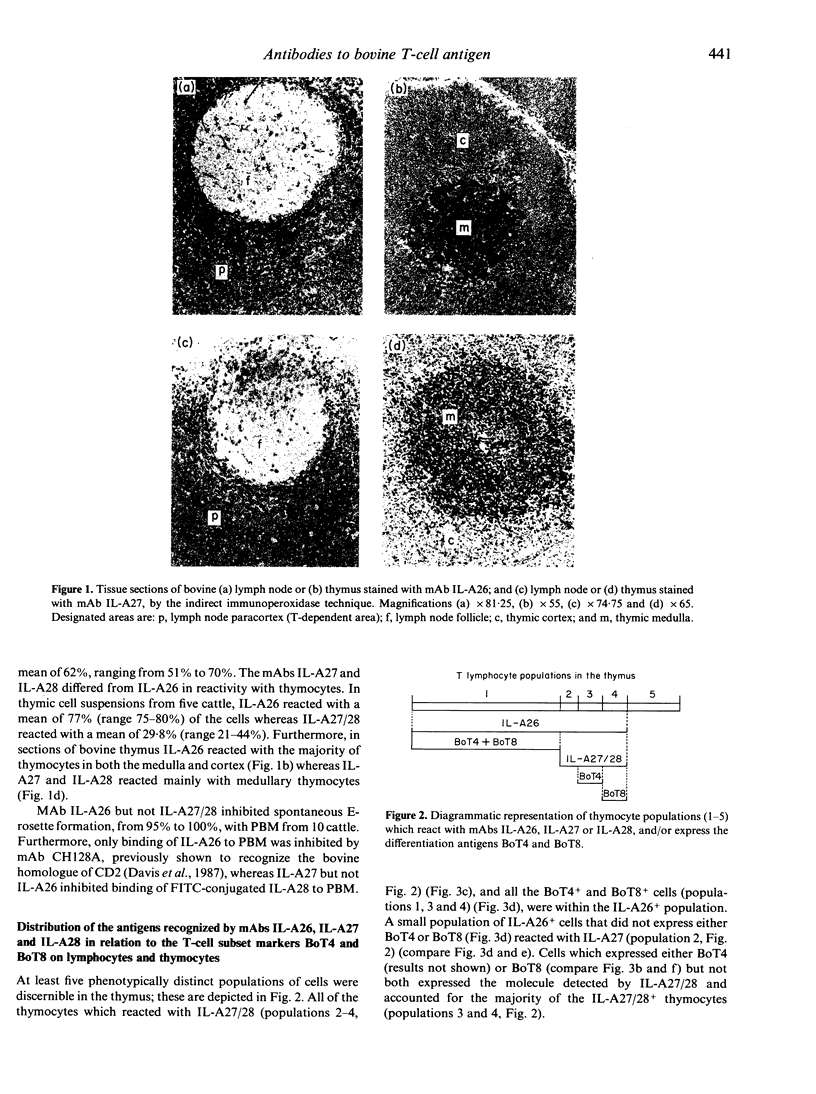
Abstract
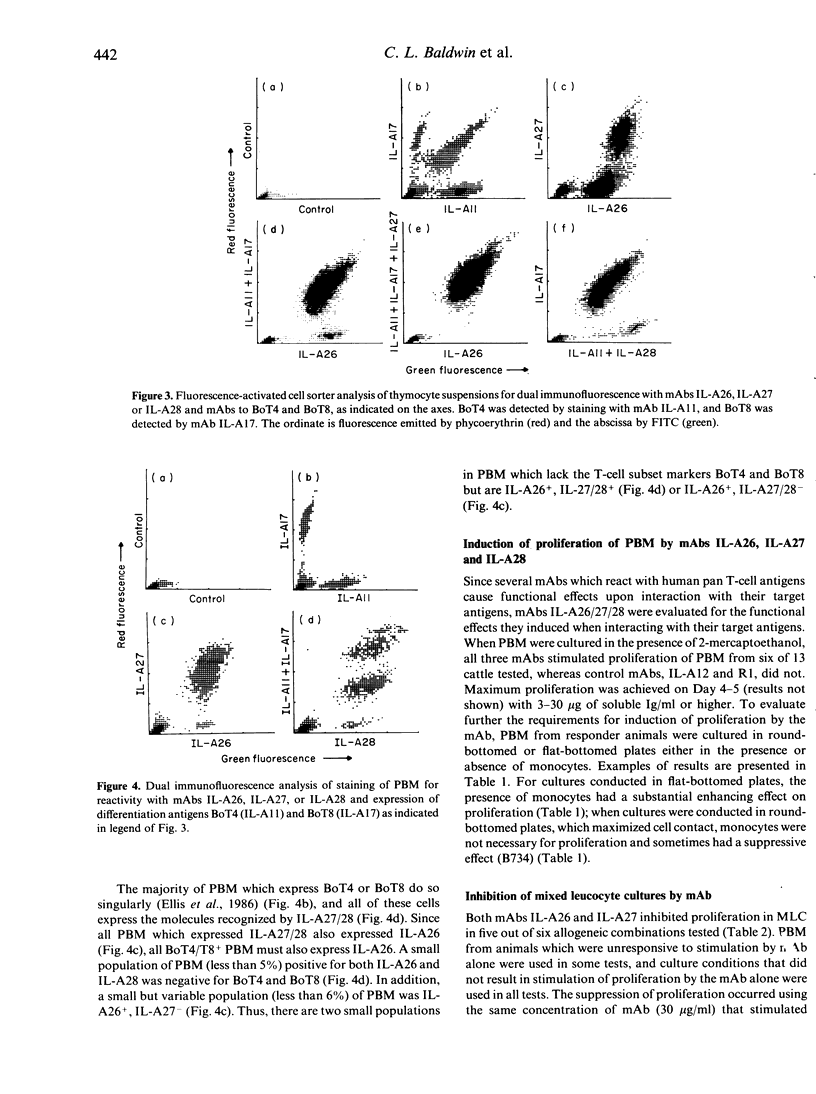
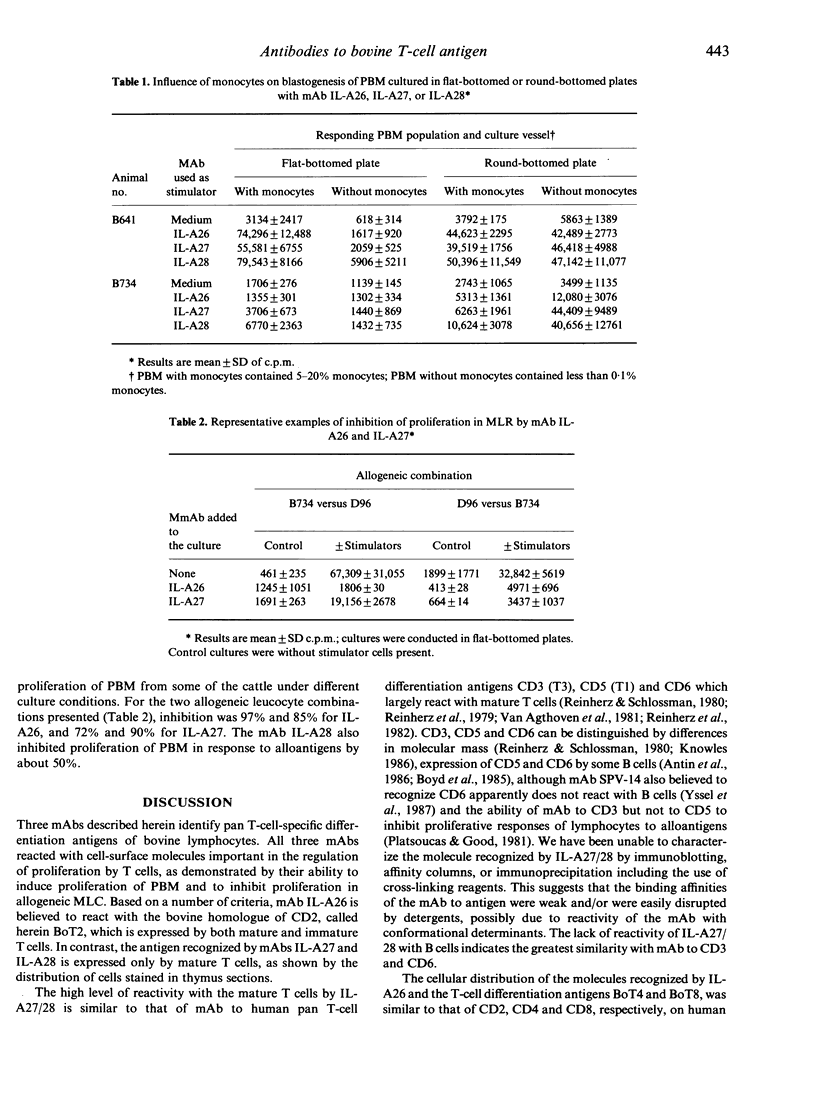
In this study we report on the tissue distribution and functional characteristics of bovine T-cell differentiation antigens recognized by the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) IL-A26, IL-A27, and IL-A28. All three mAbs are able to stimulate proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBM) and inhibit proliferation of responder cells in mixed leucocyte cultures (MLC). MAbs IL-A27 and IL-A28 are believed to react with the same molecule, which is different to that recognized by IL-A26 as determined by a number of criteria. MAbs IL-A27 and IL-A28 inhibit binding of one another, but not of IL-A26. MAbs IL-A27 and IL-A28 react with 25% of thymocytes confined to the medulla, whereas IL-A26 reacts with approximately 80% of thymocytes, including medullary and cortical populations. MAbs IL-A27 and IL-A28 react with thymocytes which express BoT4 or BoT8 singularly, whereas IL-A26 reacts with all cells which express BoT4 or BoT8, either singularly or dually, in addition to all thymocytes which react with IL-A27/28. Only IL-A26 inhibits spontaneous sheep erythrocyte (E)-rosette formation by bovine T cells. Based on tissue distribution and functional characteristics, IL-A26 is believed to recognize the bovine homologue of CD2, designated BoT2, whereas IL-A27/28 reacts with a mature T-cell antigen. Cells reactive with the mAbs constitute approximately 60% of bovine PBM. Using these mAbs in dual immunofluorescence analyses, at least three populations of bovine T cells are demonstrable in PBM. The majority of T cells are BoT4+ or BoT8+ and also react with IL-A26/27/28. A second small population of PBM is negative for BoT4 and BoT8 but is IL-A26/27/28+. A third population (less than 5%) is BoT4-/BoT8-/ILA27/28- but reacts with IL-A26.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antin J. H., Emerson S. G., Martin P., Gadol N., Ault K. A. Leu-1+ (CD5+) B cells. A major lymphoid subpopulation in human fetal spleen: phenotypic and functional studies. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):505–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Teale A. J., Naessens J. G., Goddeeris B. M., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I. Characterization of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT4 by monoclonal antibodies and function: similarity to lymphocytes defined by human T4 and murine L3T4. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4385–4391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Anderson K. C., Freedman A. S., Fisher D. C., Slaughenhoupt B., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Studies of in vitro activation and differentiation of human B lymphocytes. I. Phenotypic and functional characterization of the B cell population responding to anti-Ig antibody. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1516–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G. F., Boyd A. W., Beverley P. C. Two monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibodies have similar biologic effects and recognize the same cell surface antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1451–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceuppens J. L., Baroja M. L. Monoclonal antibodies to the CD5 antigen can provide the necessary second signal for activation of isolated resting T cells by solid-phase-bound OKT3. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1816–1821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceuppens J. L., Bloemmen F. J., Van Wauwe J. P. T cell unresponsiveness to the mitogenic activity of OKT3 antibody results from a deficiency of monocyte Fc gamma receptors for murine IgG2a and inability to cross-link the T3-Ti complex. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3882–3886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Kung P. C., Gingras S. P., Goldstein G. Does OKT3 monoclonal antibody react with an antigen-recognition structure on human T cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1805–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Hera A., Toribio M. L., Marquez C., Marcos M. A., Cabrero E., Martinez-A C. Differentiation of human mature thymocytes: existence of a T3+4-8- intermediate stage. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(6):653–658. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Baldwin C. L., MacHugh N. D., Bensaid A., Teale A. J., Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. Characterization by a monoclonal antibody and functional analysis of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT8, a molecule analogous to human CD8. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):351–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Baldwin C. L., ole-MoiYoi O., Morrison W. I. Improved methods for purification and depletion of monocytes from bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Functional evaluation of monocytes in responses to lectins. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 22;89(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90354-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I., Teale A. J., Bensaid A., Baldwin C. L. Bovine cytotoxic T-cell clones specific for cells infected with the protozoan parasite Theileria parva: parasite strain specificity and class I major histocompatibility complex restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5238–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard F. D., Ledbetter J. A., Wong J., Bieber C. P., Stinson E. B., Herzenberg L. A. A human T lymphocyte differentiation marker defined by monoclonal antibodies that block E-rosette formation. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2117–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet S., Wakasugi H., Sterkers G., Gilmour J., Tursz T., Boumsell L., Bernard A. T cell activation via CD2 [T, gp50]: the role of accessory cells in activating resting T cells via CD2. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1420–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Brown M. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of a human T lymphocyte surface protein associated with the E-rosette receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):207–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalor P. A., Morrison W. I., Goddeeris B. M., Jack R. M., Black S. J. Monoclonal antibodies identify phenotypically and functionally distinct cell types in the bovine lymphoid system. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Sep;13(1-2):121–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Ruitenberg J. J., Phillips J. H. Human CD3+ T lymphocytes that express neither CD4 nor CD8 antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):339–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Spooner C. E., Wofsy D., Tsu T. T., Beatty P. G., Gladstone P. Antibodies to Tp67 and Tp44 augment and sustain proliferative responses of activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2331–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D., Ragueneau M., Cerdan C., Dubreuil P., Lopez M., Mawas C. Anti-CD2 (sheep red blood cell receptor) monoclonal antibodies and T cell activation. I. Pairs of anti-T11.1 and T11.2 (CD2 subgroups) are strongly mitogenic for T cells in presence of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1063–1068. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Senogles D. R., Muscoplat C. C., Johnson D. W. Enumeration of T cells, B cells and monocytes in the peripheral blood of normal and lymphocytotic cattle. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Feb;35(2):306–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinder M., Musoke A. J., Morrison W. I., Roelants G. E. The bovine lymphoid system. III. A monoclonal antibody specific for bovine cell surface and serum IgM. Immunology. 1980 Jul;40(3):359–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Good R. A. Inhibition of specific cell-mediated cytotoxicity by monoclonal antibodies to human T cell antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4500–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovsky E. D., Yang T. J. Production and characterization of a bovine T cell-specific monoclonal antibody identifying a mature differentiation antigen. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):609–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody with selective reactivity with functionally mature human thymocytes and all peripheral human T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1312–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Meuer S., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Levine H., Schlossman S. F. Antigen recognition by human T lymphocytes is linked to surface expression of the T3 molecular complex. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale A. J., Baldwin C. L., Ellis J. A., Newson J., Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. Alloreactive bovine T lymphocyte clones: an analysis of function, phenotype, and specificity. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4392–4398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toribio M. L., Martinez C., Marcos M. A., Marquez C., Cabrero E., de la Hera A. A role for T3+4-6-8- transitional thymocytes in the differentiation of mature and functional T cells from human prothymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6985–6988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Landgraf B., Bentin J., Valentine M., Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Activation of resting T lymphocytes by anti-CD3 (T3) antibodies in the absence of monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J., Goossens J., Decock W., Kung P., Goldstein G. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis and E-rosette formation by the monoclonal antibody OKT11A. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):865–871. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbi W., Greaves M. F., Schneider C., Koubek K., Janossy G., Stein H., Kung P., Goldstein G. Monoclonal antibodies OKT 11 and OKT 11A have pan-T reactivity and block sheep erythrocyte "receptors". Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., De Vries J. E., Borst J., Spits H. Distribution and functional analysis of a 120- to 130-kDa T-cell surface antigen. Cell Immunol. 1987 Mar;105(1):161–173. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A., Terhorst C., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. Characterization of T cell surface glycoproteins T 1 and T 3 present on all human peripheral T lymphocytes and functionally mature thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jan;11(1):18–21. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]