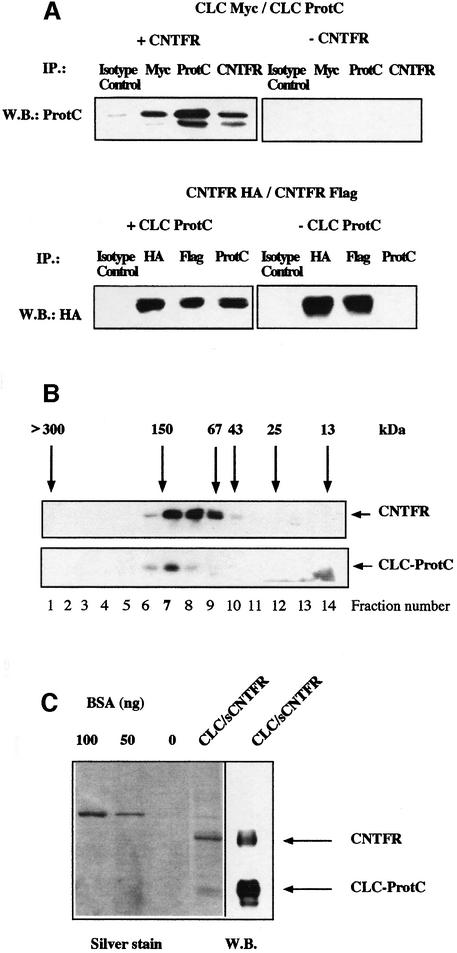
Fig. 4. Stoichiometry and composition of CLC–sCNTFR cytokine. (A) Upper panel: Cos-7 cells were co-transfected with CLC-protC, CLC-myc and either sCNTFR (+CNTFR) or an empty control vector (–CNTFR). After 72 h, supernatants were immunoprecipitated with an isotype control mAb, an anti-myc mAb, an anti-protC mAb or an anti-CNTFR mAb. Western blotting analysis was performed with a biotinylated anti-protC mAb. Lower panel: Cos-7 cells were co-transfected with CNTFR-HA, CNTFR-Flag and either CLC-protC (+CLCprotC) or with an empty control vector (–CLCprotC). Supernatants were immunoprecipitated with an isotype control mAb, an anti-HA mAb, an anti-Flag mAb or an anti-protC mAb. Western blotting was performed with a peroxidase-coupled anti-HA mAb. (B) The culture supernatant of an HEK 293 cell line stably transfected with CLC–sCNTFR was size-fractionated on a Superose 12 column. Fractions were analysed by western blotting using an anti-protC mAb to detect CLC, or the AN-E4 antibody to detect sCNTFR. Column calibration was performed using standard purified proteins. (C) SDS–PAGE analysis of purified CLC–sCNTFR. CLC–sCNTFR was purified with an anti-protC column followed by QAE HPLC. Gels were silver stained and protein concentration determined using known concentrations of BSA. Western blotting analysis of a companion lane was performed using both anti-protC and anti-CNTFR mAbs for visualization.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.