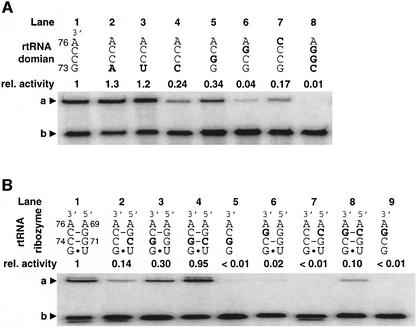
Fig. 7. Mutational studies of the aminoacyl-acceptor end of tRNA and 5′-leader ribozyme. The introduced mutations are highlighted by bold letters. The base numbers of 5′-leader ribozyme and rtRNA are assigned according to Figure 3B. (A) Self-aminoacylation activity of pre-24 and its mutants containing mutations at the acceptor end of the tRNA domain. Abbreviations: rel. activity, relative catalytic activity based on wild-type pre-24. a, Biotin-Phe-pre-24 or its mutants complexed with SAv; b, pre-24 or its mutants. The mutations were introduced into the pre-24 DNA template by PCR site-directed mutagenesis using the corresponding 3′-primer. Self-aminoacylation was carried out in the presence of 1 mM Biotin-Phe-CME and 1 µM RNA at 25°C for 30 min. (B) Trans-aminoacylation activity and compensatory mutations of rtRNA and 5′-leader ribozyme. Abbreviations: rel. activity, relative catalytic activity based on the wild-type pair of rtRNA and 5′-leader ribozyme. a, Biotin-Phe-rtRNA or its mutant complexed with SAv; b, rtRNA or its mutant. Mutant rtRNA and 5′-leader ribozyme were independently transcribed in vitro, and the trans-aminoacylation was carried out in the presence of 1 µM mutant 5′-leader ribozyme and 0.5 µM mutant rtRNA at 25°C for 30 min.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.