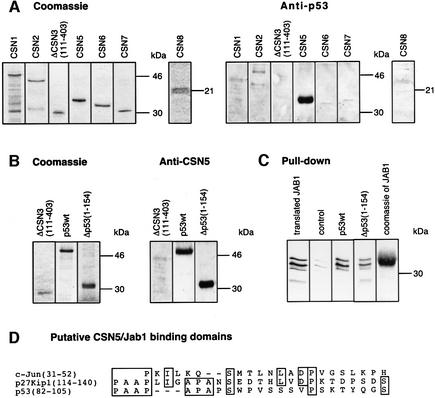
Fig. 3. p53wt and Δp53(1–154) bind to the CSN subunit 5/Jab1. (A) Far-western blots performed with immobilized, recombinant CSN subunits. Recombinant subunits used were separated by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie. The same proteins were immobilized on nitrocellulose and incubated with p53wt. After washings, the blots were tested with an anti-p53 antibody (Anti-p53). (B) Far-western blots performed with immobilized p53wt and Δp53(1–154). ΔCSN3(111–403) was used as a negative control. Immobilized proteins were incubated with recombinant CSN5/Jab1. The blots were tested with a specific anti-CSN5 antibody (Anti-CSN5). To avoid false-positive interactions, blots were stripped and re-probed with the same antibody. All specific interactions disappeared after stripping (data not shown). (C) Pull-down assays with p53wt or Δp53(1–154) and in vitro translated, 35S-labeled CSN5/Jab1. CSN5/Jab1 was translated in reticulocyte lysate using a CSN5 cDNA-pcDNA3.1 construct possessing a T7 promotor and coding for an N-terminal Flag tag (translated JAB1). The occurrence of three different bands might be due to internal starts of translation. Recombinant p53wt, Δp53(1–154) or Mdm2 (control) was bound to Ni-NTA magnetic agarose and incubated with 35S-labeled Jab1-containing lysate. After SDS–PAGE, 35S-labeled Jab1 was visualized by autoradiography. Weak bands seen in the control indicate unspecific binding of CSN5/Jab1. Coomassie of JAB1 denotes recombinant His6-tagged Jab1 separated by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie. (D) Sequence alignment of the regions of c-Jun (Claret et al., 1996) and p27Kip1 (Tomoda et al., 1999) that bind to CSN5/Jab1 with Δp53(1–154). The region with the highest homology is shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.